
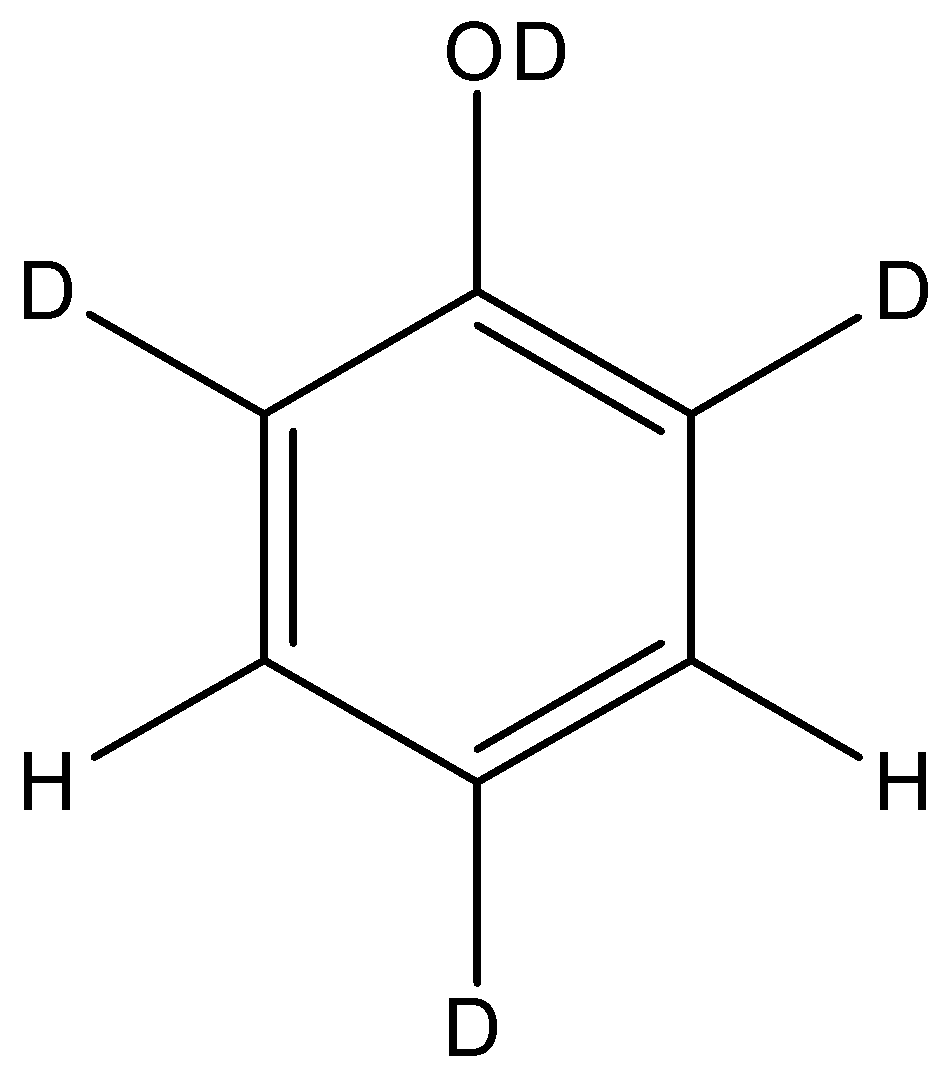
When phenol is treated with ${{D}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}/{{D}_{2}}O$ some of the hydrogen atoms get exchanged. The final product in this exchange reaction is:
A.
B.
