
Prove that $\sin \left( 90+\theta \right)=\cos \theta $ ?
Answer
531k+ views
Hint: We start off with the trigonometric formula $\sin \left( A+B \right)=\sin A\cos B+\cos A\sin B$ . In this formula, we put the value of A as ${{90}^{\circ }}$ and that of B as $\theta $ . The equation becomes $\Rightarrow \sin \left( {{90}^{\circ }}+\theta \right)=\sin {{90}^{\circ }}\cos \theta +\cos {{90}^{\circ }}\sin \theta $ . Putting the values of $\sin {{90}^{\circ }}$ and $\cos {{90}^{\circ }}$ as $1$ and $0$ respectively, we get the required identity.
Complete step by step answer:
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that studies relationships between side lengths and angles of triangles. Trigonometry is known for its many identities. These trigonometric identities are commonly used for rewriting trigonometric expressions with the aim to simplify an expression, to find a more useful form of n expression, or to solve an equation.
In this problem, we need to prove a trigonometric identity. The identity is $\sin \left( 90+\theta \right)=\cos \theta $ . In order to prove this, we need the help of some other trigonometric formula. The formula is as follows,
$\sin \left( A+B \right)=\sin A\cos B+\cos A\sin B$
In our problem, the value of A is ${{90}^{\circ }}$ and that of B is $\theta $ . So, replacing A with ${{90}^{\circ }}$ and B with $\theta $ in the above formula, we get,
$\Rightarrow \sin \left( {{90}^{\circ }}+\theta \right)=\sin {{90}^{\circ }}\cos \theta +\cos {{90}^{\circ }}\sin \theta $
Now, we know the value of $\sin {{90}^{\circ }}$ and $\cos {{90}^{\circ }}$ . The values are $1$ and $0$ respectively. So, putting these values in the above equation, we get,
$\Rightarrow \sin \left( {{90}^{\circ }}+\theta \right)=1\left( \cos \theta \right)+0\left( \sin \theta \right)$
Simplifying the above equation, we get,
$\Rightarrow \sin \left( {{90}^{\circ }}+\theta \right)=\cos \theta +0$
The above equation is nothing but,
$\Rightarrow \sin \left( {{90}^{\circ }}+\theta \right)=\cos \theta $
Thus, we can conclude that the trigonometric identity of the given problem has been proved.
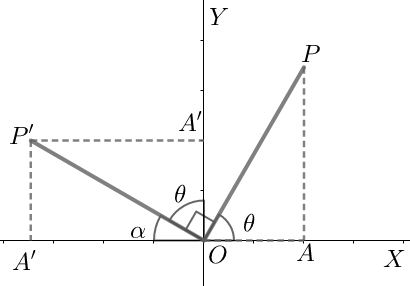
Note: We can also solve the problem in another way. We can take the help of graphical method. Now, $\sin \left( {{90}^{\circ }}+\theta \right)$ from the figure means \[\dfrac{A'P'}{OP'}\] which also equals the value $\dfrac{OA}{OP}$ since the triangles $\Delta OAP,\Delta OA'P'$ are congruent. $\dfrac{OA}{OP}$ would mean nothing but $\cos \theta $ . Hence, proved.
Complete step by step answer:
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that studies relationships between side lengths and angles of triangles. Trigonometry is known for its many identities. These trigonometric identities are commonly used for rewriting trigonometric expressions with the aim to simplify an expression, to find a more useful form of n expression, or to solve an equation.
In this problem, we need to prove a trigonometric identity. The identity is $\sin \left( 90+\theta \right)=\cos \theta $ . In order to prove this, we need the help of some other trigonometric formula. The formula is as follows,
$\sin \left( A+B \right)=\sin A\cos B+\cos A\sin B$
In our problem, the value of A is ${{90}^{\circ }}$ and that of B is $\theta $ . So, replacing A with ${{90}^{\circ }}$ and B with $\theta $ in the above formula, we get,
$\Rightarrow \sin \left( {{90}^{\circ }}+\theta \right)=\sin {{90}^{\circ }}\cos \theta +\cos {{90}^{\circ }}\sin \theta $
Now, we know the value of $\sin {{90}^{\circ }}$ and $\cos {{90}^{\circ }}$ . The values are $1$ and $0$ respectively. So, putting these values in the above equation, we get,
$\Rightarrow \sin \left( {{90}^{\circ }}+\theta \right)=1\left( \cos \theta \right)+0\left( \sin \theta \right)$
Simplifying the above equation, we get,
$\Rightarrow \sin \left( {{90}^{\circ }}+\theta \right)=\cos \theta +0$
The above equation is nothing but,
$\Rightarrow \sin \left( {{90}^{\circ }}+\theta \right)=\cos \theta $
Thus, we can conclude that the trigonometric identity of the given problem has been proved.
Note: We can also solve the problem in another way. We can take the help of graphical method. Now, $\sin \left( {{90}^{\circ }}+\theta \right)$ from the figure means \[\dfrac{A'P'}{OP'}\] which also equals the value $\dfrac{OA}{OP}$ since the triangles $\Delta OAP,\Delta OA'P'$ are congruent. $\dfrac{OA}{OP}$ would mean nothing but $\cos \theta $ . Hence, proved.

Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Who is known as the "Little Master" in Indian cricket history?

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

State and explain Ohms law class 10 physics CBSE

Distinguish between soap and detergent class 10 chemistry CBSE

a Why did Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments class 10 biology CBSE

Draw the diagram of the sectional view of the human class 10 biology CBSE




