
What is the principal value of ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)+{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ ?
Answer
616.8k+ views
Hint: For solving this question first, we will go through some important aspects like domain and range of the inverse trigonometric functions $y={{\cos }^{-1}}x$ and $y={{\sin }^{-1}}x$ . First, we will use one of the basic formulas of the trigonometric ratio to write $\cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3}=-\dfrac{1}{2}$ in the given term. After that, we will use one of the basic formula of inverse trigonometric functions, i.e. ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( -\dfrac{1}{2} \right)=\dfrac{2\pi }{3}$ to find the value of ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ . After that, we will use formula $\sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$ and ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{3}$ to find the value of ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ . Then, we will easily find the value of ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)+{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ .
Complete step-by-step solution -
Given:
We have to find the principal value of the following:
${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)+{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$
Now, we will find the principal values of ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ and ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ separately and then, we will add them to find the principal value of ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)+{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ .
Calculation for the principal value of ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ :
Now, before we proceed we should know about the inverse trigonometric function $y={{\cos }^{-1}}x$ . For more clarity look at the figure given below:
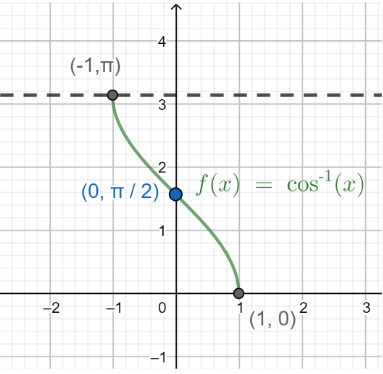
In the above figure, the plot $y=f\left( x \right)={{\cos }^{-1}}x$ is shown. And we should know that the function $y={{\cos }^{-1}}x$ is defined for $x\in \left[ -1,1 \right]$ and its range is $y\in \left[ 0,\pi \right]$ then, $y$ is the principal value of ${{\cos }^{-1}}x$ .
Now, we will use the above concept for giving the correct principal value of ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ .
Now, before we proceed further we should know the following formulas:
$\begin{align}
& \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3}=\cos \left( \pi -\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)=-\cos \dfrac{\pi }{3}=-\dfrac{1}{2}..................\left( 1 \right) \\
& {{\cos }^{-1}}\left( -\dfrac{1}{2} \right)=\dfrac{2\pi }{3}...........\left( 2 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we will use the above two formulas to solve this question.
We have, ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ .
Now, we will use the formula from the equation (1) to write $\cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3}=-\dfrac{1}{2}$ in the term ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{\cos }^{-1}}\left( -\dfrac{1}{2} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we will use the formula from the equation (2) to write ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( -\dfrac{1}{2} \right)=\dfrac{2\pi }{3}$ in the above line. Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{\cos }^{-1}}\left( -\dfrac{1}{2} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \\
\end{align}$
Now, from the above result, we conclude that the principal value of the expression ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ will be equal to $\dfrac{2\pi }{3}$ . Then,
${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)=\dfrac{2\pi }{3}.....................\left( 3 \right)$
Calculation for the principal value of ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ :
Now, before we proceed we should know about the inverse trigonometric function $y={{\sin }^{-1}}x$ . For more clarity look at the figure given below:
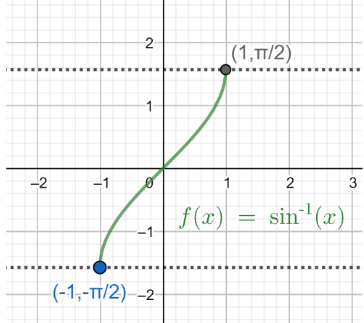
In the above figure, the plot $y=f\left( x \right)={{\sin }^{-1}}x$ is shown. And we should know that the function $y={{\sin }^{-1}}x$ is defined for $x\in \left[ -1,1 \right]$ and its range is $y\in \left[ -\dfrac{\pi }{2},\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right]$ then, $y$ is the principal value of ${{\sin }^{-1}}x$ .
Now, we will use the above concept for giving the correct principal value of ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ .
Now, before we proceed further we should know the following formulas:
$\begin{align}
& \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3}=\sin \left( \pi -\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)=\sin \dfrac{\pi }{3}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}.................\left( 4 \right) \\
& {{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{3}...........\left( 5 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we will use the above two formulas to solve this question.
We have, ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ .
Now, we will use the formula from the equation (4) to write $\sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$ in the term ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we will use the formula from the equation (5) to write ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{3}$ in the above line. Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{\pi }{3} \\
\end{align}$
Now, from the above result, we conclude that the principal value of the expression ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ will be equal to $\dfrac{\pi }{3}$ . Then,
${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{3}.....................\left( 6 \right)$
Now, we will use the result of the equation (3) and (6) to find the principal value of ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)+{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)+{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{2\pi }{3}+\dfrac{\pi }{3} \\
& \Rightarrow \pi \\
\end{align}$
Now, from the above result, we conclude that principal value of the ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)+{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ is equal to $\pi $ .
