
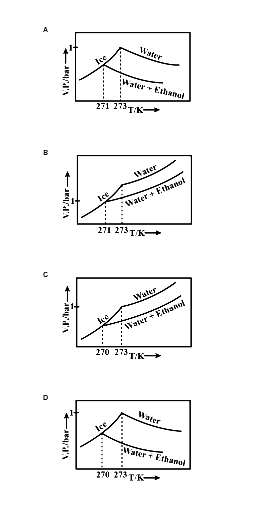
Pure water freezes at 273 K and 1 bar. The addition of 34.5 g of ethanol to 500g of water changes the freezing point of the solution. Use the freezing point depression constant of water as 2 K kg/mol. The figures shown below represent plots of vapour pressure (V.P). among the following, the option representing a change in the freezing point is:

Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: The lowering of vapour pressure causes a lowering of the freezing point compared to that of the pure solvent. The solid phase is in dynamic equilibrium with the liquid phase is the freezing point of the substance. It is defined as the temperature at which the vapour pressure of the substance in its liquid phase is equal to its vapour pressure in the solid phase.
Complete answer:
The properties of solutions depend on the decrease of vapour pressure are:
(1) relative lowering of the vapour pressure of the solvent
(2) depression of freezing point of the solvent
(3) elevation of a boiling point of the solvent
(4) osmotic pressure of the solution
Depression of freezing point: A solution will freeze when its vapour pressure equals the vapour pressure of the pure solid solvent. Thus, the freezing point of the solvent decreases.
Let ${{T}_{f}}^{o}\And {{T}_{f}}$ be the freezing point of pure solvent and non-volatile solute respectively.
Then, depression in freezing point $\Delta {{T}_{f}}={{T}_{f}}^{o}-{{T}_{f}}$
The depression freezing point for a dilute solution is directly proportional to molality (m) of the solution. thus,
\[\begin{align}
& \Delta {{T}_{f}}\infty m \\
& \Delta {{T}_{f}}={{K}_{f}}m--(1) \\
\end{align}\]
Where ${{K}_{f}}$ is freezing point depression constant.
Weight of ethanol = 34.5g
Molar mass of ethanol = 46 g/mol
The number of moles of ethanol n= $\dfrac{Weight\text{ }of\text{ }ethanol}{Molar\text{ }mass\text{ }of\text{ }ethanol}=\dfrac{34.5g}{46.g/mol}=0.75mol$
Weight of pure water = 500g= 0.5Kg
The molality of ethanol, ${{m}_{{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH}}=\dfrac{moles\text{ }of\text{ }ethanol}{Weight\text{ }of\text{ }pure\text{ }water(Kg)}=\dfrac{0.75mol}{0.5Kg}=1.5m$
${{K}_{f}}$ is freezing point depression constant =2 K kg/mol
Substitute the above values in equation (1), \[\Delta {{T}_{f}}={{K}_{f}}m=2X1.5=3K\]
The freezing point of pure water ${{T}_{f}}^{o}$= 273K
The freezing point of a solution ${{T}_{f}}={{T}_{f}}^{o}-\Delta {{T}_{f}}=273-3=270K$
From the above values, with an increase in temperature, the vapour pressure of pure water and mixture increases. Given four graphs, option C represents the correct graph. In the graph, the freezing point of the solution showed 270K.
Note:
The properties depend on the number of solute particles irrespective of their nature relative to the total number of particles present in the solution. Such properties are called colligative properties. (colligative: from Latin: co means together, ligare means to bind).
Complete answer:
The properties of solutions depend on the decrease of vapour pressure are:
(1) relative lowering of the vapour pressure of the solvent
(2) depression of freezing point of the solvent
(3) elevation of a boiling point of the solvent
(4) osmotic pressure of the solution
Depression of freezing point: A solution will freeze when its vapour pressure equals the vapour pressure of the pure solid solvent. Thus, the freezing point of the solvent decreases.
Let ${{T}_{f}}^{o}\And {{T}_{f}}$ be the freezing point of pure solvent and non-volatile solute respectively.
Then, depression in freezing point $\Delta {{T}_{f}}={{T}_{f}}^{o}-{{T}_{f}}$
The depression freezing point for a dilute solution is directly proportional to molality (m) of the solution. thus,
\[\begin{align}
& \Delta {{T}_{f}}\infty m \\
& \Delta {{T}_{f}}={{K}_{f}}m--(1) \\
\end{align}\]
Where ${{K}_{f}}$ is freezing point depression constant.
Weight of ethanol = 34.5g
Molar mass of ethanol = 46 g/mol
The number of moles of ethanol n= $\dfrac{Weight\text{ }of\text{ }ethanol}{Molar\text{ }mass\text{ }of\text{ }ethanol}=\dfrac{34.5g}{46.g/mol}=0.75mol$
Weight of pure water = 500g= 0.5Kg
The molality of ethanol, ${{m}_{{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH}}=\dfrac{moles\text{ }of\text{ }ethanol}{Weight\text{ }of\text{ }pure\text{ }water(Kg)}=\dfrac{0.75mol}{0.5Kg}=1.5m$
${{K}_{f}}$ is freezing point depression constant =2 K kg/mol
Substitute the above values in equation (1), \[\Delta {{T}_{f}}={{K}_{f}}m=2X1.5=3K\]
The freezing point of pure water ${{T}_{f}}^{o}$= 273K
The freezing point of a solution ${{T}_{f}}={{T}_{f}}^{o}-\Delta {{T}_{f}}=273-3=270K$
From the above values, with an increase in temperature, the vapour pressure of pure water and mixture increases. Given four graphs, option C represents the correct graph. In the graph, the freezing point of the solution showed 270K.
Note:
The properties depend on the number of solute particles irrespective of their nature relative to the total number of particles present in the solution. Such properties are called colligative properties. (colligative: from Latin: co means together, ligare means to bind).
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




