
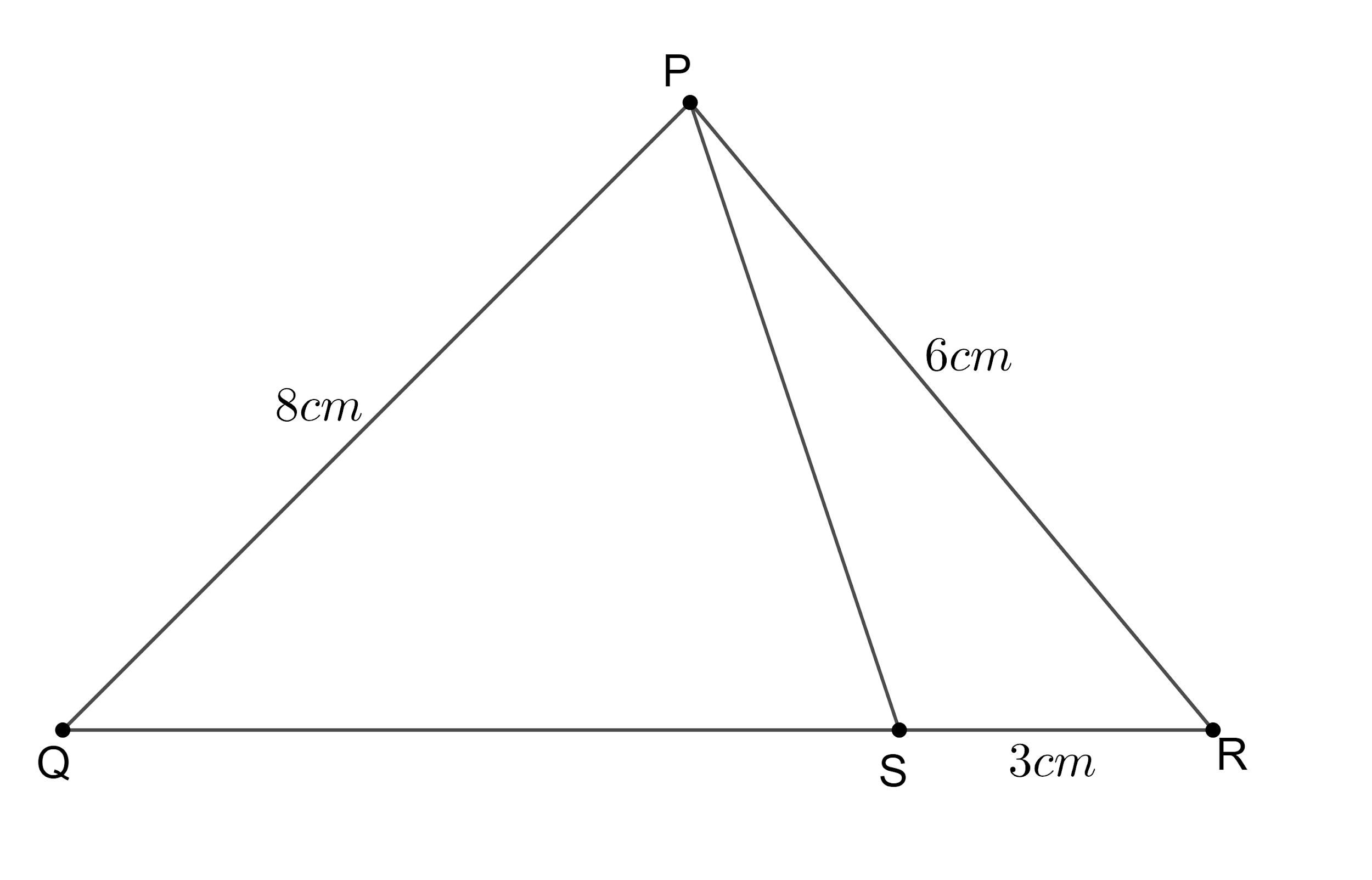
PQR is a triangle, S is a point on the side QR of $\Delta PQR$ such that $\angle PSR=\angle QPR$. Given $QP=8cm$, $PR=6cm$ and $SR=3cm$.
