
How do you prove $ \displaystyle \lim_{x \to 0}\dfrac{\sin x}{x}=1 $ without using l’hopital’s rule (or the derivative of $ \sin x $ at all)?
Answer
560.7k+ views
Hint: Try to Develop the inequality by considering the areas of different regions of the geometric picture which is required for the above proof. Then simplify the inequality as necessary for applying the Squeeze Theorem. Then use Squeeze Theorem to prove $ \displaystyle \lim_{x \to 0}\dfrac{\sin x}{x}=1 $ .
Complete step by step answer:
We know Trigonometric functions are continuous everywhere. Let’s consider a small part of a point on the unit circle which results in small changes in its x- and y-coordinates. As these are periodic functions so they have neither a finite nor an infinite limit at infinity.
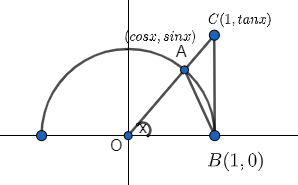
As we know, area of triangle $ =\dfrac{1}{2}\times base\times height $
So, area of $ \vartriangle OAB=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 1\times \sin x=\dfrac{\sin x}{2} $
Similarly, area of $ \vartriangle OCB=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 1\times \tan x=\dfrac{\tan x}{2} $
Now, area of sector $ =\dfrac{\theta }{2\pi }\times \pi {{r}^{2}} $
So, area of sector OAB $ =\dfrac{x}{2\pi }\times \pi {{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}=\dfrac{x}{2} $
We can conclude from the above figure that;
Area of $ \vartriangle OAB $ $ \le $ Area of sector OAB $ \le $ Area of $ \vartriangle OCB $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{\sin x}{2}\le \dfrac{x}{2}\le \dfrac{\tan x}{2};\forall x\left[ 0,\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right] $
Frist multiplying 2 throughout, we get
$ \Rightarrow \sin x\le x\le \tan x $
Then dividing $ \sin x $ throughout, we get
$ \begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{\sin x}{\sin x}\le \dfrac{x}{\sin x}\le \dfrac{\tan x}{\sin x} \\
& \Rightarrow 1\le \dfrac{x}{\sin x}\le \dfrac{1}{\cos x} \\
\end{align} $
Now taking reciprocal, we get
$ \Rightarrow 1\ge \dfrac{\sin x}{x}\ge \cos x $ (Since the inequality reverses when reciprocal is taken)
It can be written as
$ \Rightarrow \cos x\le \dfrac{\sin x}{x}\le 1;\forall x\in \left( -\dfrac{\pi }{2},\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right) $ (Since $ \cos x $ , $ \dfrac{\sin x}{x} $ ,1 are even functions)
Squeeze Theorem: If we have the inequalities $ g\left( x \right)\le f\left( x \right)\le h\left( x \right) $ which hold for all x in an open interval containing number ‘c’ and $ \displaystyle \lim_{x \to c}g\left( x \right)=\displaystyle \lim_{x \to c}h\left( x \right)=L $ then $ \displaystyle \lim_{x \to c}f\left( x \right) $ will also be L.
Let’s use the Squeeze Theorem for our inequality;
$ \Rightarrow \displaystyle \lim_{x \to 0}\cos x\le \displaystyle \lim_{x \to 0}\dfrac{\sin x}{x}\le \displaystyle \lim_{x \to 0}1 $
Since $ \displaystyle \lim_{x \to 0}\cos x=1 $ and $ \displaystyle \lim_{x \to 0}1=1 $
So by Squeeze Theorem
$ \displaystyle \lim_{x \to 0}\dfrac{\sin x}{x}=1 $
Hence proved.
Note:
Changes to the inequality should be done properly. Like if we take reciprocal then the whole inequality reverses. Squeeze Theorem should be applied as $ g\left( x \right)=\cos x,f\left( x \right)=\dfrac{\sin x}{x} $ & $ h\left( x \right)=1 $ .
Informally the $ \displaystyle \lim_{x \to 0}\dfrac{\sin x}{x}=1 $ means for a small ‘x’ $ \sin x\approx x $ .
Complete step by step answer:
We know Trigonometric functions are continuous everywhere. Let’s consider a small part of a point on the unit circle which results in small changes in its x- and y-coordinates. As these are periodic functions so they have neither a finite nor an infinite limit at infinity.

