
How will you prepare
(i) 2-Methylbutan-1-ol from an alkene
(ii) Cyclohexylmethanol from a Grignard reagent
(iii) 1-phenylethanol from acetaldehyde
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: There are various methods of preparation of alcohol such as acid catalysed hydration of alkene, hydroboration oxidation, reduction of aldehyde and ketone, reaction of Grignard reagent with aldehyde or ketone etc.
Complete step by step answer:
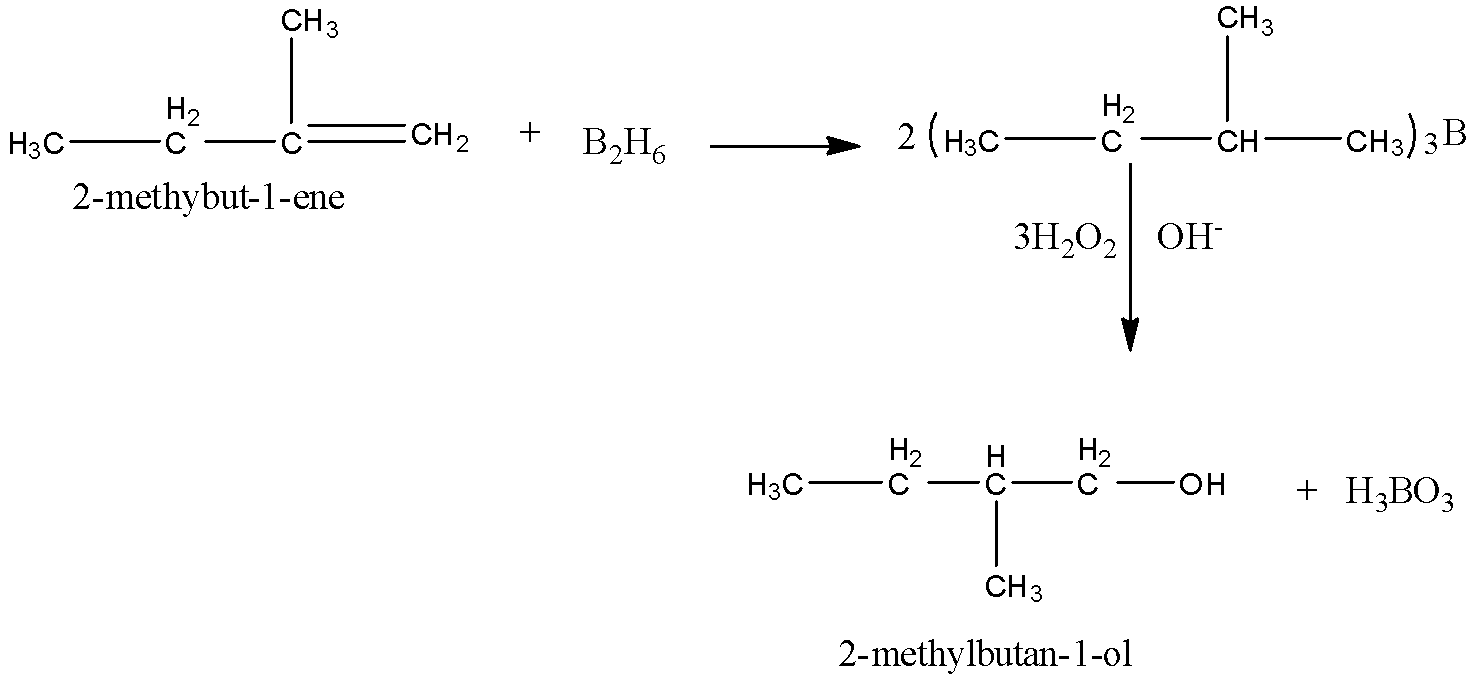
(i)Here, we have to obtain 2-methylbutan-1-ol from an alkene. We know that alcohol can be obtained from alkene by hydroboration oxidation reaction. In this reaction, diborane${\left( {{\rm{B}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)_2}$ undergoes reaction with alkene to produce trialkyl boranes as addition product. Then, the trialkyl boranes undergoes oxidation to form alcohol by ${{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}$ (hydrogen peroxide) in presence of aqueous NaOH.