(i) Prove $\Delta PQR\sim\Delta SPR$?
(ii) Find the length of the QR and PS?
(iii) $\dfrac{\text{area of }\Delta \text{PQR}}{\text{area of }\Delta \text{SPR}}$.

Answer
577.2k+ views
Hint: We start solving the problem by checking the common angles and common sides of both triangles $\Delta PQR$ and $\Delta SPR$ to check whether those triangles satisfy AAA or ASA or SAS properties. After proving the similarity of triangles, we take the proportion of sides of the triangles to get the values of unknown sides. We then use Heron's formula to find the area of both the triangles and then take the ratio of them to get the required solution.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the problem, we are given that S is a point on the side QR of $\Delta PQR$ such that $\angle PSR=\angle QPR$ and also $QP=8cm$, $PR=6cm$ and $SR=3cm$.
(i) We need to prove that $\Delta PQR\sim\Delta SPR$.
From the figure we can see that $PR=PR$ (common side for both triangles).
$\Rightarrow \angle PRQ=\angle PRS$ (common angle for both triangles).
$\Rightarrow \angle PSR=\angle QPR$ (given in the problem).
We know that from ASA property, if two angles and one side is equal in both of the given triangles, then we can say that the given triangles are similar.
So, we get $\Delta PQR\sim\Delta SPR$.
(ii) Now, we need to find the length of the sides QR and PS.
Let us take the proportions of sides as the given triangles are similar.
So, we get $\dfrac{PQ}{SP}=\dfrac{QR}{PR}=\dfrac{PR}{SR}$.
Let us substitute the values given in the problem.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{8}{SP}=\dfrac{QR}{6}=\dfrac{6}{3}$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{8}{SP}=\dfrac{QR}{6}=2$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{8}{SP}=2$ and $\dfrac{QR}{6}=2$.
$\Rightarrow SP=4$ and $QR=12$.
(iii) Now, we need to find the ratio $\dfrac{\text{area of }\Delta \text{PQR}}{\text{area of }\Delta \text{SPR}}$.
We know that the area of the triangle is defined as $\sqrt{s\left( s-a \right)\left( s-b \right)\left( s-c \right)}$, where ‘s’ is half the perimeter of the triangle i.e., $s=\dfrac{a+b+c}{2}$ and ‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’ are the sides of the triangle.
Let us find the area of $\Delta PQR$ first.
So, we get $s=\dfrac{8+6+12}{2}=\dfrac{26}{2}=13$.
So, area of $\Delta PQR$ is $\sqrt{13\left( 13-8 \right)\left( 13-6 \right)\left( 13-2 \right)}=\sqrt{13\times 5\times 7\times 1}=\sqrt{455}$.
Now, let us find the area of $\Delta SPR$.
So, we get $s=\dfrac{6+3+4}{2}=\dfrac{13}{2}=6.5$.
So, area of $\Delta SPR$ is $\sqrt{6.5\left( 6.5-6 \right)\left( 6.5-3 \right)\left( 6.5-4 \right)}=\sqrt{6.5\times 0.5\times 3.5\times 2.5}=\sqrt{28.4375}$.
Now, let us take the ratio $\dfrac{\text{area of }\Delta \text{PQR}}{\text{area of }\Delta \text{SPR}}$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{area of }\Delta \text{PQR}}{\text{area of }\Delta \text{SPR}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{455}}{\sqrt{28.4375}}$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{area of }\Delta \text{PQR}}{\text{area of }\Delta \text{SPR}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{455}{28.4375}}$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{area of }\Delta \text{PQR}}{\text{area of }\Delta \text{SPR}}=\sqrt{16}$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{area of }\Delta \text{PQR}}{\text{area of }\Delta \text{SPR}}=4$.
So, we have found the ratio $\dfrac{\text{area of }\Delta \text{PQR}}{\text{area of }\Delta \text{SPR}}$ as 4.
