
Polymer of $\alpha - D$ glucose is
(A) Glycogen
(B) Cellulose
(C) Inulin
(D) Callose
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: Polysaccharides are polymers or chains of monosaccharides and are macromolecules. They are threads (literally a cotton thread) containing different monosaccharides as building blocks and are branched or unbranched. In a polysaccharide the individual monosaccharides are linked by a glycosidic bond. The right end of a polysaccharide is reducing end while the left end is non-reducing end.
Complete answer:
There are two types of polysaccharides namely:
Homopolysaccharides: they are polysaccharides that consist of only one type of monosaccharide monomer. Starch and glycogen both are polymers of glucose and serve as a storage form in plants and animals respectively.
Heteropolysaccharides: these consist of more than one type of monosaccharide monomer, that is they are heteropolymers and are more complex polysaccharides.
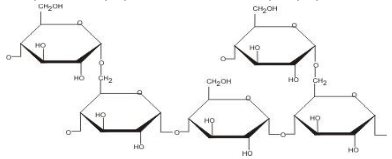
Diagram showing the polymer in which glucose molecules are linked
Now let us know the polymer given in options :-
Glycogen :- Glycogen is made up of about 30,000 glucose residues. It's a branched structure having $\alpha $1,4 and 1, 6 linkage. It gives red colour with iodine. Thus, this option is correct.
Cellulose :- Cellulose is the main structural unbranched homopolysaccharide of plants. One molecule of cellulose has about 6000 $\beta $-glucose residues and not $\alpha $ residues. Thus, this option is not correct.
Inulin :- Inulin is a polymer of fructose. It is a storage polysaccharide of roots and tubers of dahlia and related plants.
Callose :- it is a type of plant polysaccharide but it is made up of $\beta $ 1, 3 glucose linkage. Thus this option is not correct.
Our required answer is A) glycogen.
Note: One more polymer of glucose is starch. Starch has two components - amylose (an unbranched polymer) and amylopectin (a branched polymer).
Amylopectin : Consists of 2000 - 200,000 glucose molecules forming straight chain and branches (after 25 glucose units). Branching point has a $\alpha $ 1-6 glycosidic linkage.
Amylose : Consists of , $\alpha $ 1-4 glycosidic linkage between $\alpha - D$ glucose molecules. It is a straight chain of 200 - 1000 glucose units. It is helical, each turn consists of 6 glucose units.
Complete answer:
There are two types of polysaccharides namely:
Homopolysaccharides: they are polysaccharides that consist of only one type of monosaccharide monomer. Starch and glycogen both are polymers of glucose and serve as a storage form in plants and animals respectively.
Heteropolysaccharides: these consist of more than one type of monosaccharide monomer, that is they are heteropolymers and are more complex polysaccharides.

Diagram showing the polymer in which glucose molecules are linked
Now let us know the polymer given in options :-
Glycogen :- Glycogen is made up of about 30,000 glucose residues. It's a branched structure having $\alpha $1,4 and 1, 6 linkage. It gives red colour with iodine. Thus, this option is correct.
Cellulose :- Cellulose is the main structural unbranched homopolysaccharide of plants. One molecule of cellulose has about 6000 $\beta $-glucose residues and not $\alpha $ residues. Thus, this option is not correct.
Inulin :- Inulin is a polymer of fructose. It is a storage polysaccharide of roots and tubers of dahlia and related plants.
Callose :- it is a type of plant polysaccharide but it is made up of $\beta $ 1, 3 glucose linkage. Thus this option is not correct.
Our required answer is A) glycogen.
Note: One more polymer of glucose is starch. Starch has two components - amylose (an unbranched polymer) and amylopectin (a branched polymer).
Amylopectin : Consists of 2000 - 200,000 glucose molecules forming straight chain and branches (after 25 glucose units). Branching point has a $\alpha $ 1-6 glycosidic linkage.
Amylose : Consists of , $\alpha $ 1-4 glycosidic linkage between $\alpha - D$ glucose molecules. It is a straight chain of 200 - 1000 glucose units. It is helical, each turn consists of 6 glucose units.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




