
Pili, Fimbriae, and flagella
A. Play a role in motility in bacteria
B. Are surface structures of bacteria
C. Play a role in motility in eukaryotic cells
D. Are elongated tubular structures made of special phospholipid
Answer
575.1k+ views
Hint: Pili are small structures that are usually used to exchange the genetic material between prokaryotic cells. Fimbriae are attachment structures that are smaller than the pili. These are also present on the cell wall of unicellular prokaryotes. Flagella are thin cylindrical structures present in some unicellular prokaryotes or eukaryotes.
Complete answer: The pili, fimbriae, and flagella are structures present on the cell wall of bacterial cells. Bacteria are mostly prokaryotic unicellular organisms. These are prokaryotes because they lack a true nucleus. All of the given structures constitute the surface components of many bacteria.
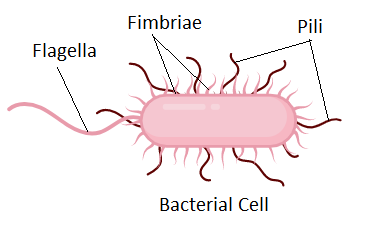
Pili are fibrous structures made of pilin protein which are used for the exchange of genetic material between bacterial cells. These are usually called sex pili as they help in the conjugation process of bacteria by transferring genetic information. They also help in the adhesion of two bacterial cells by forming a fibrous thin tube structure. The fimbriae are a shorter version of pili. They are small appendages like structures present on the surface of the cell wall of many gram-negative bacteria. Their size ranges from 3 to 10 nanometers. Fimbriae help bacteria to attach to animals' skin or each other. The attachment occurs through adhesins produced by fimbriae. Flagella are tubular long structures present on the cell wall base of most of the bacterial cells and some of the unicellular eukaryotic cells (cells having a true nucleus). These are thin at the tip and a little broader at the base embedded in the upper layer of the cell wall. They are made of a cellular protein called flagellin. These structures help in detecting nearby organisms and also help in locomotion.
Thus, option B is the right answer.
Note: All the given structures play a vital role in the reproduction and development of bacterial cells. The pili can be classified as common pili and sex pili. The common pili function to provide adhesion. The common pili attachment to cells in humans is the first step in any pili containing bacterial strains. Some of the pili are also classified as biofilm formation pili, phage transduction pili, etc. based on their special functions.
Complete answer: The pili, fimbriae, and flagella are structures present on the cell wall of bacterial cells. Bacteria are mostly prokaryotic unicellular organisms. These are prokaryotes because they lack a true nucleus. All of the given structures constitute the surface components of many bacteria.

Pili are fibrous structures made of pilin protein which are used for the exchange of genetic material between bacterial cells. These are usually called sex pili as they help in the conjugation process of bacteria by transferring genetic information. They also help in the adhesion of two bacterial cells by forming a fibrous thin tube structure. The fimbriae are a shorter version of pili. They are small appendages like structures present on the surface of the cell wall of many gram-negative bacteria. Their size ranges from 3 to 10 nanometers. Fimbriae help bacteria to attach to animals' skin or each other. The attachment occurs through adhesins produced by fimbriae. Flagella are tubular long structures present on the cell wall base of most of the bacterial cells and some of the unicellular eukaryotic cells (cells having a true nucleus). These are thin at the tip and a little broader at the base embedded in the upper layer of the cell wall. They are made of a cellular protein called flagellin. These structures help in detecting nearby organisms and also help in locomotion.
Thus, option B is the right answer.
Note: All the given structures play a vital role in the reproduction and development of bacterial cells. The pili can be classified as common pili and sex pili. The common pili function to provide adhesion. The common pili attachment to cells in humans is the first step in any pili containing bacterial strains. Some of the pili are also classified as biofilm formation pili, phage transduction pili, etc. based on their special functions.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