Thus, ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)+{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)=\pi $.
Note: Here, the student should first understand what is asked in the question and then proceed in the right direction to get the correct answer quickly. Moreover, we should avoid writing ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)=\dfrac{2\pi }{3}$ directly and use the basic concepts of domain and range of the inverse trigonometric functions $y={{\cos }^{-1}}x$ and $y={{\sin }^{-1}}x$ correctly. And after giving calculating the values of ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ and ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ , we should check for the validity of our answer by checking whether it lies in the range of its inverse trigonometric function or not.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Given:
We have to find the principal value of the following:
${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)+{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$
Now, we will find the principal values of ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ and ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ separately and then, we will add them to find the principal value of ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)+{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ .
Calculation for the principal value of ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ :
Now, before we proceed we should know about the inverse trigonometric function $y={{\cos }^{-1}}x$ . For more clarity look at the figure given below:

In the above figure, the plot $y=f\left( x \right)={{\cos }^{-1}}x$ is shown. And we should know that the function $y={{\cos }^{-1}}x$ is defined for $x\in \left[ -1,1 \right]$ and its range is $y\in \left[ 0,\pi \right]$ then, $y$ is the principal value of ${{\cos }^{-1}}x$ .
Now, we will use the above concept for giving the correct principal value of ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ .
Now, before we proceed further we should know the following formulas:
$\begin{align}
& \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3}=\cos \left( \pi -\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)=-\cos \dfrac{\pi }{3}=-\dfrac{1}{2}..................\left( 1 \right) \\
& {{\cos }^{-1}}\left( -\dfrac{1}{2} \right)=\dfrac{2\pi }{3}...........\left( 2 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we will use the above two formulas to solve this question.
We have, ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ .
Now, we will use the formula from the equation (1) to write $\cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3}=-\dfrac{1}{2}$ in the term ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{\cos }^{-1}}\left( -\dfrac{1}{2} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we will use the formula from the equation (2) to write ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( -\dfrac{1}{2} \right)=\dfrac{2\pi }{3}$ in the above line. Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{\cos }^{-1}}\left( -\dfrac{1}{2} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \\
\end{align}$
Now, from the above result, we conclude that the principal value of the expression ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ will be equal to $\dfrac{2\pi }{3}$ . Then,
${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)=\dfrac{2\pi }{3}.....................\left( 3 \right)$
Calculation for the principal value of ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ :
Now, before we proceed we should know about the inverse trigonometric function $y={{\sin }^{-1}}x$ . For more clarity look at the figure given below:
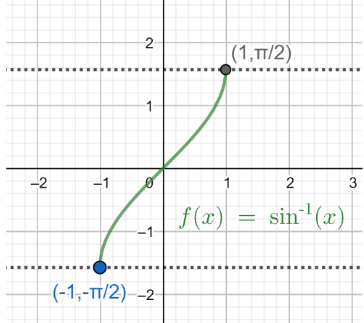
In the above figure, the plot $y=f\left( x \right)={{\sin }^{-1}}x$ is shown. And we should know that the function $y={{\sin }^{-1}}x$ is defined for $x\in \left[ -1,1 \right]$ and its range is $y\in \left[ -\dfrac{\pi }{2},\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right]$ then, $y$ is the principal value of ${{\sin }^{-1}}x$ .
Now, we will use the above concept for giving the correct principal value of ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ .
Now, before we proceed further we should know the following formulas:
$\begin{align}
& \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3}=\sin \left( \pi -\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)=\sin \dfrac{\pi }{3}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}.................\left( 4 \right) \\
& {{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{3}...........\left( 5 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we will use the above two formulas to solve this question.
We have, ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ .
Now, we will use the formula from the equation (4) to write $\sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$ in the term ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we will use the formula from the equation (5) to write ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{3}$ in the above line. Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{\pi }{3} \\
\end{align}$
Now, from the above result, we conclude that the principal value of the expression ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ will be equal to $\dfrac{\pi }{3}$ . Then,
${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{3}.....................\left( 6 \right)$
Now, we will use the result of the equation (3) and (6) to find the principal value of ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)+{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)+{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{2\pi }{3}+\dfrac{\pi }{3} \\
& \Rightarrow \pi \\
\end{align}$
Now, from the above result, we conclude that principal value of the ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)+{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ is equal to $\pi $ .
Thus, ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)+{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)=\pi $.
Note: Here, the student should first understand what is asked in the question and then proceed in the right direction to get the correct answer quickly. Moreover, we should avoid writing ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)=\dfrac{2\pi }{3}$ directly and use the basic concepts of domain and range of the inverse trigonometric functions $y={{\cos }^{-1}}x$ and $y={{\sin }^{-1}}x$ correctly. And after giving calculating the values of ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ and ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)$ , we should check for the validity of our answer by checking whether it lies in the range of its inverse trigonometric function or not.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




