
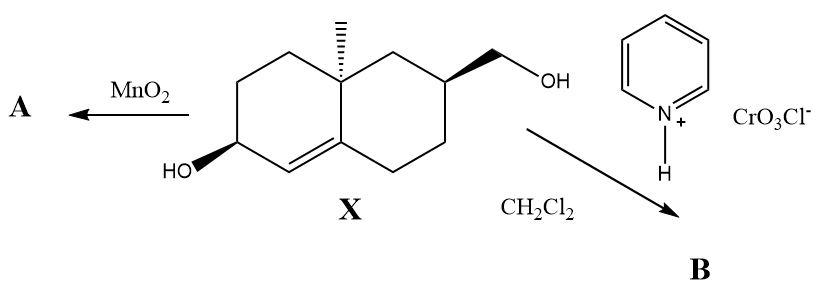
Pyridinium chlorochromate and $ Mn{O_2} $ are used as selective oxidizing agents in organic synthesis. What would be the oxidation products of the compound $ X $ when it reacts separately with PCC and $ Mn{O_2} $ ?

Answer
503.1k+ views
Hint: PCC stands for Pyridinium chlorochromate. Both Pyridinium chlorochromate and manganese dioxide are oxidizing agents that act on the alcohol functional group and transform it into aldehyde or ketones.
Complete answer:
The selectivity of chemical reagents in organic synthesis is based on the fact that they do not attack all the functional groups present in an organic molecule. A selective reagent reacts at specific sites where the functional group is present in a preferred form.
Both Pyridinium chlorochromate and manganese dioxide are selective oxidizing agents.
Pyridinium chlorochromate is used to carry out the elective transformation of a primary alcohol into an aldehyde. It leaves the secondary and tertiary alcohol groups unreacted and therefore it is impossible to produce a ketone with the aid of Pyridinium chlorochromate.
Manganese dioxide $ (Mn{O_2}) $ is also an oxidizing agent but only oxidizes those primary or secondary alcohols that are allylic or benzylic in nature. All other alcohol groups remain unreacted.
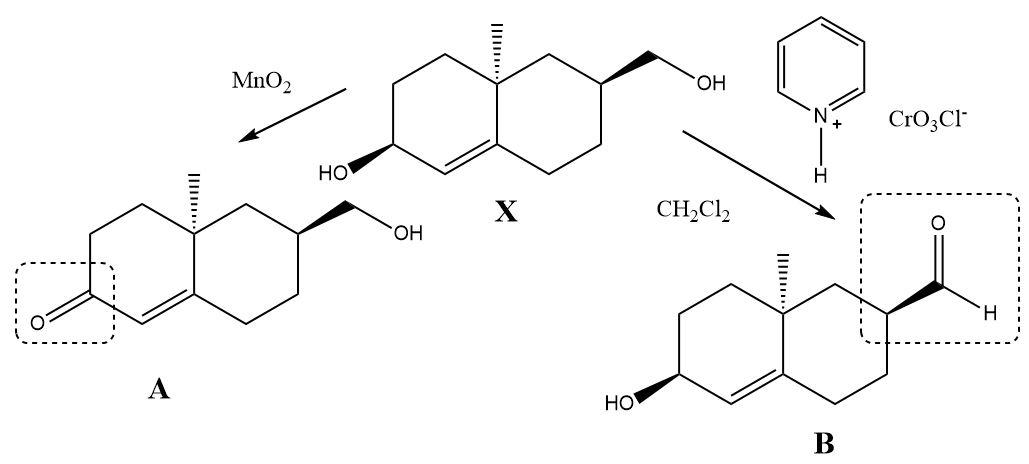
The compound $ X $ contains two types of alcohol groups in it. One of them is a simple primary alcohol and the other is an allylic secondary alcohol. When Pyridinium chlorochromate reacts with the compound then only the primary alcohol gets converted into an aldehyde and when manganese dioxide reacts separately then a ketone is formed at the place of the allylic alcohol. The double bond present in the molecule remains unaffected during both the oxidation reactions.
The oxidation products can be shown as follows:
Note:
The allylic group is a group attached to a carbon atom placed adjacent to a double bond. The conversion of an allylic alcohol into a ketone formed adjacent to a double bond is highly stable due to the conjugation involved between the carbonyl carbon and the double bond.
Complete answer:
The selectivity of chemical reagents in organic synthesis is based on the fact that they do not attack all the functional groups present in an organic molecule. A selective reagent reacts at specific sites where the functional group is present in a preferred form.
Both Pyridinium chlorochromate and manganese dioxide are selective oxidizing agents.
Pyridinium chlorochromate is used to carry out the elective transformation of a primary alcohol into an aldehyde. It leaves the secondary and tertiary alcohol groups unreacted and therefore it is impossible to produce a ketone with the aid of Pyridinium chlorochromate.
Manganese dioxide $ (Mn{O_2}) $ is also an oxidizing agent but only oxidizes those primary or secondary alcohols that are allylic or benzylic in nature. All other alcohol groups remain unreacted.
The compound $ X $ contains two types of alcohol groups in it. One of them is a simple primary alcohol and the other is an allylic secondary alcohol. When Pyridinium chlorochromate reacts with the compound then only the primary alcohol gets converted into an aldehyde and when manganese dioxide reacts separately then a ketone is formed at the place of the allylic alcohol. The double bond present in the molecule remains unaffected during both the oxidation reactions.
The oxidation products can be shown as follows:

Note:
The allylic group is a group attached to a carbon atom placed adjacent to a double bond. The conversion of an allylic alcohol into a ketone formed adjacent to a double bond is highly stable due to the conjugation involved between the carbonyl carbon and the double bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