As we know, area of triangle $ =\dfrac{1}{2}\times base\times height $
So, area of $ \vartriangle OAB=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 1\times \sin x=\dfrac{\sin x}{2} $
Similarly, area of $ \vartriangle OCB=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 1\times \tan x=\dfrac{\tan x}{2} $
Now, area of sector $ =\dfrac{\theta }{2\pi }\times \pi {{r}^{2}} $
So, area of sector OAB $ =\dfrac{x}{2\pi }\times \pi {{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}=\dfrac{x}{2} $
We can conclude from the above figure that;
Area of $ \vartriangle OAB $ $ \le $ Area of sector OAB $ \le $ Area of $ \vartriangle OCB $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{\sin x}{2}\le \dfrac{x}{2}\le \dfrac{\tan x}{2};\forall x\left[ 0,\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right] $
Frist multiplying 2 throughout, we get
$ \Rightarrow \sin x\le x\le \tan x $
Then dividing $ \sin x $ throughout, we get
$ \begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{\sin x}{\sin x}\le \dfrac{x}{\sin x}\le \dfrac{\tan x}{\sin x} \\
& \Rightarrow 1\le \dfrac{x}{\sin x}\le \dfrac{1}{\cos x} \\
\end{align} $
Now taking reciprocal, we get
$ \Rightarrow 1\ge \dfrac{\sin x}{x}\ge \cos x $ (Since the inequality reverses when reciprocal is taken)
It can be written as
$ \Rightarrow \cos x\le \dfrac{\sin x}{x}\le 1;\forall x\in \left( -\dfrac{\pi }{2},\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right) $ (Since $ \cos x $ , $ \dfrac{\sin x}{x} $ ,1 are even functions)
Squeeze Theorem: If we have the inequalities $ g\left( x \right)\le f\left( x \right)\le h\left( x \right) $ which hold for all x in an open interval containing number ‘c’ and $ \displaystyle \lim_{x \to c}g\left( x \right)=\displaystyle \lim_{x \to c}h\left( x \right)=L $ then $ \displaystyle \lim_{x \to c}f\left( x \right) $ will also be L.
Let’s use the Squeeze Theorem for our inequality;
$ \Rightarrow \displaystyle \lim_{x \to 0}\cos x\le \displaystyle \lim_{x \to 0}\dfrac{\sin x}{x}\le \displaystyle \lim_{x \to 0}1 $
Since $ \displaystyle \lim_{x \to 0}\cos x=1 $ and $ \displaystyle \lim_{x \to 0}1=1 $
So by Squeeze Theorem
$ \displaystyle \lim_{x \to 0}\dfrac{\sin x}{x}=1 $
Hence proved.
Note:
Changes to the inequality should be done properly. Like if we take reciprocal then the whole inequality reverses. Squeeze Theorem should be applied as $ g\left( x \right)=\cos x,f\left( x \right)=\dfrac{\sin x}{x} $ & $ h\left( x \right)=1 $ .
Informally the $ \displaystyle \lim_{x \to 0}\dfrac{\sin x}{x}=1 $ means for a small ‘x’ $ \sin x\approx x $ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
The draft of the Preamble of the Indian Constitution class 10 social science CBSE

Who gave "Inqilab Zindabad" slogan?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

What is the minimum age for fighting the election in class 10 social science CBSE

Write an application to the principal requesting five class 10 english CBSE

My birthday is June 27 a On b Into c Between d In class 10 english CBSE




