
Predict the major product of acid catalyzed dehydration:
(i). $1-methyl\;cyclohexanol$
(ii). $Butan-1-ol$
Answer
510.9k+ views
Hint: The acid catalyzed dehydration reaction implies the removal of a water molecule from the compound in the form of hydroxyl ion and hydrogen ion from the adjacent carbon. Hence, for the given compounds, the alcohol group will be removed with a hydrogen ion from an adjacent carbon. If two products are possible, then the major product will be the one that is more substituted.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us consider the first compound
(i) The structural formula of the compound $1-methyl\;cyclohexanol$ can be shown as
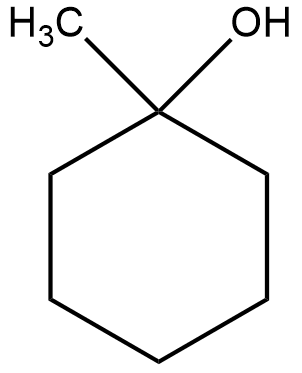
Now, the acid catalyzed dehydration can be shown as
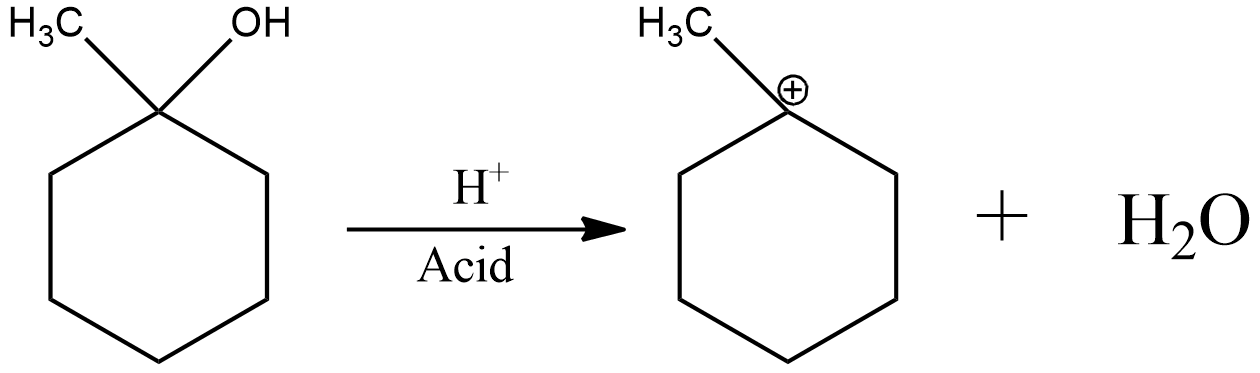
Now, the charge of electron deficiency is on a tertiary carbon. Hence, it is already stable.
Now, to remove the deficiency, the carbon will form a double bond with one of its adjacent carbon, which loses hydrogen ion to form the double bond. As here the electron deficient carbon has three adjacent carbons, three products will be formed as shown below
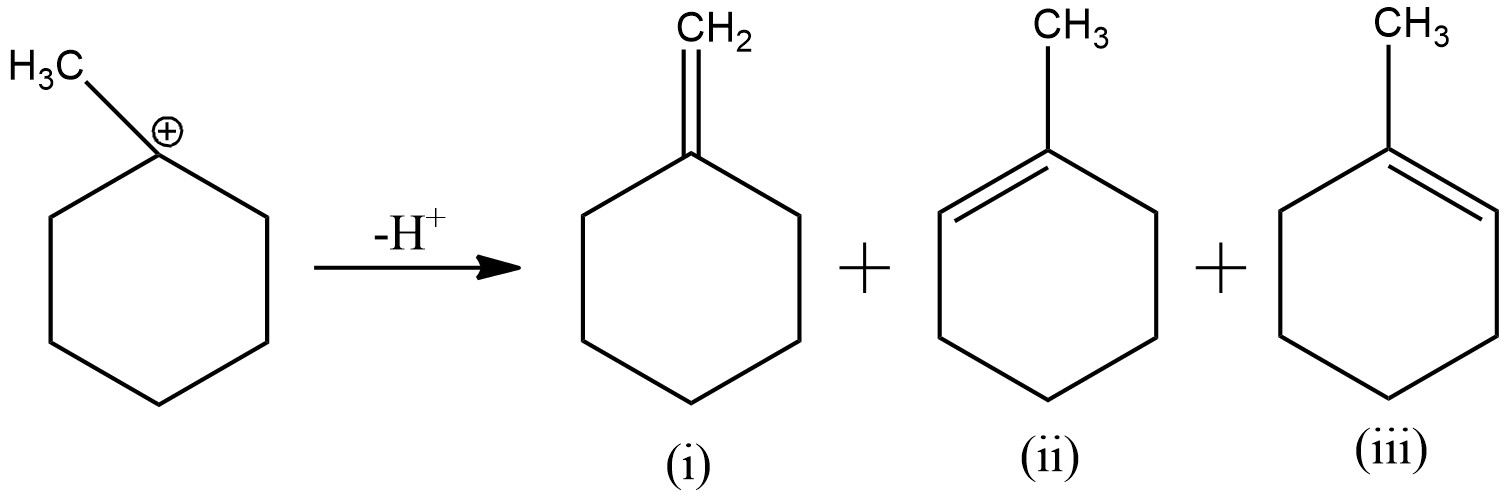
