
Plot \[A \times B\] and \[B \times A\] on XY-plane if: \[A = \left\{ {x:x \in N,1 \le x \le 5} \right\}\] and \[B = \left\{ {y:y \in W,y < 3} \right\}\].
Answer
561.3k+ views
Hint: Here, we need to plot the Cartesian products. First, we will write the sets in roster form. Then, we will find their Cartesian products. Finally, we will plot the ordered pairs in the Cartesian products on the XY plane.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The given sets \[A = \left\{ {x:x \in N,1 \le x \le 5} \right\}\] and \[B = \left\{ {y:y \in W,y < 3} \right\}\] are in set-builder form.
We will rewrite the sets A and B using the roster method.
First, let us find the elements of set A.
The value of \[x\] in set \[A = \left\{ {x:x \in N,1 \le x \le 5} \right\}\] is any natural number between 1 and 5, both included.
The possible values of \[x\] are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5.
Therefore, we can rewrite set A using roster method as
\[A = \left\{ {1,2,3,4,5} \right\}\]
Next, we will find the elements of set B.
The value of \[y\] in set \[B = \left\{ {y:y \in W,y < 3} \right\}\] is any whole number less than 3.
The possible values of \[y\] are 0, 1, 2.
Therefore, we can rewrite set B using roster method as
\[B = \left\{ {0,1,2} \right\}\]
Now, we will find the Cartesian product \[A \times B\].
The Cartesian product \[A \times B\] of two sets A and B is the set of all possible ordered pairs \[\left( {x,y} \right)\], where \[x \in A\] and \[y \in B\].
The first component \[x\] of ordered pair \[\left( {x,y} \right)\] in the Cartesian product \[A \times B\] can be 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5, because \[A = \left\{ {1,2,3,4,5} \right\}\].
The second component \[y\] of ordered pair \[\left( {x,y} \right)\] in the Cartesian product \[A \times B\] can be 0, 1, or 2, because \[B = \left\{ {0,1,2} \right\}\].
Therefore, we get the Cartesian product \[A \times B\] as
\[A \times B = \left\{ \begin{array}{l}\left( {1,0} \right),\left( {2,0} \right),\left( {3,0} \right),\left( {4,0} \right),\left( {5,0} \right),\left( {1,1} \right),\left( {2,1} \right),\left( {3,1} \right),\\\left( {4,1} \right),\left( {5,1} \right),\left( {1,2} \right),\left( {2,2} \right),\left( {3,2} \right),\left( {4,2} \right),\left( {5,2} \right)\end{array} \right\}\]
Now, we will plot the ordered pairs \[\left( {x,y} \right)\] of the Cartesian product \[A \times B\] on the XY-plane.
Plotting the points, we get the graph as
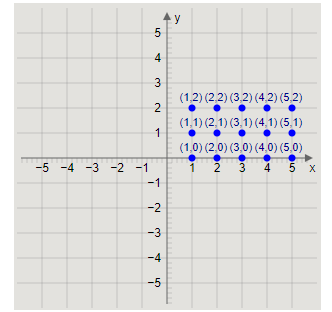
Now, we will find the Cartesian product \[B \times A\].
The Cartesian product \[B \times A\] of two sets A and B is the set of all possible ordered pairs \[\left( {y,x} \right)\], where \[y \in B\] and \[x \in A\].
The first component \[y\] of ordered pair \[\left( {y,x} \right)\] in the Cartesian product \[B \times A\] can be 0, 1, or 2, because \[B = \left\{ {0,1,2} \right\}\].
The second component \[x\] of ordered pair \[\left( {y,x} \right)\] in the Cartesian product \[B \times A\] can be 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5, because \[A = \left\{ {1,2,3,4,5} \right\}\].
Therefore, we get the Cartesian product \[B \times A\] as
\[B \times A = \left\{ \begin{array}{l}\left( {0,1} \right),\left( {1,1} \right),\left( {2,1} \right),\left( {0,2} \right),\left( {1,2} \right),\left( {2,2} \right),\left( {0,3} \right),\left( {1,3} \right),\\\left( {2,3} \right),\left( {0,4} \right),\left( {1,4} \right),\left( {2,4} \right),\left( {0,5} \right),\left( {1,5} \right),\left( {2,5} \right)\end{array} \right\}\]
Now, we will plot the ordered pairs \[\left( {y,x} \right)\] of the Cartesian product \[B \times A\] on XY-plane.
Plotting the points, we get the graph as
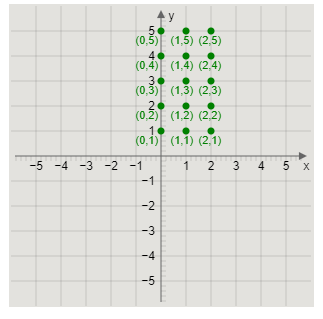
Note: We rewrite the sets A and B using roster method. A set is said to be written using roster method if all the elements of the set are written.