Here, the final product that needs to be obtained is 2-methylbutanol. So, we have to take
2-methylbut-1-ene as reactant.
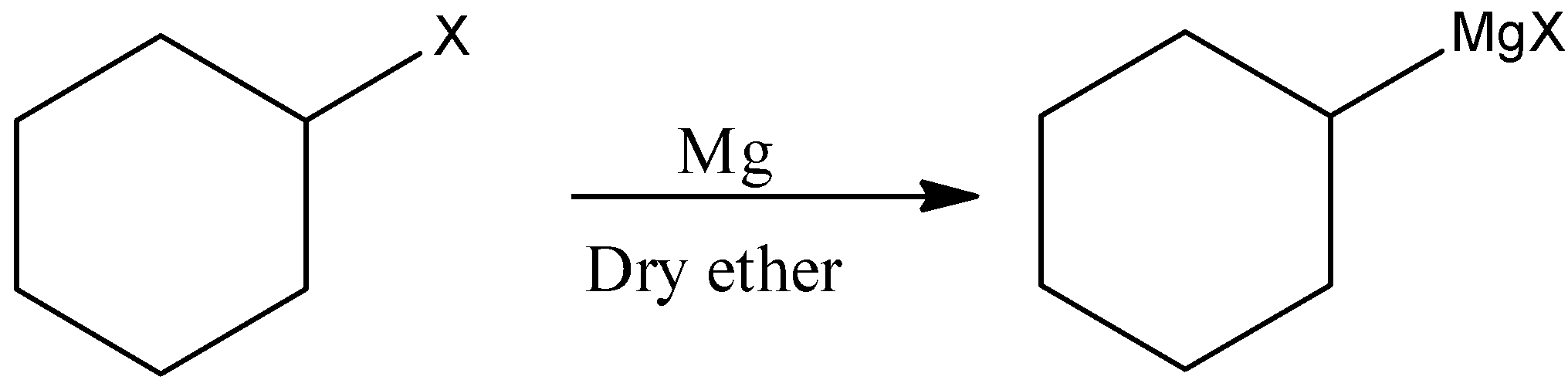
(ii)Here, we have to produce Cyclohexylmethanol from a Grignard reagent. We know that the reaction of the Grignard reagent with aldehyde or ketone can produce alcohol. The first step of the reaction is the nucleophilic addition of Grignard reagent to the carbonyl group to form an adduct. Hydrolysis of the adduct gives alcohol.