The second and third products are just a mirror image of each other. Hence, they will be considered as one product.
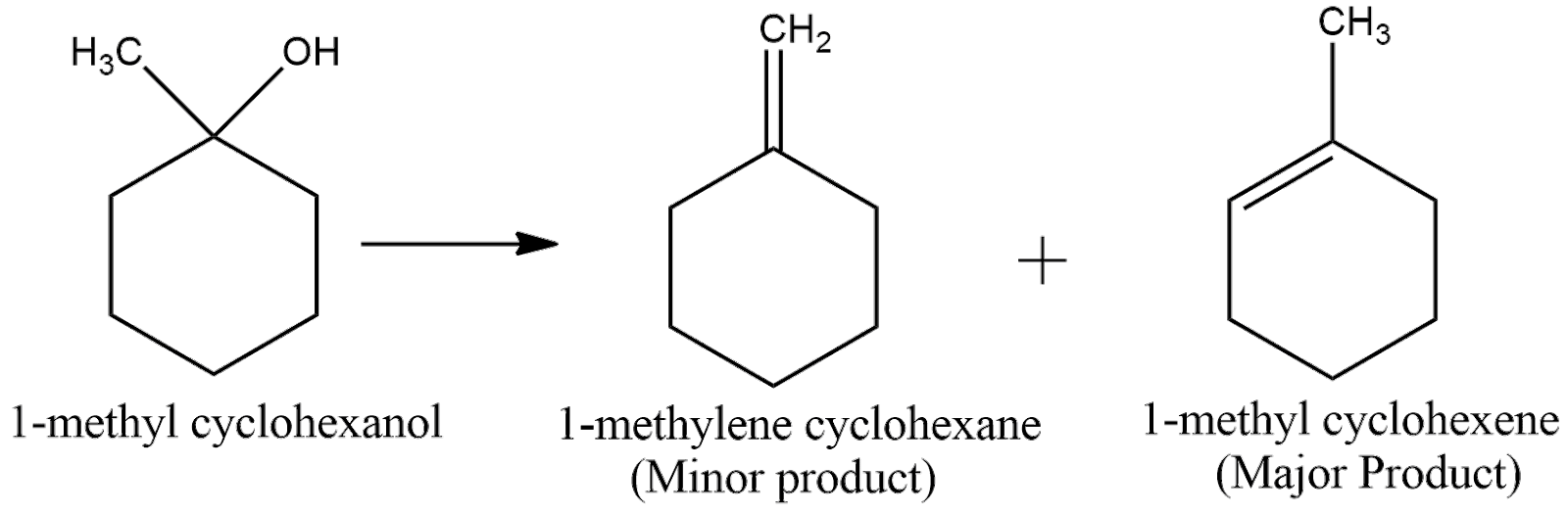
Now, according to Saytzeff Rule, the alkene having more number of carbon groups attached to the double bonded carbon is obtained in more proportion. From the above figure, we can understand that the second product has more carbon groups attached to the double bond carbon. Hence, the second product is the major product. Thus, the overall reaction can be expressed as
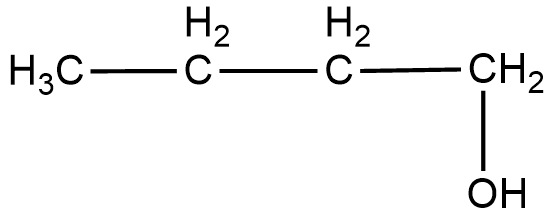
(ii) The structural formula of the compound $Butan-1-ol$ can be shown as
Now, the acid catalyzed dehydration can be shown as
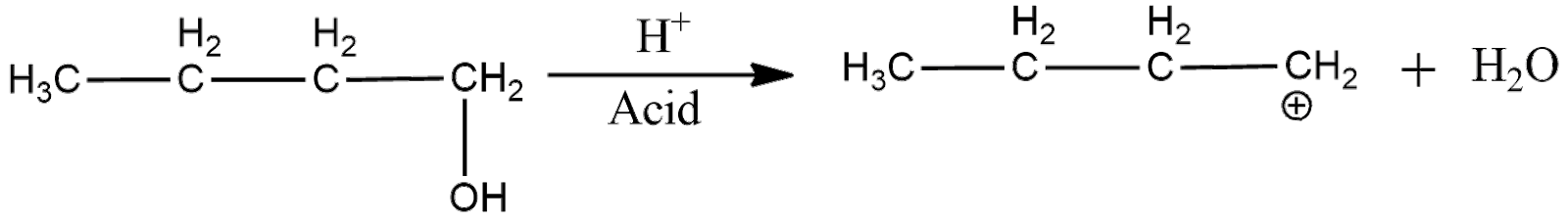
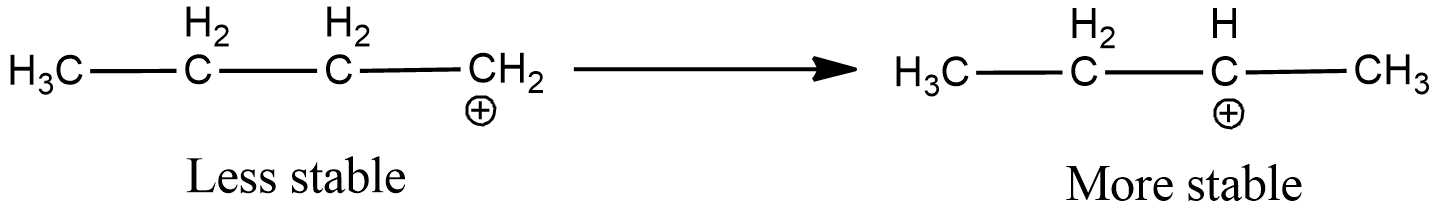
Now, the electron deficient carbon is primary. Hence, the positive charge will move to the adjacent secondary carbon as it is more stable.
Now, to remove the deficiency, the carbon will form a double bond with one of its adjacent carbon, which loses hydrogen ion to form the double bond. As here the electron deficient carbon has two adjacent carbons, two products will be formed as shown below
