
Particle A makes a perfectly elastic collision with another particle B at rest. They fly apart in opposite directions with equal speeds. If their masses are ${m}_{A}$ and ${m}_{B}$ respectively. Then:
A.2${m}_{A}={m}_{B}$
B.$3{m}_{A}={m}_{B}$
C.4${m}_{A}= {m}_{B}$
D.$\sqrt{3}{m}_{A}={m}_{B}$
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: Apply law of conservation of linear momentum and find the ratio of initial velocity and final velocity. Then, applying the law of conservation, find the ratio of initial and final velocities. Equate both the ratios and find the mass of both the particles.
Complete answer:
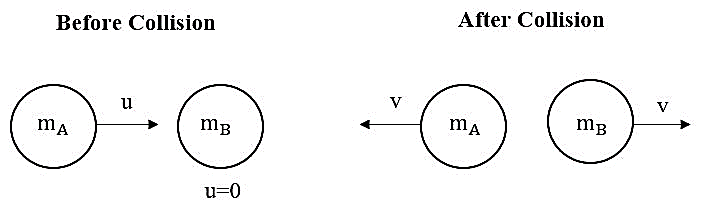
Given: Initial velocity of particle B=0
Final velocity of both the particles is the same.
Let initial velocity of particle A be u .
Final velocity of both the particles i.e. A and B be v
According to the law of conservation of momentum,
${m}_{A}u + {m}_{B}× 0= {m}_{A} v + {m}_{B} (-v)$
$\Rightarrow {m}_{A}u= {m}_{A} v + {m}_{B} (-v)$
$\Rightarrow {m}_{A}u= v({m}_{A}-{m}_{B})$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac {u}{v}= \dfrac {({m}_{A}-{m}_{B})}{{m}_{A}}$...(1)
Now, applying law of conservation of energy we get,
$\dfrac {1}{2}{m}_{A}{u}^{2} + {1}{2}{m}_{B}{0}^{2}= {1}{2}{m}_{A}{v}^{2}+{1}{2}{m}_{B}{v}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac {1}{2}{m}_{A}{u}^{2}= {1}{2}{m}_{A}{v}^{2}+{1}{2}{m}_{B}{v}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac {1}{2}{m}_{A}{u}^{2}= \dfrac {1}{2}{v}^{2}( {m}_{A}+{m}_{B})$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac {{u}^{2}}{{v}^{2}}= \dfrac {{m}_{A}+{m}_{B}}{{m}_{A}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac {u}{v}=\sqrt{\dfrac{{m}_{A}+{m}_{B}}{{m}_{A}}}$ ...(2)
Equating equation. (1) and equation. (2) we get,
$ \dfrac {({m}_{A}-{m}_{B})}{{m}_{A}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{{m}_{A}+{m}_{B}}{{m}_{A}}}$
Squaring above equation we get,
$\dfrac {{m}_{A}^{2}-2{m}_{A}{m}_{B}+{m}_{B}^{2}}{{m}_{A}^{2}}=\dfrac {{m}_{A}+{m}_{B}}{{m}_{A}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac {{m}_{A}^{2}-2{m}_{A}{m}_{B}+{m}_{B}^{2}}{{m}_{B}^{2}}={m}_{A}^{2}+{m}_{A}+{m}_{B}$
$\Rightarrow {m}_{B}^{2}={ m}_{A}+{m}_{B}$
$\Rightarrow {m}_{B}= 3{m}_{A}$
So, the correct answer is option B i.e. $3{m}_{A}={m}_{B}$.
Note:
To solve these types of questions, students must have knowledge about the conservation laws and the collisions. When two particles come together, collision takes place. There are two types of collisions namely: 1) Elastic Collision 2) Inelastic Collision. So, to check whether a collision is elastic or inelastic, you can equate kinetic energy of the particles. After a collision, if the kinetic energy remains the same as before, then it is called an elastic collision. After a collision, if the kinetic energy does not remain the same as before, then it is called an elastic collision.
Complete answer:
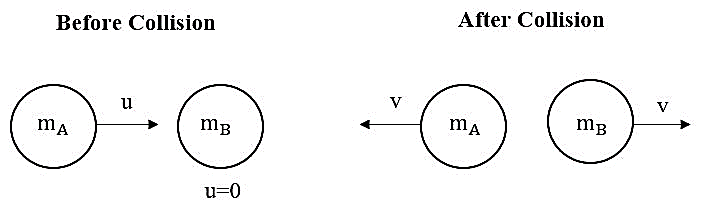
Given: Initial velocity of particle B=0
Final velocity of both the particles is the same.
Let initial velocity of particle A be u .
Final velocity of both the particles i.e. A and B be v
According to the law of conservation of momentum,
${m}_{A}u + {m}_{B}× 0= {m}_{A} v + {m}_{B} (-v)$
$\Rightarrow {m}_{A}u= {m}_{A} v + {m}_{B} (-v)$
$\Rightarrow {m}_{A}u= v({m}_{A}-{m}_{B})$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac {u}{v}= \dfrac {({m}_{A}-{m}_{B})}{{m}_{A}}$...(1)
Now, applying law of conservation of energy we get,
$\dfrac {1}{2}{m}_{A}{u}^{2} + {1}{2}{m}_{B}{0}^{2}= {1}{2}{m}_{A}{v}^{2}+{1}{2}{m}_{B}{v}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac {1}{2}{m}_{A}{u}^{2}= {1}{2}{m}_{A}{v}^{2}+{1}{2}{m}_{B}{v}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac {1}{2}{m}_{A}{u}^{2}= \dfrac {1}{2}{v}^{2}( {m}_{A}+{m}_{B})$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac {{u}^{2}}{{v}^{2}}= \dfrac {{m}_{A}+{m}_{B}}{{m}_{A}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac {u}{v}=\sqrt{\dfrac{{m}_{A}+{m}_{B}}{{m}_{A}}}$ ...(2)
Equating equation. (1) and equation. (2) we get,
$ \dfrac {({m}_{A}-{m}_{B})}{{m}_{A}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{{m}_{A}+{m}_{B}}{{m}_{A}}}$
Squaring above equation we get,
$\dfrac {{m}_{A}^{2}-2{m}_{A}{m}_{B}+{m}_{B}^{2}}{{m}_{A}^{2}}=\dfrac {{m}_{A}+{m}_{B}}{{m}_{A}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac {{m}_{A}^{2}-2{m}_{A}{m}_{B}+{m}_{B}^{2}}{{m}_{B}^{2}}={m}_{A}^{2}+{m}_{A}+{m}_{B}$
$\Rightarrow {m}_{B}^{2}={ m}_{A}+{m}_{B}$
$\Rightarrow {m}_{B}= 3{m}_{A}$
So, the correct answer is option B i.e. $3{m}_{A}={m}_{B}$.
Note:
To solve these types of questions, students must have knowledge about the conservation laws and the collisions. When two particles come together, collision takes place. There are two types of collisions namely: 1) Elastic Collision 2) Inelastic Collision. So, to check whether a collision is elastic or inelastic, you can equate kinetic energy of the particles. After a collision, if the kinetic energy remains the same as before, then it is called an elastic collision. After a collision, if the kinetic energy does not remain the same as before, then it is called an elastic collision.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