First we have to prepare Grignard reagent.
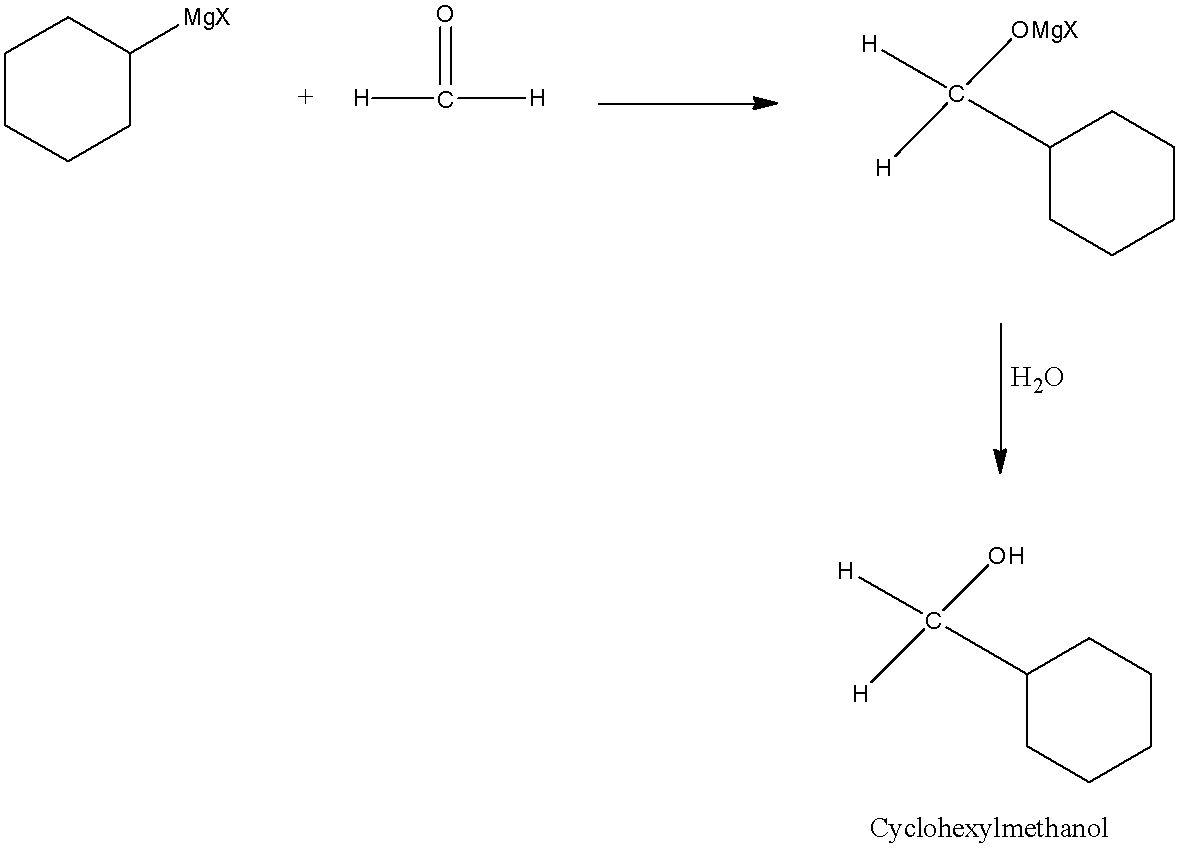
The carbonyl compound needed for this reaction is formaldehyde (HCHO).
Now, Grignard reagent undergoes reaction with formaldehyde.
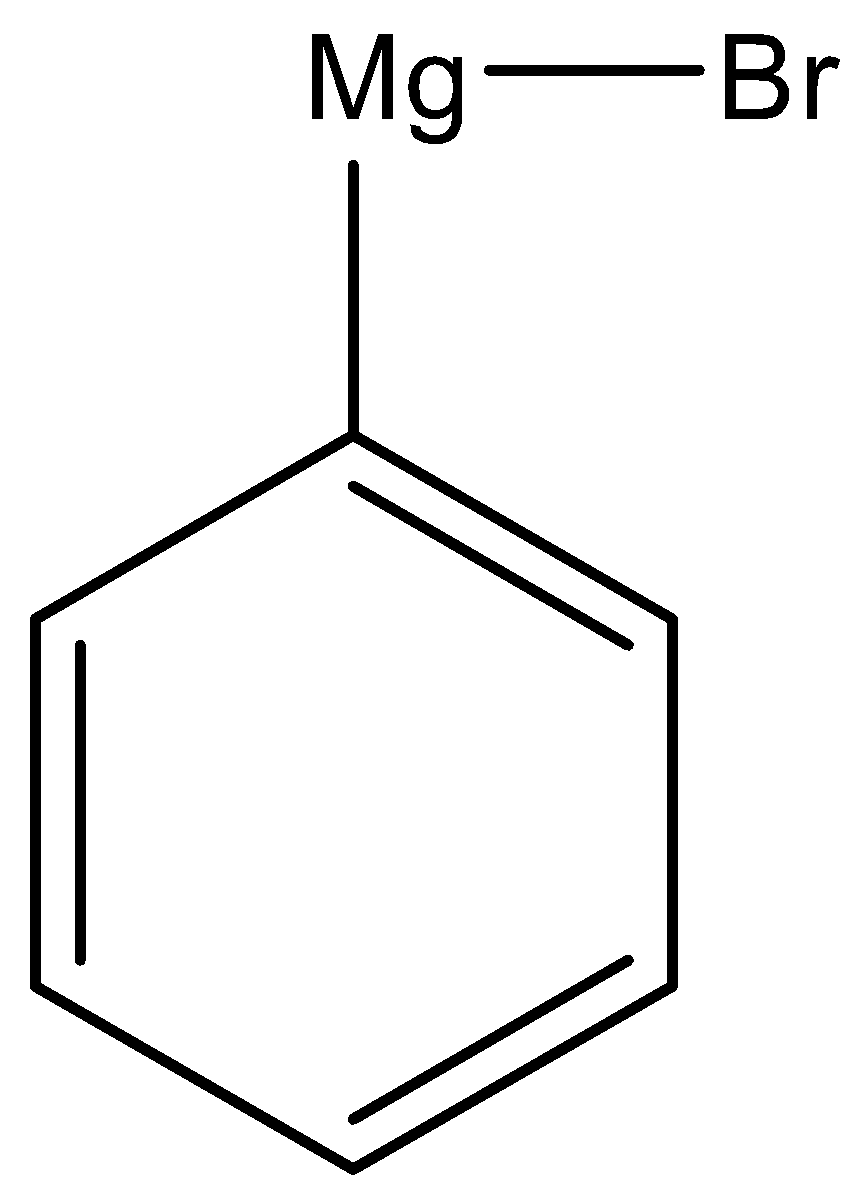
(iii) Here, we have to prepare 1-phenylethanol from acetaldehyde. Again we have to use Grignard reagent to obtain 1-phenylethanol.
