
What is the principal focus for concave lenses?
A. It is a point on the principal axis of a concave lens, from where a parallel beam of light rays, parallel to the principal axis, after passing through the lens, appears to come.
B. It is a point on the principal axis of a concave lens, from where a perpendicular beam of light rays, travelling parallel to the principal axis, after passing through the lens, appears to come.
C. It is a point on the principal axis of a convex lens, from where a parallel beam of light rays, travelling parallel to the principal axis, after passing through the lens, appears to come.
D. None
Answer
612.9k+ views
Hint: Use the formula for the image of the lens i.e. $\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$, where u is the position of the object from the lens and v is the position of the image formed from the lens (according to sign convection). Then check what happens when the object is placed at the focus of a concave lens and at the focus of a convex lens.
Complete step by step answer:
Lens is a transparent medium bounded by two refracting surfaces, such that at least one surface is spherical. There are mainly two types of lenses- convex lens and concave lens. Convex lens is also called converging lens and concave is also called diverging lens. Convex lens is thick at the middle and the thickness decreases until the end. Concave lens is thinnest at the middle and the thickness increases until the end.
When light from an object passes through these lenses they refract the light and form an image of that object. This is given by the formula $\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$ ……(1) , where u is the position of the object from the lens and v is the position of the image formed from the lens (according to sign convection). F is the focus of the lens and f is the distance of the focus from the lens. For a convex lens, the value of f is taken positive and for concave lens, the value f is taken negative. Now we will see what this focus of the lens is. Suppose an object is at the focus of a concave lens, then u = -f. Substitute the value of u in equation (1).
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{(-f)}=\dfrac{1}{(-f)}\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=-\dfrac{2}{f}$
$\Rightarrow v=-\dfrac{f}{2}$ This means that the image of the object will be formed at a distance $\dfrac{f}{2}$ of behind the lens.
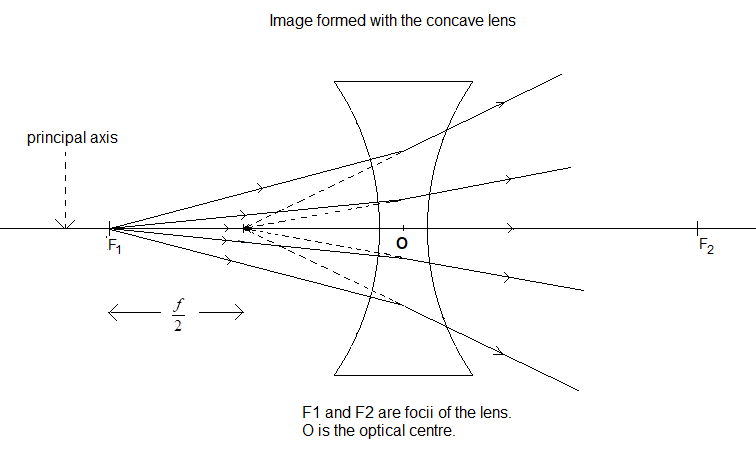
Let us do the same process for a convex lens. Here u = f.
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{(-f)}=\dfrac{1}{f}\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{f}-\dfrac{1}{f}=0$
$\Rightarrow v\to \infty $. This means the image of the object will be formed at infinite distance in front of the lens.
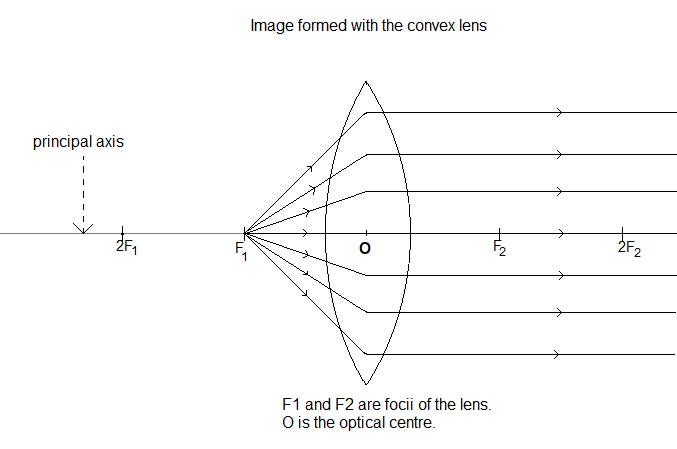
Therefore, the principal focus of a concave lens is a point on the principal axis of a convex lens, from where a parallel beam of light rays, travelling parallel to the principal axis, after passing through the lens, appears to come.
Hence, the correct option is (c).
Note: Students may make mistakes in following the sign convention for the position of the object and the image. The direction of the incident rays is taken as positive direction and the opposite direction to this is taken as negative. u is always negative, since its distance from the lens is always in the opposite direction of the light rays. The value of f for convex lens is taken as positive and for concave, it is taken negative. If the value of v is positive that means the image is formed in the direction of the incident light rays, from the lens. If it's formed in the opposite direction, it will be negative.
Complete step by step answer:
Lens is a transparent medium bounded by two refracting surfaces, such that at least one surface is spherical. There are mainly two types of lenses- convex lens and concave lens. Convex lens is also called converging lens and concave is also called diverging lens. Convex lens is thick at the middle and the thickness decreases until the end. Concave lens is thinnest at the middle and the thickness increases until the end.
When light from an object passes through these lenses they refract the light and form an image of that object. This is given by the formula $\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$ ……(1) , where u is the position of the object from the lens and v is the position of the image formed from the lens (according to sign convection). F is the focus of the lens and f is the distance of the focus from the lens. For a convex lens, the value of f is taken positive and for concave lens, the value f is taken negative. Now we will see what this focus of the lens is. Suppose an object is at the focus of a concave lens, then u = -f. Substitute the value of u in equation (1).
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{(-f)}=\dfrac{1}{(-f)}\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=-\dfrac{2}{f}$
$\Rightarrow v=-\dfrac{f}{2}$ This means that the image of the object will be formed at a distance $\dfrac{f}{2}$ of behind the lens.

Let us do the same process for a convex lens. Here u = f.
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{(-f)}=\dfrac{1}{f}\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{f}-\dfrac{1}{f}=0$
$\Rightarrow v\to \infty $. This means the image of the object will be formed at infinite distance in front of the lens.

Therefore, the principal focus of a concave lens is a point on the principal axis of a convex lens, from where a parallel beam of light rays, travelling parallel to the principal axis, after passing through the lens, appears to come.
Hence, the correct option is (c).
Note: Students may make mistakes in following the sign convention for the position of the object and the image. The direction of the incident rays is taken as positive direction and the opposite direction to this is taken as negative. u is always negative, since its distance from the lens is always in the opposite direction of the light rays. The value of f for convex lens is taken as positive and for concave, it is taken negative. If the value of v is positive that means the image is formed in the direction of the incident light rays, from the lens. If it's formed in the opposite direction, it will be negative.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