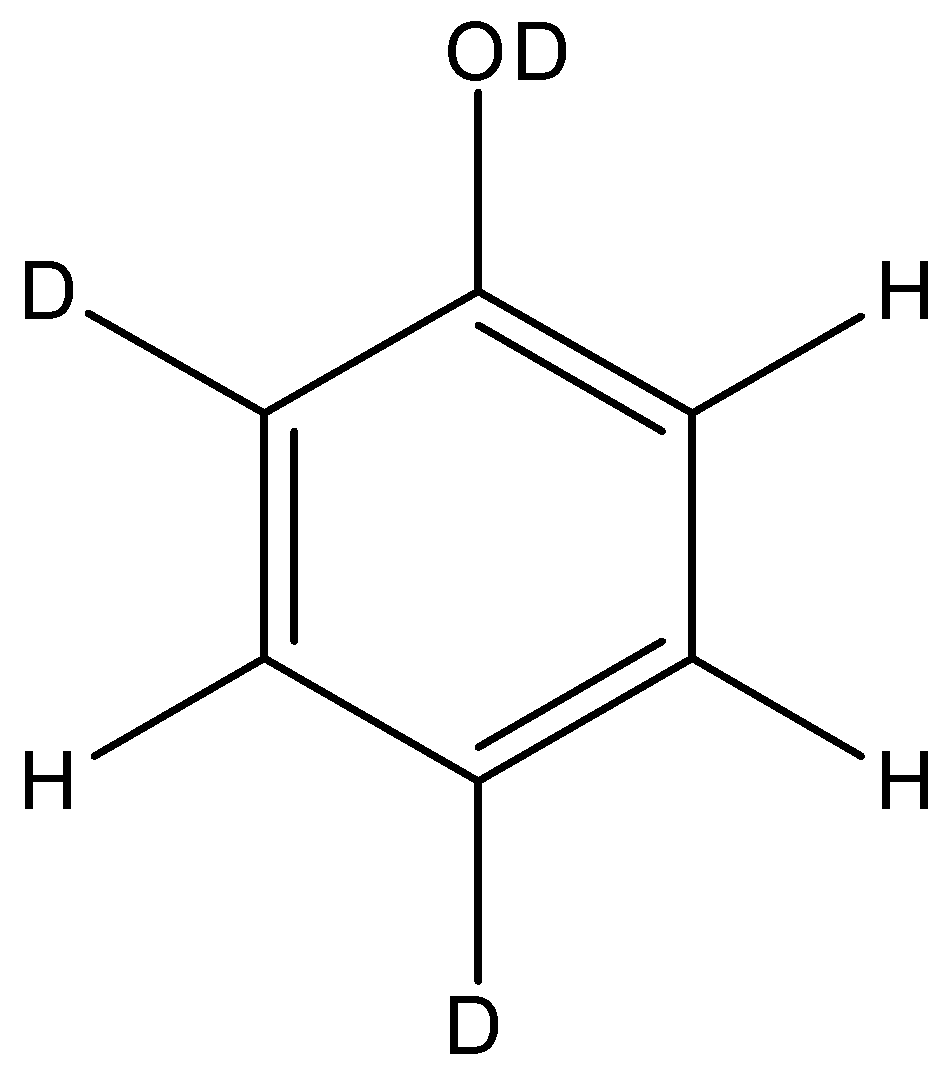
C.
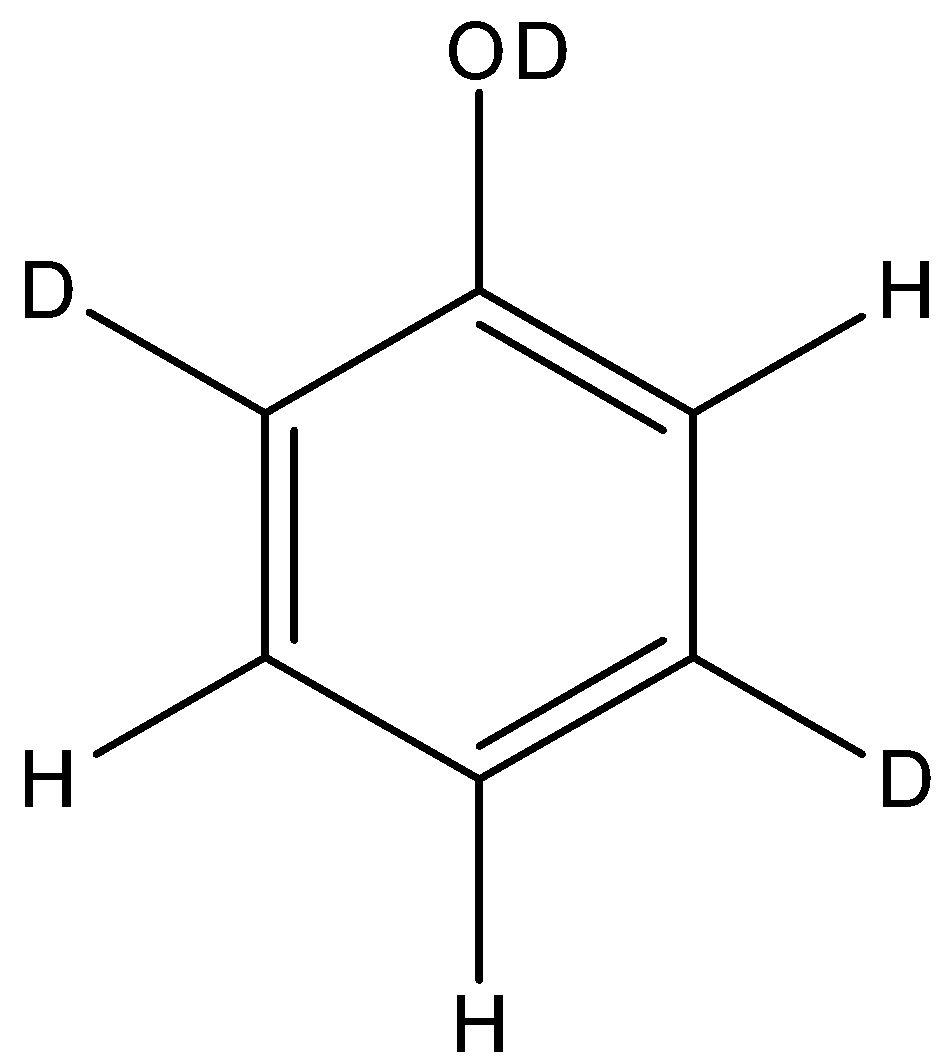
D.
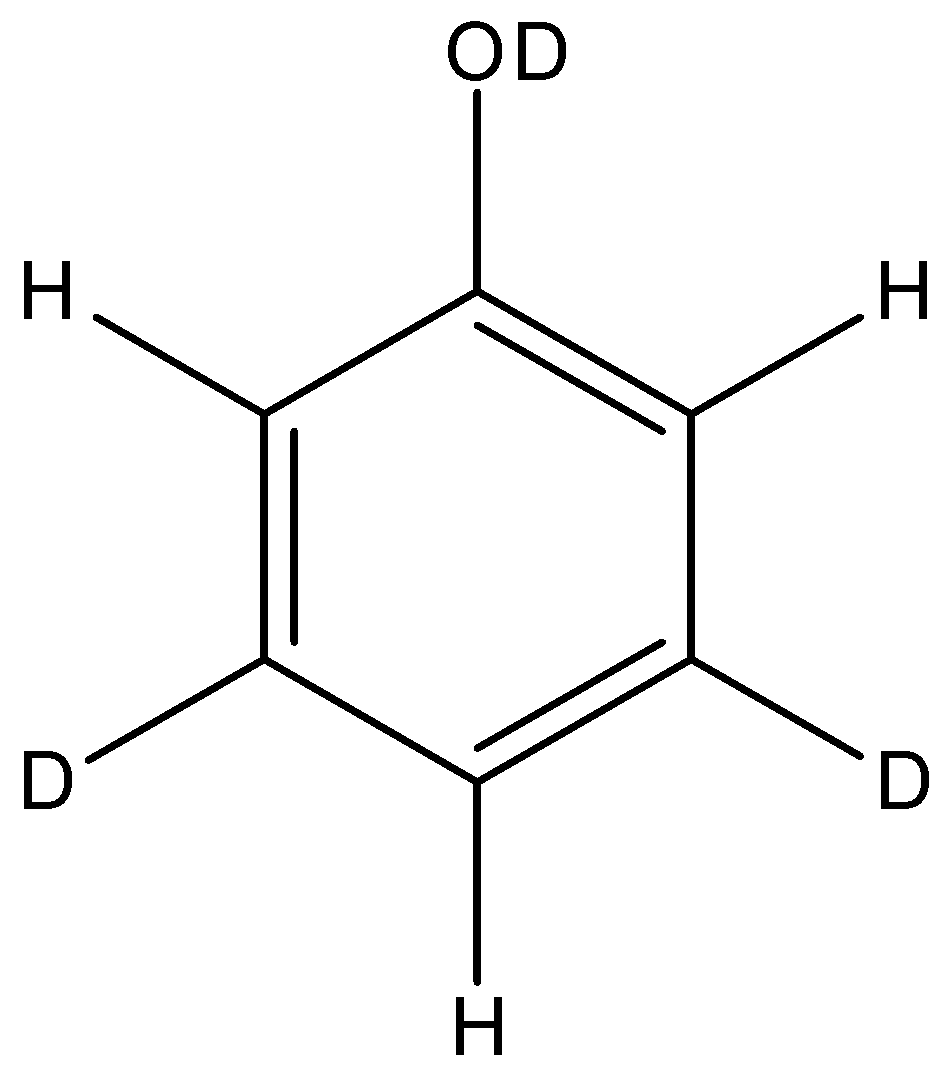




Answer
598.2k+ views
Hint: Think about the conditions in which replacement is likely to occur, will the sites of replacement be electron rich or electron deficient? Consider the resonating structures of phenol that are possible in acidic medium.