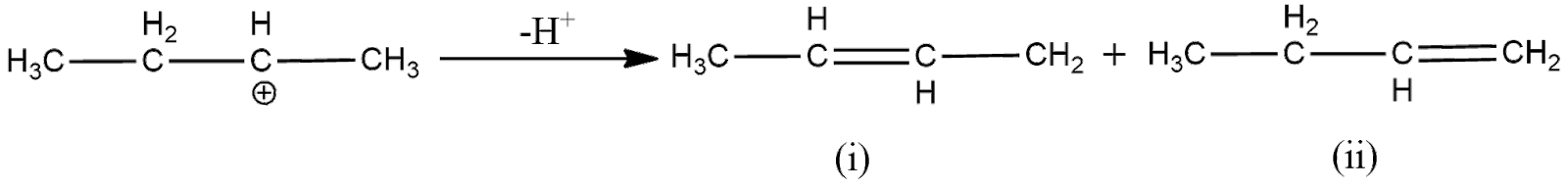
Now, according to Saytzeff Rule, the alkene having more number of carbon groups attached to the double bonded carbon is obtained in more proportion. From the above figure, we can understand that the first product has more carbon groups attached to the double bond carbon. Hence, the first product is the major product. Thus, the overall reaction can be expressed as
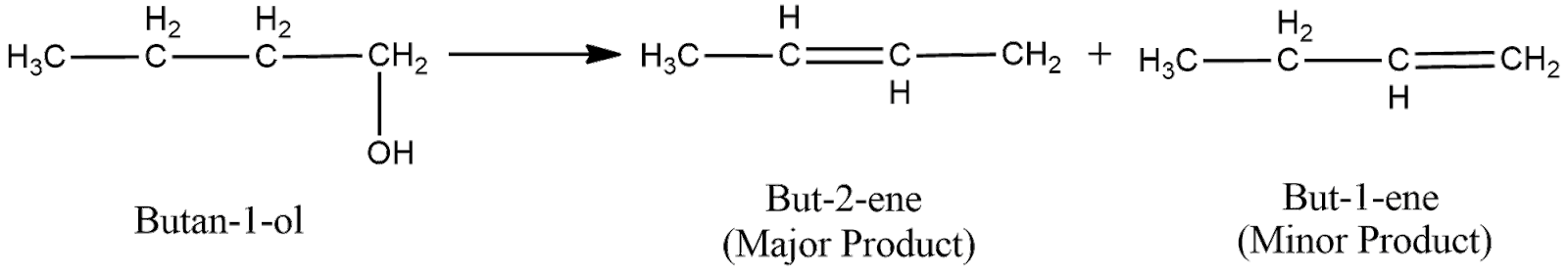
Note:
Here, for removing water molecules, we should always first remove the hydroxyl ion and show the electron deficient carbon. If the electron deficient carbon is primary, the positive charge will shift to a secondary carbon to make the deficiency stable. If a tertiary carbon is present, the positive charge will be the most stable there, due to the positive inductive effect of carbon groups. Finally the electron deficient carbon makes a double bond if the adjacent carbon. If a choice is available, the double bond is always formed with the more substituted carbon.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us consider the first compound
(i) The structural formula of the compound $1-methyl\;cyclohexanol$ can be shown as