As the phenyl group is present in the product, the Grignard reagent must contain phenyl group. So, for this reaction we have to use the following Grignard reagent.
The reaction takes place in two steps.
Step 1: Nucleophilic attack of the alkyl group of the Grignard reagent to the electrophilic carbon atom of aldehyde to form an addition product.
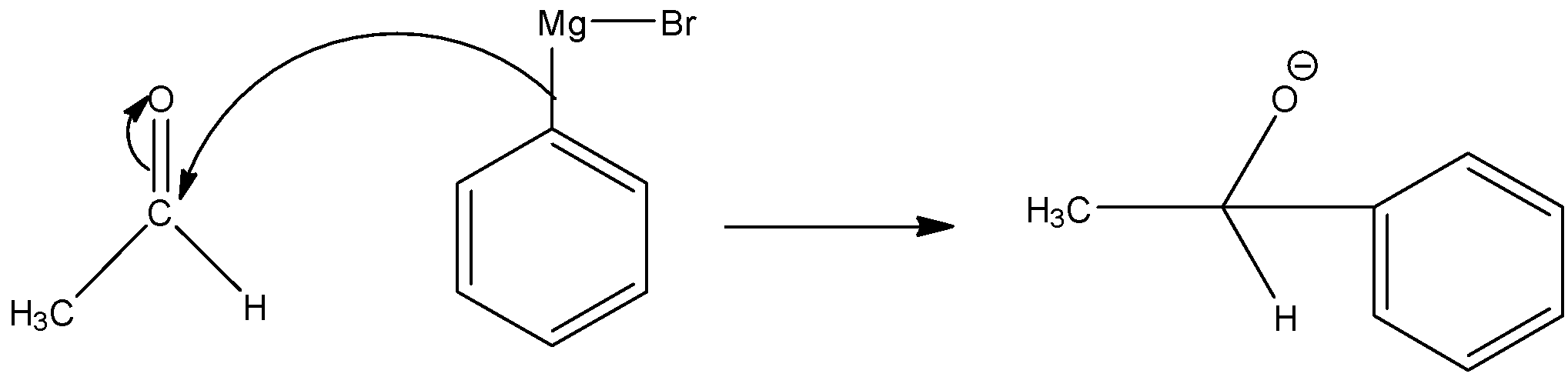
Step 2: The addition product undergoes hydrolysis to form 1-phenylethanol.
