
Why is the pyramid of energy always upright? Explain.
Answer
598.5k+ views
Hint: An ecological pyramid is a graphical representation to show the relationship between different organisms in an ecosystem and each of the bars that make up the pyramid represents a different trophic level. Ecological pyramids are generally of three types: the pyramid of the number, pyramid of biomass, and a pyramid of energy (showing the rate of energy flow).
Complete answer:
One of the ways for an ecosystem to work at its fullest is that there has to be a flow of energy. The energy is achieved in the form of food in the ecosystem. The topmost source of this energy is the sun and producers like green plants trap solar energy to convert it into the chemical energy for getting their food. A part of this energy is passed on to producers now. The primary producer is then eaten by the primary consumer; this is again eaten by a secondary consumer. This secondary consumer may be eaten by a tertiary consumer, and so on. The energy gets carried from one consumer to the next higher level of consumer. The food chain is made up of this link from producers and ending at apex predator species or decomposer species. The pyramid of energy is always upright as the energy flow in a food chain is always unidirectional. In an ecosystem, food is passed from one trophic level to the next higher trophic level. This transfer results in the passage of energy through these trophic levels and some energy is always lost as heat in each step to the atmosphere and never goes back to the sun. Thus, the pyramid of energy is always upright.
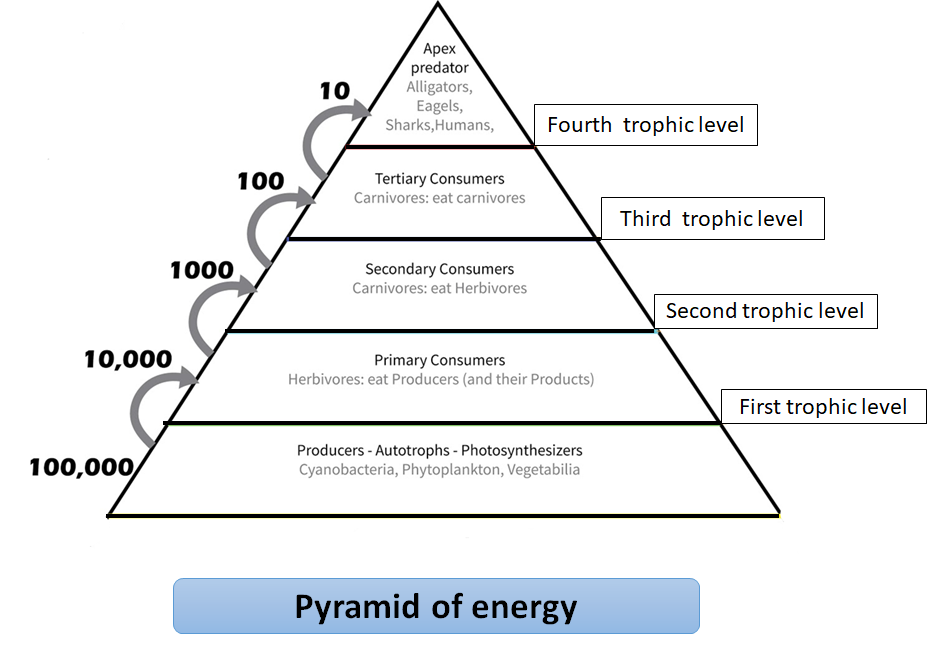
Note: The pyramid of number and biomass can either be upright or inverted or dumbbell-shaped, this depends on the nature of the food chain. A trophic level is the group of organisms that occupy the same level in a food chain and the same nutritional relationship to the primary sources of energy in an ecosystem.
Complete answer:
One of the ways for an ecosystem to work at its fullest is that there has to be a flow of energy. The energy is achieved in the form of food in the ecosystem. The topmost source of this energy is the sun and producers like green plants trap solar energy to convert it into the chemical energy for getting their food. A part of this energy is passed on to producers now. The primary producer is then eaten by the primary consumer; this is again eaten by a secondary consumer. This secondary consumer may be eaten by a tertiary consumer, and so on. The energy gets carried from one consumer to the next higher level of consumer. The food chain is made up of this link from producers and ending at apex predator species or decomposer species. The pyramid of energy is always upright as the energy flow in a food chain is always unidirectional. In an ecosystem, food is passed from one trophic level to the next higher trophic level. This transfer results in the passage of energy through these trophic levels and some energy is always lost as heat in each step to the atmosphere and never goes back to the sun. Thus, the pyramid of energy is always upright.

Note: The pyramid of number and biomass can either be upright or inverted or dumbbell-shaped, this depends on the nature of the food chain. A trophic level is the group of organisms that occupy the same level in a food chain and the same nutritional relationship to the primary sources of energy in an ecosystem.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