Complete step by step answer:
Phenol is present in the acidic medium of ${{D}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}/{{D}_{2}}O$.We know that the hydroxyl group is an electron donating group on the benzene ring since the oxygen atom has multiple lone pairs which can be used to stabilize the ring. The resonance structures are as follows:
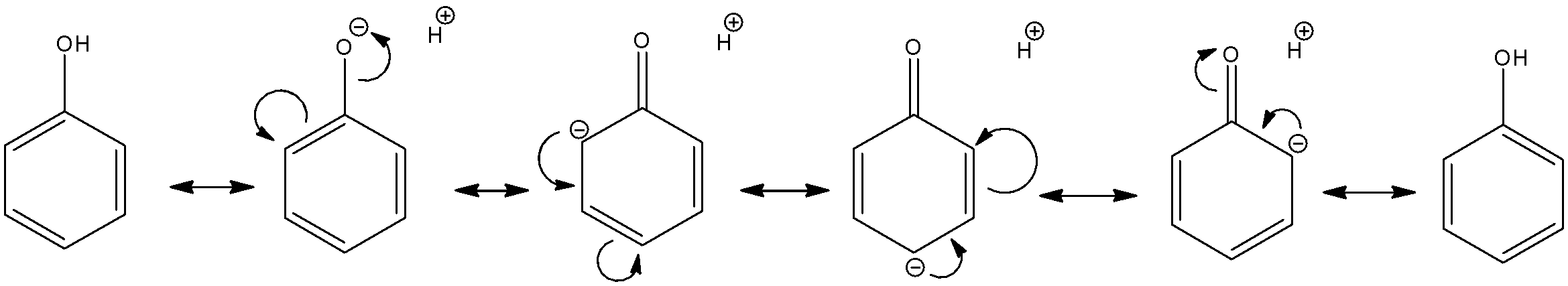
As we can see here, the hydrogen atom on $O{{H}^{-}}$ moiety is an acidic proton, thus, it will definitely get exchanged during the reaction. So, the $O{{H}^{-}}$ functional group will become a $O{{D}^{-}}$ functional group.
We also see that the ortho- as well as para- sites have an electron rich nature. The electron donation oxygen causes electrons to be concentrated at the 2,4,6 sites. Thus, the electrophilic groups like ${{H}^{+}}$ or ${{D}^{+}}$ will be attracted to these sites. Since, the medium present is ${{D}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}/{{D}_{2}}O$, these sites will exchange hydrogen for deuterium. So, the final product will have deuterium in the $O{{D}^{-}}$ group as well as all the ortho- and para- sites.
