
How to prepare 1-phenyl-3-methyl-2-butanol?
Answer
546k+ views
Hint: Aromatic compounds (benzene) can have carbon chain added through Friedal-crafts reactions. Organolithium reagents help in nucleophilic addition reactions. Sodium borohydrides are used as reducing agents for carbonyl compounds.
Complete answer:
We have been given to write about the preparation method of 1-phenyl-3-methyl-2-butanol. As the name suggests, this compound contains a benzene ring with a 4-carbon chain on the first carbon of benzene. This 4-carbon chain has a methyl group on carbon-3 and a hydroxyl group on carbon-2, which makes it a secondary alcohol.
The preparation of 1-phenyl-3-methyl-2-butanol involves friedel-craft acylation of benzene employing a catalyst used to synthesis organic compounds called oxalyl chloride\[(COC{{l}_{2}})\] that helps its formation into a carbon chain on position-1. Then the carbonyl adjacent from the benzene on this carbon chain is reduced, while the other carbonyl is unaffected. Then an organolithium reagent $({{C}_{3}}{{H}_{8}}Li)$ is used to carry a nucleophilic addition that removes the chloride group. The last step involves the use of a reducing agent, sodium borohydride $(NaB{{H}_{4}})$ and water that converts the carbonyl into secondary alcohol. Water helps in the addition of the hydrogen to the oxygen anion. The reaction is as follows:
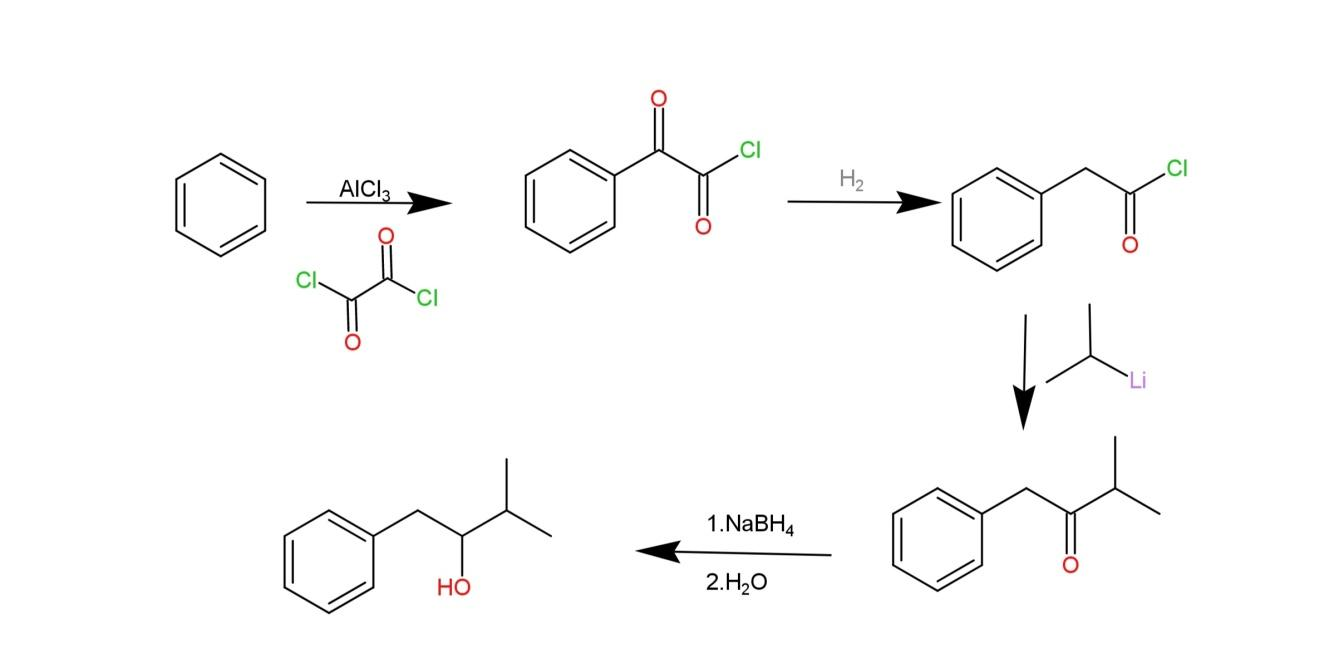
Hence, through the above reaction we can prepare 1-phenyl-3-methyl-2-butanol.
Note:
Friedel-crafts acylation is used in this reaction because; we have to obtain a secondary alcohol, which can be formed from the acyl group. While, friedel-crafts alkylation will be involved if we have to add up only a carbon chain to the benzene ring.
Complete answer:
We have been given to write about the preparation method of 1-phenyl-3-methyl-2-butanol. As the name suggests, this compound contains a benzene ring with a 4-carbon chain on the first carbon of benzene. This 4-carbon chain has a methyl group on carbon-3 and a hydroxyl group on carbon-2, which makes it a secondary alcohol.
The preparation of 1-phenyl-3-methyl-2-butanol involves friedel-craft acylation of benzene employing a catalyst used to synthesis organic compounds called oxalyl chloride\[(COC{{l}_{2}})\] that helps its formation into a carbon chain on position-1. Then the carbonyl adjacent from the benzene on this carbon chain is reduced, while the other carbonyl is unaffected. Then an organolithium reagent $({{C}_{3}}{{H}_{8}}Li)$ is used to carry a nucleophilic addition that removes the chloride group. The last step involves the use of a reducing agent, sodium borohydride $(NaB{{H}_{4}})$ and water that converts the carbonyl into secondary alcohol. Water helps in the addition of the hydrogen to the oxygen anion. The reaction is as follows:

Hence, through the above reaction we can prepare 1-phenyl-3-methyl-2-butanol.
Note:
Friedel-crafts acylation is used in this reaction because; we have to obtain a secondary alcohol, which can be formed from the acyl group. While, friedel-crafts alkylation will be involved if we have to add up only a carbon chain to the benzene ring.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