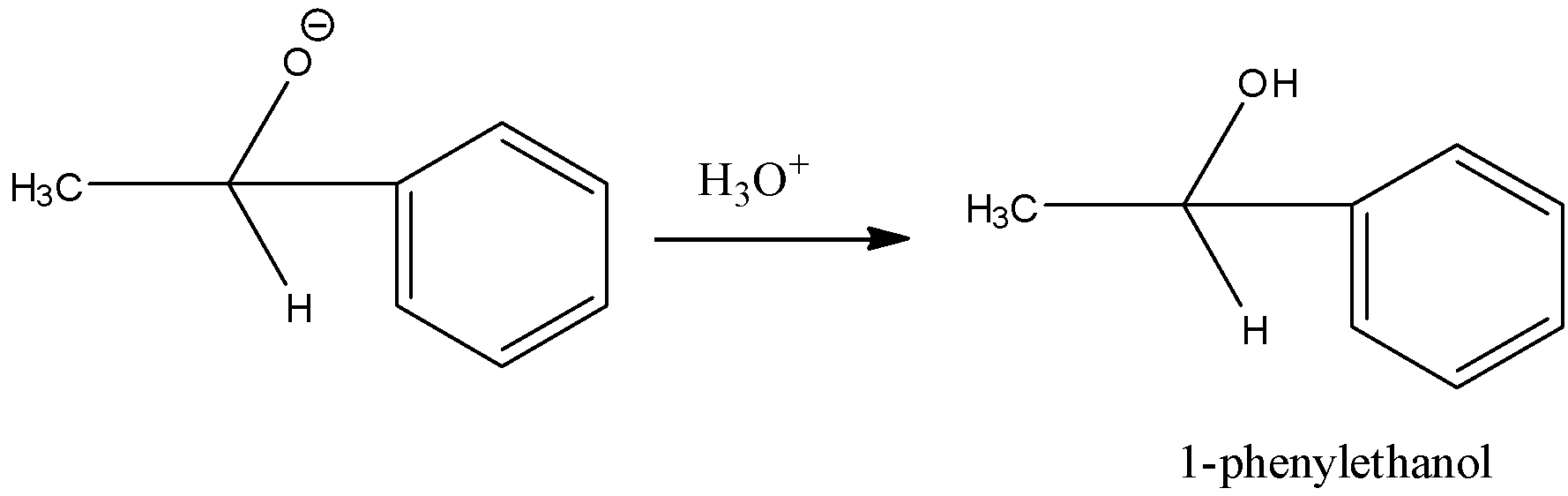
Note: Always remember that in the reaction of Grignard reagent and aldehyde or ketone, primary alcohol is produced when Grignard reagent undergoes reaction with methanal (formaldehyde), a secondary alcohol with other aldehydes and a tertiary alcohol with ketones.
Complete step by step answer:
(i)Here, we have to obtain 2-methylbutan-1-ol from an alkene. We know that alcohol can be obtained from alkene by hydroboration oxidation reaction. In this reaction, diborane${\left( {{\rm{B}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)_2}$ undergoes reaction with alkene to produce trialkyl boranes as addition product. Then, the trialkyl boranes undergoes oxidation to form alcohol by ${{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}$ (hydrogen peroxide) in presence of aqueous NaOH.
Here, the final product that needs to be obtained is 2-methylbutanol. So, we have to take
2-methylbut-1-ene as reactant.

(ii)Here, we have to produce Cyclohexylmethanol from a Grignard reagent. We know that the reaction of the Grignard reagent with aldehyde or ketone can produce alcohol. The first step of the reaction is the nucleophilic addition of Grignard reagent to the carbonyl group to form an adduct. Hydrolysis of the adduct gives alcohol.
First we have to prepare Grignard reagent.

The carbonyl compound needed for this reaction is formaldehyde (HCHO).
Now, Grignard reagent undergoes reaction with formaldehyde.

(iii) Here, we have to prepare 1-phenylethanol from acetaldehyde. Again we have to use Grignard reagent to obtain 1-phenylethanol.
As the phenyl group is present in the product, the Grignard reagent must contain phenyl group. So, for this reaction we have to use the following Grignard reagent.

The reaction takes place in two steps.
Step 1: Nucleophilic attack of the alkyl group of the Grignard reagent to the electrophilic carbon atom of aldehyde to form an addition product.

Step 2: The addition product undergoes hydrolysis to form 1-phenylethanol.

Note: Always remember that in the reaction of Grignard reagent and aldehyde or ketone, primary alcohol is produced when Grignard reagent undergoes reaction with methanal (formaldehyde), a secondary alcohol with other aldehydes and a tertiary alcohol with ketones.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