Now, the acid catalyzed dehydration can be shown as

Now, the charge of electron deficiency is on a tertiary carbon. Hence, it is already stable.
Now, to remove the deficiency, the carbon will form a double bond with one of its adjacent carbon, which loses hydrogen ion to form the double bond. As here the electron deficient carbon has three adjacent carbons, three products will be formed as shown below

The second and third products are just a mirror image of each other. Hence, they will be considered as one product.
Now, according to Saytzeff Rule, the alkene having more number of carbon groups attached to the double bonded carbon is obtained in more proportion. From the above figure, we can understand that the second product has more carbon groups attached to the double bond carbon. Hence, the second product is the major product. Thus, the overall reaction can be expressed as

(ii) The structural formula of the compound $Butan-1-ol$ can be shown as

Now, the acid catalyzed dehydration can be shown as

Now, the electron deficient carbon is primary. Hence, the positive charge will move to the adjacent secondary carbon as it is more stable.

Now, to remove the deficiency, the carbon will form a double bond with one of its adjacent carbon, which loses hydrogen ion to form the double bond. As here the electron deficient carbon has two adjacent carbons, two products will be formed as shown below

Now, according to Saytzeff Rule, the alkene having more number of carbon groups attached to the double bonded carbon is obtained in more proportion. From the above figure, we can understand that the first product has more carbon groups attached to the double bond carbon. Hence, the first product is the major product. Thus, the overall reaction can be expressed as
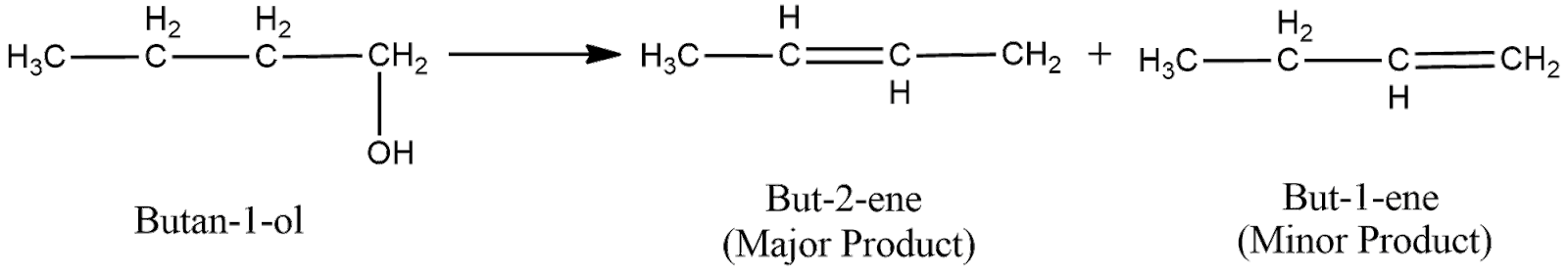
Note:
Here, for removing water molecules, we should always first remove the hydroxyl ion and show the electron deficient carbon. If the electron deficient carbon is primary, the positive charge will shift to a secondary carbon to make the deficiency stable. If a tertiary carbon is present, the positive charge will be the most stable there, due to the positive inductive effect of carbon groups. Finally the electron deficient carbon makes a double bond if the adjacent carbon. If a choice is available, the double bond is always formed with the more substituted carbon.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




