
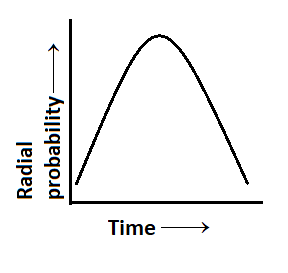
Radial probability distribution curve is shown for s-orbital. The curve is:
A. 1s
B. 2s
C. 3s
D. 4s

Answer
609k+ views
Hint: This curve helps to find out the points in space where the probability density of finding an electron is maximum from the nucleus and also points where electron density is zero. Those points where the probability density of finding an electron is 0 are called nodes.
Formula: Total number of radial nodes =$n - l - 1$ where n is the principal quantum number and \[l\] is the azimuthal quantum number. For s-orbital, value of $l = 0$.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Probability density at a point is defined as “probability per unit volume in limit that volume is infinitesimally”.
Radial probability distribution at a given radius is the probability density of an electron in an infinitesimally thin spherical shell at that radius and is a function of radial distance from the nucleus. There are also many points where the value of radial probability distribution is zero and those points are known as radial nodes.
As we have already mentioned above the formula for calculating total number of radial nodes is “\[n - l - 1\]”. So, by using the above formula we can easily calculate the radial node for all the above 4 options.
In 1s, the value of n = 1 and the value of l = 0. So, on applying the above formula the total number of radial nodes is 1 - 0 - 1 = 0.
For 2s, value of n = 2 and value of l = 0. So, total number of radial nodes is
2 - 0 - 1 = 1.
Similarly for 3s, value of n = 3 and value of l = 0. So, total number of radial nodes is
3 - 0 - 1 = 1.
For 4s, value of n = 4, and value of l = 0. So, total number of radial nodes is
4 - 0 - 1 = 1.
Also, for the above given curve, we can easily see that there is no radial node i.e. the total number of radial nodes is 0.
Hence, from the above arguments and calculations we can conclude that option A is the correct option.
Note: It should be remembered that the radial node is calculated from the Schrodinger wave equation and we should know how to calculate it from the Schrodinger wave equation.
Formula: Total number of radial nodes =$n - l - 1$ where n is the principal quantum number and \[l\] is the azimuthal quantum number. For s-orbital, value of $l = 0$.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Probability density at a point is defined as “probability per unit volume in limit that volume is infinitesimally”.
Radial probability distribution at a given radius is the probability density of an electron in an infinitesimally thin spherical shell at that radius and is a function of radial distance from the nucleus. There are also many points where the value of radial probability distribution is zero and those points are known as radial nodes.
As we have already mentioned above the formula for calculating total number of radial nodes is “\[n - l - 1\]”. So, by using the above formula we can easily calculate the radial node for all the above 4 options.
In 1s, the value of n = 1 and the value of l = 0. So, on applying the above formula the total number of radial nodes is 1 - 0 - 1 = 0.
For 2s, value of n = 2 and value of l = 0. So, total number of radial nodes is
2 - 0 - 1 = 1.
Similarly for 3s, value of n = 3 and value of l = 0. So, total number of radial nodes is
3 - 0 - 1 = 1.
For 4s, value of n = 4, and value of l = 0. So, total number of radial nodes is
4 - 0 - 1 = 1.
Also, for the above given curve, we can easily see that there is no radial node i.e. the total number of radial nodes is 0.
Hence, from the above arguments and calculations we can conclude that option A is the correct option.
Note: It should be remembered that the radial node is calculated from the Schrodinger wave equation and we should know how to calculate it from the Schrodinger wave equation.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




