
Porous wood contains
a) Fibres
b) Sieve tubes
c) Tracheids
d) Vessels
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: The wood of dicot angiosperms is called hardwood. The wood is hard and weighty with a harsh surface. for example, oak, maple, or pecan, which are not Monocot. It has a more slow development rate.
Complete step by step answer:
Hardwoods will in general have expansive leaves, Hardwoods have vessel components that transport water all through the wood; under a magnifying instrument, these components show up as pores. The pores in hardwoods are a great deal of what gives hardwood its noticeable grain.
In hardwoods, the extent of constituent cell types — vessel individuals, strands, and parenchyma — relies fundamentally upon species. Vessel individuals and strands are consistently present and pivotally arranged; hub parenchyma is only here and there missing. Beams in hardwoods are made altogether of spiral parenchyma cells.
So the correct answer is 'Vessels'.
Additional information: Hardwoods are regularly more costly and once in a while additionally testing to work with, their upside is that most — however not all — are denser, which means numerous hardwoods will last longer than softwoods. Therefore, hardwoods are bound to be found in excellent furnishings, decks, ground surface, and development that requirements to last. As indicated by the overall size and dissemination of pores, woods of expansive leaf species are additionally ordered into ring-permeable and diffuse-permeable sorts. In ring-permeable woods, for example, oak and chestnut, the pores of earlywood are enormously contrasted and those of latewood. In diffuse-permeable woods, for example, basswood and well known, all pores are about a similar size and equitably dispersed.
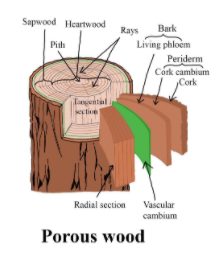
Note: Polarization microscopy, X beams, electron microscopy, and different procedures give data with respect to the structure of cell dividers and different highlights covered up to light magnifying instruments. Cell dividers are translucent. They are made out of a slender, external essential divider, and a much thicker optional divider, the last made of three layers.
Complete step by step answer:
Hardwoods will in general have expansive leaves, Hardwoods have vessel components that transport water all through the wood; under a magnifying instrument, these components show up as pores. The pores in hardwoods are a great deal of what gives hardwood its noticeable grain.
In hardwoods, the extent of constituent cell types — vessel individuals, strands, and parenchyma — relies fundamentally upon species. Vessel individuals and strands are consistently present and pivotally arranged; hub parenchyma is only here and there missing. Beams in hardwoods are made altogether of spiral parenchyma cells.
So the correct answer is 'Vessels'.
Additional information: Hardwoods are regularly more costly and once in a while additionally testing to work with, their upside is that most — however not all — are denser, which means numerous hardwoods will last longer than softwoods. Therefore, hardwoods are bound to be found in excellent furnishings, decks, ground surface, and development that requirements to last. As indicated by the overall size and dissemination of pores, woods of expansive leaf species are additionally ordered into ring-permeable and diffuse-permeable sorts. In ring-permeable woods, for example, oak and chestnut, the pores of earlywood are enormously contrasted and those of latewood. In diffuse-permeable woods, for example, basswood and well known, all pores are about a similar size and equitably dispersed.

Note: Polarization microscopy, X beams, electron microscopy, and different procedures give data with respect to the structure of cell dividers and different highlights covered up to light magnifying instruments. Cell dividers are translucent. They are made out of a slender, external essential divider, and a much thicker optional divider, the last made of three layers.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