Note: We need to take the proportion of sides by following the rule that the sides opposite to the equal angles are equal in order to avoid mistakes. We can also find the area of the triangles using the formula \[Area=\dfrac{1}{2}\times base\times height\]. We should not confuse ‘s’ with the perimeter of the triangle. Similarly, we can expect problems to find the angles present in triangles using the cosine or sine rule.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the problem, we are given that S is a point on the side QR of $\Delta PQR$ such that $\angle PSR=\angle QPR$ and also $QP=8cm$, $PR=6cm$ and $SR=3cm$.
(i) We need to prove that $\Delta PQR\sim\Delta SPR$.
From the figure we can see that $PR=PR$ (common side for both triangles).
$\Rightarrow \angle PRQ=\angle PRS$ (common angle for both triangles).
$\Rightarrow \angle PSR=\angle QPR$ (given in the problem).
We know that from ASA property, if two angles and one side is equal in both of the given triangles, then we can say that the given triangles are similar.
So, we get $\Delta PQR\sim\Delta SPR$.
(ii) Now, we need to find the length of the sides QR and PS.
Let us take the proportions of sides as the given triangles are similar.
So, we get $\dfrac{PQ}{SP}=\dfrac{QR}{PR}=\dfrac{PR}{SR}$.
Let us substitute the values given in the problem.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{8}{SP}=\dfrac{QR}{6}=\dfrac{6}{3}$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{8}{SP}=\dfrac{QR}{6}=2$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{8}{SP}=2$ and $\dfrac{QR}{6}=2$.
$\Rightarrow SP=4$ and $QR=12$.
(iii) Now, we need to find the ratio $\dfrac{\text{area of }\Delta \text{PQR}}{\text{area of }\Delta \text{SPR}}$.
We know that the area of the triangle is defined as $\sqrt{s\left( s-a \right)\left( s-b \right)\left( s-c \right)}$, where ‘s’ is half the perimeter of the triangle i.e., $s=\dfrac{a+b+c}{2}$ and ‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’ are the sides of the triangle.
Let us find the area of $\Delta PQR$ first.
So, we get $s=\dfrac{8+6+12}{2}=\dfrac{26}{2}=13$.
So, area of $\Delta PQR$ is $\sqrt{13\left( 13-8 \right)\left( 13-6 \right)\left( 13-2 \right)}=\sqrt{13\times 5\times 7\times 1}=\sqrt{455}$.
Now, let us find the area of $\Delta SPR$.
So, we get $s=\dfrac{6+3+4}{2}=\dfrac{13}{2}=6.5$.
So, area of $\Delta SPR$ is $\sqrt{6.5\left( 6.5-6 \right)\left( 6.5-3 \right)\left( 6.5-4 \right)}=\sqrt{6.5\times 0.5\times 3.5\times 2.5}=\sqrt{28.4375}$.
Now, let us take the ratio $\dfrac{\text{area of }\Delta \text{PQR}}{\text{area of }\Delta \text{SPR}}$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{area of }\Delta \text{PQR}}{\text{area of }\Delta \text{SPR}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{455}}{\sqrt{28.4375}}$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{area of }\Delta \text{PQR}}{\text{area of }\Delta \text{SPR}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{455}{28.4375}}$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{area of }\Delta \text{PQR}}{\text{area of }\Delta \text{SPR}}=\sqrt{16}$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{area of }\Delta \text{PQR}}{\text{area of }\Delta \text{SPR}}=4$.
So, we have found the ratio $\dfrac{\text{area of }\Delta \text{PQR}}{\text{area of }\Delta \text{SPR}}$ as 4.
Note: We need to take the proportion of sides by following the rule that the sides opposite to the equal angles are equal in order to avoid mistakes. We can also find the area of the triangles using the formula \[Area=\dfrac{1}{2}\times base\times height\]. We should not confuse ‘s’ with the perimeter of the triangle. Similarly, we can expect problems to find the angles present in triangles using the cosine or sine rule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

The Equation xxx + 2 is Satisfied when x is Equal to Class 10 Maths

Which Country is Called "The Land of Festivals"?

What is Contraception List its four different methods class 10 biology CBSE




