
What is the radius of curvature of a spherical surface?
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint:The distance from the pole to the centre of curvature is the radius of curvature of the surface. Spherometer is the instrument which measures the radius of the curvature of spherical surfaces.
Step by step solution:
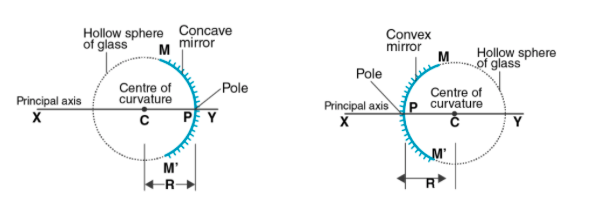
Spherical surfaces are the part of the sphere which is used to form the image as per requirement of an object using principle of reflection of light. The given below figure represents the two types of surface i.e. convex surface and concave surface both spherical surfaces.
As shown in the diagram the linear distance between pole and centre of curvature is called radius of curvature. When the radius of curvature becomes infinite the spherical mirror behaves as the plane surfaces. The radius of curvature lies on the principal axis of the spherical surface.
The sign convention for the optical radius of curvature is as follows:
If the vertex lies to the left of the centre of curvature, the radius of curvature is positive.
If the vertex lies to the right of the centre of curvature, the radius of curvature is negative.
Thus when viewing a biconvex lens from the side, the left surface radius of curvature is positive, and the right radius of curvature is negative.
The radius of curvature is measured by the instrument known as Spherometer.A spherometer is one of the vital scientific devices that measure the radius of curvature of any spherical surface precisely. The smallest value that is measured by the spherometer is called least count.
The spherical surfaces have immense application such as used in cars mirror, In solar power stations large big surfaces are used to collect huge amounts of sunlight used for power generation and crucial energy resources.
Note:However, in areas of optics other than design, other sign conventions are sometimes used. In particular, many undergraduate physics textbooks use the Gaussian sign convention in which convex surfaces of lenses are always positive. Care should be taken when using formulas taken from different sources.
Step by step solution:
Spherical surfaces are the part of the sphere which is used to form the image as per requirement of an object using principle of reflection of light. The given below figure represents the two types of surface i.e. convex surface and concave surface both spherical surfaces.
As shown in the diagram the linear distance between pole and centre of curvature is called radius of curvature. When the radius of curvature becomes infinite the spherical mirror behaves as the plane surfaces. The radius of curvature lies on the principal axis of the spherical surface.

The sign convention for the optical radius of curvature is as follows:
If the vertex lies to the left of the centre of curvature, the radius of curvature is positive.
If the vertex lies to the right of the centre of curvature, the radius of curvature is negative.
Thus when viewing a biconvex lens from the side, the left surface radius of curvature is positive, and the right radius of curvature is negative.
The radius of curvature is measured by the instrument known as Spherometer.A spherometer is one of the vital scientific devices that measure the radius of curvature of any spherical surface precisely. The smallest value that is measured by the spherometer is called least count.
The spherical surfaces have immense application such as used in cars mirror, In solar power stations large big surfaces are used to collect huge amounts of sunlight used for power generation and crucial energy resources.
Note:However, in areas of optics other than design, other sign conventions are sometimes used. In particular, many undergraduate physics textbooks use the Gaussian sign convention in which convex surfaces of lenses are always positive. Care should be taken when using formulas taken from different sources.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




