
What is oxyhemoglobin and how is it formed?
Answer
504.3k+ views
Hint: Haemoglobin is the iron-containing pigment present in the blood which is responsible for the red colour of the blood. When the haemoglobin is loaded with oxygen, it forms oxyhaemoglobin. Its role is to transport oxygen to all the cells and tissues of the body.
Complete answer:
The RBC are the blood cells that contain a pigment called haemoglobin which provides red colour to the blood. Haemoglobin is an iron-containing protein that is found in all vertebrates. It mainly transports both oxygen and carbon dioxide from the lungs to tissues and vice versa.
The structure of haemoglobin is a very complex quaternary structure that contains several subunits and globular proteins. The iron occupies the central position at which all the four globular proteins are attached. It is roughly a tetrahedral structure. Each molecule of haemoglobin carries 4 molecules of oxygen and forms oxyhaemoglobin. The iron exists in its ferrous state which oxidises reversibly and temporarily to form oxyhaemoglobin.
During respiration when the oxygen is taken in by the lungs, the alveoli exchange the gases with the blood. This leads to the formation of oxyhaemoglobin. The oxygen as a result of which binds with the heme component or the iron of the haemoglobin. This results in the carrying of oxygen by the blood to all the parts of the body where the cells utilise oxygen to perform several functions and produce energy.
The structure of oxyhaemoglobin is given below.
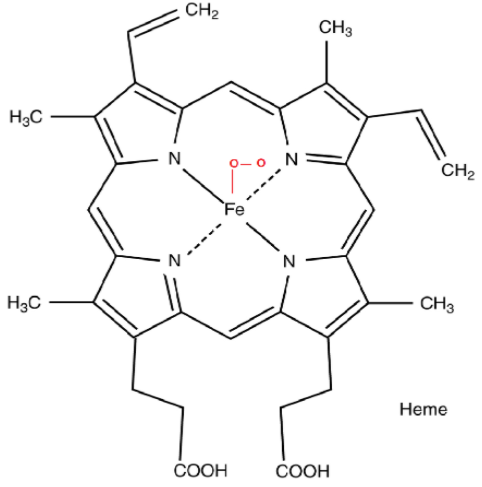
Note: A normal healthy adult contains around 12-20 gm of haemoglobin per 100 ml of blood. The deficiency of haemoglobin leads to a disease called anaemia. In this, the oxygen is not supplied to all the parts of the body as a result of which the person faces breathlessness and fatigue.
Complete answer:
The RBC are the blood cells that contain a pigment called haemoglobin which provides red colour to the blood. Haemoglobin is an iron-containing protein that is found in all vertebrates. It mainly transports both oxygen and carbon dioxide from the lungs to tissues and vice versa.
The structure of haemoglobin is a very complex quaternary structure that contains several subunits and globular proteins. The iron occupies the central position at which all the four globular proteins are attached. It is roughly a tetrahedral structure. Each molecule of haemoglobin carries 4 molecules of oxygen and forms oxyhaemoglobin. The iron exists in its ferrous state which oxidises reversibly and temporarily to form oxyhaemoglobin.
During respiration when the oxygen is taken in by the lungs, the alveoli exchange the gases with the blood. This leads to the formation of oxyhaemoglobin. The oxygen as a result of which binds with the heme component or the iron of the haemoglobin. This results in the carrying of oxygen by the blood to all the parts of the body where the cells utilise oxygen to perform several functions and produce energy.
The structure of oxyhaemoglobin is given below.

Note: A normal healthy adult contains around 12-20 gm of haemoglobin per 100 ml of blood. The deficiency of haemoglobin leads to a disease called anaemia. In this, the oxygen is not supplied to all the parts of the body as a result of which the person faces breathlessness and fatigue.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




