
What is the production of hydrogenation of trans-2-butene?
Answer
533.1k+ views
Hint :In hydrogenation, double and triple bonds get broken to single bonds. Thus, the double bond in trans-2-butene gets reduced to a single bond.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The product of hydrogenation of trans-2-butene is simple butane.
Hydrogenation is a reaction in which triple bonds get reduced to double bonds, and double bonds get reduced to single bonds. It is a chemical reaction in which molecular hydrogen and any other compound are subjected to a chemical reaction under the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum.
Now, there is a double bond in the given compound i.e. trans-2-butene. As hydrogenation reduces the double bond to single, here also the same will happen.
The below given figure is of trans-2-butene.
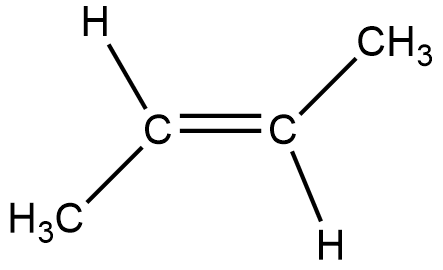
Now, after hydrogenation the double bond gets broken into a single bond, and thus both the carbon atoms get an extra hydrogen to comply with the reduced double bond.
The below given is the product after hydrogenation, which is just simple butane.

Thus, if any element or compound is subjected to a chemical reaction with molecular hydrogen, it undergoes hydrogenation and loses its triple bond to double bond and its double bond to single bond. Double hydrogenation on triple bonds can make it a single bond.
Note :
Any compound can reduce its double or triple bond to single through hydrogenation. There are other methods too, but this method is more reliable on most of the compounds.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The product of hydrogenation of trans-2-butene is simple butane.
Hydrogenation is a reaction in which triple bonds get reduced to double bonds, and double bonds get reduced to single bonds. It is a chemical reaction in which molecular hydrogen and any other compound are subjected to a chemical reaction under the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum.
Now, there is a double bond in the given compound i.e. trans-2-butene. As hydrogenation reduces the double bond to single, here also the same will happen.
The below given figure is of trans-2-butene.

Now, after hydrogenation the double bond gets broken into a single bond, and thus both the carbon atoms get an extra hydrogen to comply with the reduced double bond.
The below given is the product after hydrogenation, which is just simple butane.

Thus, if any element or compound is subjected to a chemical reaction with molecular hydrogen, it undergoes hydrogenation and loses its triple bond to double bond and its double bond to single bond. Double hydrogenation on triple bonds can make it a single bond.
Note :
Any compound can reduce its double or triple bond to single through hydrogenation. There are other methods too, but this method is more reliable on most of the compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

Which out of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition class 11 chemistry CBSE




