
Oxymercuration-demercuration reaction \[{\text{Hg(OAC}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/THF - }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O followed by NaB}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}},{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{OH)}}\]on \[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH = C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\]produces:
A)\[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CO}}\]
B) \[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH(OH)C}}{{\text{H}}_3}\]
C) \[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH(OH)C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}\]
D) \[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COC}}{{\text{H}}_3}\]
Answer
572.7k+ views
Hint:Oxymercuration-demarcation reaction is an alternative method of hydration of alkene. Given alkene is an asymmetric alkene. Additions take place according to Markovnikov’s rule. The first step of the reaction is the formation of cyclic mercurinium ions. The second step is the opening of mercurinium ion by the nucleophilic attack of water. Finally, demercuration takes place by reduction with \[{\text{NaB}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\] the reagent.
Complete solution:
As we know that Oxymercuration-demercuration reaction is a hydration reaction so the product of the reaction will be alcohol.Hence, Option (A) and (D) are the incorrect answers.
Now we will see the detail mechanism of the Oxymercuration-demercuration reaction.
Step1: Formation of cyclic mercurinium ion: Nucleophilic attack of \[\pi \] electrons of \[{\text{C = C}}\]on electrophilic \[{\text{Hg}}\] and loss of an acetate ion.
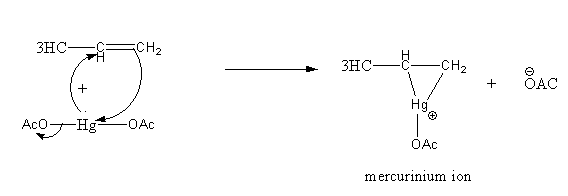
Step2: Opening of mercurinium ion by nucleophilic attack of water. Attack of water takes place according to Markovnikov’s rule, that is it attacks on the more substituted carbon atom.
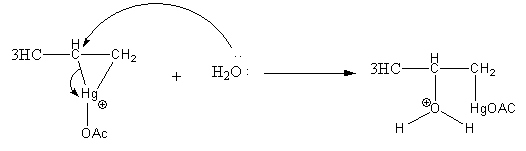
Step3: Deprotonation of oxonium ion by base acetate ion.
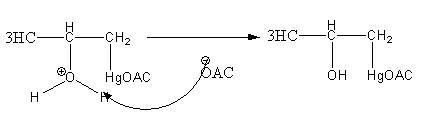
Step4: Breaking of \[{\text{C - Hg}}\] bond and formation of \[{\text{C - H}}\] by reduction with\[{\text{NaB}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\].
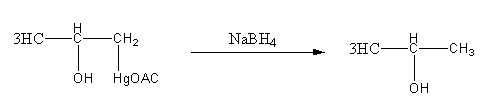
Thus, option (D) is incorrect as the product is not diol.
Thus, the correct options are (B).
Note:Oxymercuration-demercuration reaction involves the transformation of \[{\text{C = C}}\] to \[{\text{OH - C - C - H}}\] bond. More substituted alcohol is the major product. It is an electrophilic addition type of reaction.
Complete solution:
As we know that Oxymercuration-demercuration reaction is a hydration reaction so the product of the reaction will be alcohol.Hence, Option (A) and (D) are the incorrect answers.
Now we will see the detail mechanism of the Oxymercuration-demercuration reaction.
Step1: Formation of cyclic mercurinium ion: Nucleophilic attack of \[\pi \] electrons of \[{\text{C = C}}\]on electrophilic \[{\text{Hg}}\] and loss of an acetate ion.

Step2: Opening of mercurinium ion by nucleophilic attack of water. Attack of water takes place according to Markovnikov’s rule, that is it attacks on the more substituted carbon atom.

Step3: Deprotonation of oxonium ion by base acetate ion.

Step4: Breaking of \[{\text{C - Hg}}\] bond and formation of \[{\text{C - H}}\] by reduction with\[{\text{NaB}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\].
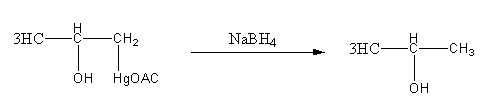
Thus, option (D) is incorrect as the product is not diol.
Thus, the correct options are (B).
Note:Oxymercuration-demercuration reaction involves the transformation of \[{\text{C = C}}\] to \[{\text{OH - C - C - H}}\] bond. More substituted alcohol is the major product. It is an electrophilic addition type of reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