We used the terms ‘whole number’ and ‘natural number’ in the solution.
Whole numbers include the numbers 0, and all the positive integers like 1, 2, 3, etc. They are the basic numbers we use when counting objects.
For example: 0, 1, 2, 100, 400, 52225, are all whole numbers.
Natural numbers include all the positive integers like 1, 2, 3, etc.
For example: 1, 2, 100, 400, 52225, are all whole numbers.
Whole numbers include all the natural numbers, and the number 0.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The given sets \[A = \left\{ {x:x \in N,1 \le x \le 5} \right\}\] and \[B = \left\{ {y:y \in W,y < 3} \right\}\] are in set-builder form.
We will rewrite the sets A and B using the roster method.
First, let us find the elements of set A.
The value of \[x\] in set \[A = \left\{ {x:x \in N,1 \le x \le 5} \right\}\] is any natural number between 1 and 5, both included.
The possible values of \[x\] are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5.
Therefore, we can rewrite set A using roster method as
\[A = \left\{ {1,2,3,4,5} \right\}\]
Next, we will find the elements of set B.
The value of \[y\] in set \[B = \left\{ {y:y \in W,y < 3} \right\}\] is any whole number less than 3.
The possible values of \[y\] are 0, 1, 2.
Therefore, we can rewrite set B using roster method as
\[B = \left\{ {0,1,2} \right\}\]
Now, we will find the Cartesian product \[A \times B\].
The Cartesian product \[A \times B\] of two sets A and B is the set of all possible ordered pairs \[\left( {x,y} \right)\], where \[x \in A\] and \[y \in B\].
The first component \[x\] of ordered pair \[\left( {x,y} \right)\] in the Cartesian product \[A \times B\] can be 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5, because \[A = \left\{ {1,2,3,4,5} \right\}\].
The second component \[y\] of ordered pair \[\left( {x,y} \right)\] in the Cartesian product \[A \times B\] can be 0, 1, or 2, because \[B = \left\{ {0,1,2} \right\}\].
Therefore, we get the Cartesian product \[A \times B\] as
\[A \times B = \left\{ \begin{array}{l}\left( {1,0} \right),\left( {2,0} \right),\left( {3,0} \right),\left( {4,0} \right),\left( {5,0} \right),\left( {1,1} \right),\left( {2,1} \right),\left( {3,1} \right),\\\left( {4,1} \right),\left( {5,1} \right),\left( {1,2} \right),\left( {2,2} \right),\left( {3,2} \right),\left( {4,2} \right),\left( {5,2} \right)\end{array} \right\}\]
Now, we will plot the ordered pairs \[\left( {x,y} \right)\] of the Cartesian product \[A \times B\] on the XY-plane.
Plotting the points, we get the graph as

Now, we will find the Cartesian product \[B \times A\].
The Cartesian product \[B \times A\] of two sets A and B is the set of all possible ordered pairs \[\left( {y,x} \right)\], where \[y \in B\] and \[x \in A\].
The first component \[y\] of ordered pair \[\left( {y,x} \right)\] in the Cartesian product \[B \times A\] can be 0, 1, or 2, because \[B = \left\{ {0,1,2} \right\}\].
The second component \[x\] of ordered pair \[\left( {y,x} \right)\] in the Cartesian product \[B \times A\] can be 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5, because \[A = \left\{ {1,2,3,4,5} \right\}\].
Therefore, we get the Cartesian product \[B \times A\] as
\[B \times A = \left\{ \begin{array}{l}\left( {0,1} \right),\left( {1,1} \right),\left( {2,1} \right),\left( {0,2} \right),\left( {1,2} \right),\left( {2,2} \right),\left( {0,3} \right),\left( {1,3} \right),\\\left( {2,3} \right),\left( {0,4} \right),\left( {1,4} \right),\left( {2,4} \right),\left( {0,5} \right),\left( {1,5} \right),\left( {2,5} \right)\end{array} \right\}\]
Now, we will plot the ordered pairs \[\left( {y,x} \right)\] of the Cartesian product \[B \times A\] on XY-plane.
Plotting the points, we get the graph as

Note: We rewrite the sets A and B using roster method. A set is said to be written using roster method if all the elements of the set are written.
We used the terms ‘whole number’ and ‘natural number’ in the solution.
Whole numbers include the numbers 0, and all the positive integers like 1, 2, 3, etc. They are the basic numbers we use when counting objects.
For example: 0, 1, 2, 100, 400, 52225, are all whole numbers.
Natural numbers include all the positive integers like 1, 2, 3, etc.
For example: 1, 2, 100, 400, 52225, are all whole numbers.
Whole numbers include all the natural numbers, and the number 0.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