So, the final structure of the phenol after the reaction will be:
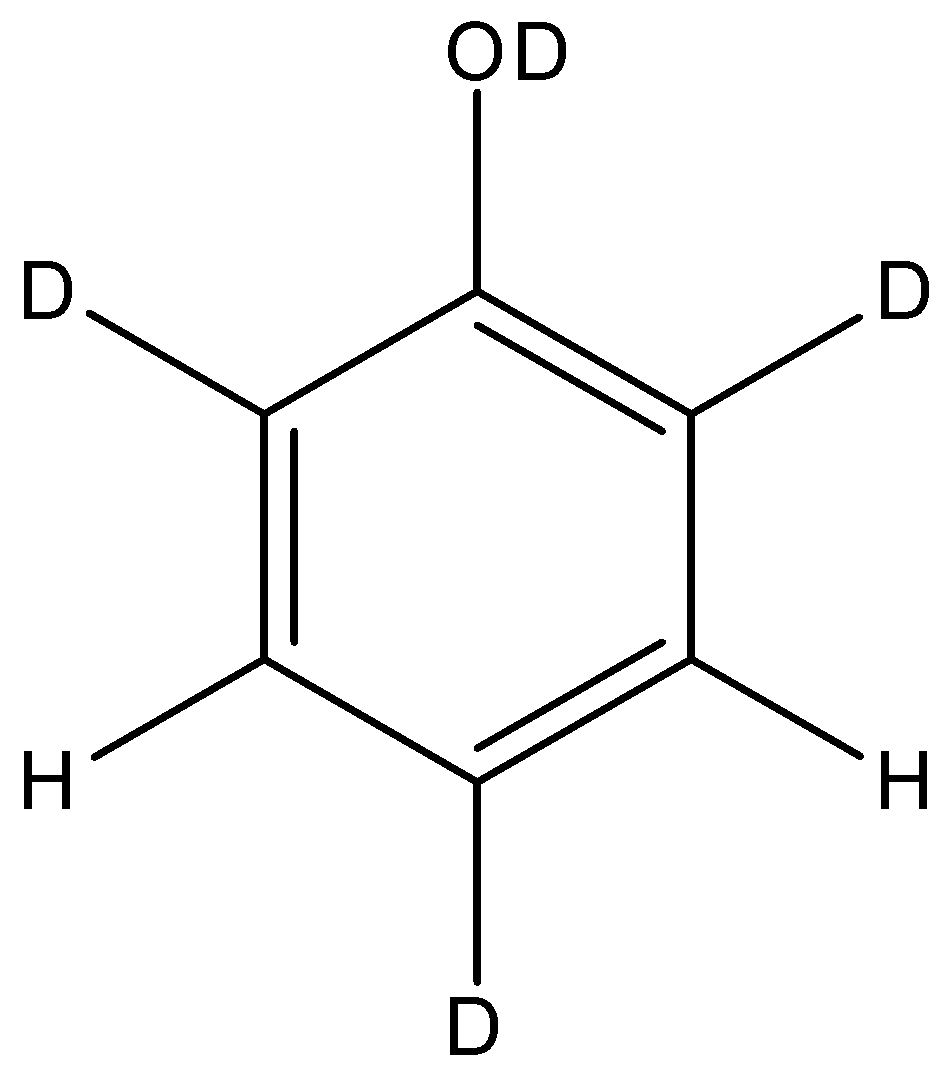
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: It may seem like the hydroxyl group will be an electron withdrawing group due to the fact that oxygen is a highly electronegative atom. But take into consideration the fact that oxygen is an element from the second period and thus has no vacant d-orbitals to accept electrons after its valency has been satisfied. So after it has formed 2 bonds, it will act as an electron donating group.
Complete step by step answer:
Phenol is present in the acidic medium of ${{D}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}/{{D}_{2}}O$.We know that the hydroxyl group is an electron donating group on the benzene ring since the oxygen atom has multiple lone pairs which can be used to stabilize the ring. The resonance structures are as follows:

As we can see here, the hydrogen atom on $O{{H}^{-}}$ moiety is an acidic proton, thus, it will definitely get exchanged during the reaction. So, the $O{{H}^{-}}$ functional group will become a $O{{D}^{-}}$ functional group.
We also see that the ortho- as well as para- sites have an electron rich nature. The electron donation oxygen causes electrons to be concentrated at the 2,4,6 sites. Thus, the electrophilic groups like ${{H}^{+}}$ or ${{D}^{+}}$ will be attracted to these sites. Since, the medium present is ${{D}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}/{{D}_{2}}O$, these sites will exchange hydrogen for deuterium. So, the final product will have deuterium in the $O{{D}^{-}}$ group as well as all the ortho- and para- sites.
So, the final structure of the phenol after the reaction will be:

So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: It may seem like the hydroxyl group will be an electron withdrawing group due to the fact that oxygen is a highly electronegative atom. But take into consideration the fact that oxygen is an element from the second period and thus has no vacant d-orbitals to accept electrons after its valency has been satisfied. So after it has formed 2 bonds, it will act as an electron donating group.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




