
Radial symmetry is found in which of the following?
A) Planaria
B) Taenia
C) Fasciola
D) Sea anemone
Answer
497.1k+ views
Hint: Body symmetry refers to the similarity with the arrangement of parts on the opposite sides of the body of a three-dimensional animal. The body of other animals can be divided into two equal halves into one or more planes called symmetrical. There are two types of symmetry – radial and bilateral symmetry.
Complete answer:
According to this question, we have to know about radial symmetry. If the body of an animal can be divided into two equal halves by cutting it in any plane passing through the central axis are called radial symmetry and the animals that show this type of symmetry are termed radiata. This permits an animal to detect food or danger approaching from any side. Radially symmetrical animals have a mouth or oral end and an opposite aboral end but no left and right sides, e.g., cnidarians (sea anemone, jellyfish and corals), ctenophores (comb jellies), etc.
Planaria – It is a flatworm that is free living. It inhabits freshwater, ponds and streams. It shows bilateral symmetry.
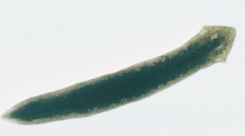
Taenia – It is a tapeworm having a flat, white and ribbon-like body. It occurs in the small intestine of man and its larvae occur in the muscles of pig. It shows bilateral symmetry.
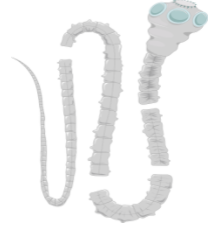
Fasciola – It is the liver fluke having a dorsiventrally flattened leaf-like body. It occurs as a parasite in the liver and bile ducts of sheep and goats. It shows bilateral symmetry.
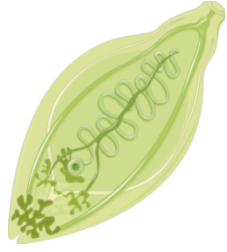
Sea anemone – It is a marine and sedentary cnidarian found attached to the empty shell of gastropods occupied by hermit crabs. It shows radial symmetry.

So, the correct answer is option (D) Sea anemone.
Note: The sea anemone protects the crab from enemies with its stinging cells, in return the anemone is carried by the crab to new feeding grounds and gets pieces of dropping from the crab’s prey. This is beneficial to both the partners and is called mutualism.
Complete answer:
According to this question, we have to know about radial symmetry. If the body of an animal can be divided into two equal halves by cutting it in any plane passing through the central axis are called radial symmetry and the animals that show this type of symmetry are termed radiata. This permits an animal to detect food or danger approaching from any side. Radially symmetrical animals have a mouth or oral end and an opposite aboral end but no left and right sides, e.g., cnidarians (sea anemone, jellyfish and corals), ctenophores (comb jellies), etc.
Planaria – It is a flatworm that is free living. It inhabits freshwater, ponds and streams. It shows bilateral symmetry.

Taenia – It is a tapeworm having a flat, white and ribbon-like body. It occurs in the small intestine of man and its larvae occur in the muscles of pig. It shows bilateral symmetry.

Fasciola – It is the liver fluke having a dorsiventrally flattened leaf-like body. It occurs as a parasite in the liver and bile ducts of sheep and goats. It shows bilateral symmetry.

Sea anemone – It is a marine and sedentary cnidarian found attached to the empty shell of gastropods occupied by hermit crabs. It shows radial symmetry.

So, the correct answer is option (D) Sea anemone.
Note: The sea anemone protects the crab from enemies with its stinging cells, in return the anemone is carried by the crab to new feeding grounds and gets pieces of dropping from the crab’s prey. This is beneficial to both the partners and is called mutualism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




