
Oxygen molecule is:
(A). diamagnetic with no unpaired electrons
(B). diamagnetic with two paired electrons
(C). paramagnetic with two unpaired electrons
(D). paramagnetic with no paired electrons
Answer
577.2k+ views
Hint: According to the molecular orbital theory, the molecular orbital structure of oxygen contains two unpaired electrons in the antibonding orbitals. The molecule having unpaired electrons in the configuration is known as paramagnetic in nature.
Complete step by step answer:
The electronic configuration of oxygen (atomic number$z = 8$ ) in the ground state is:
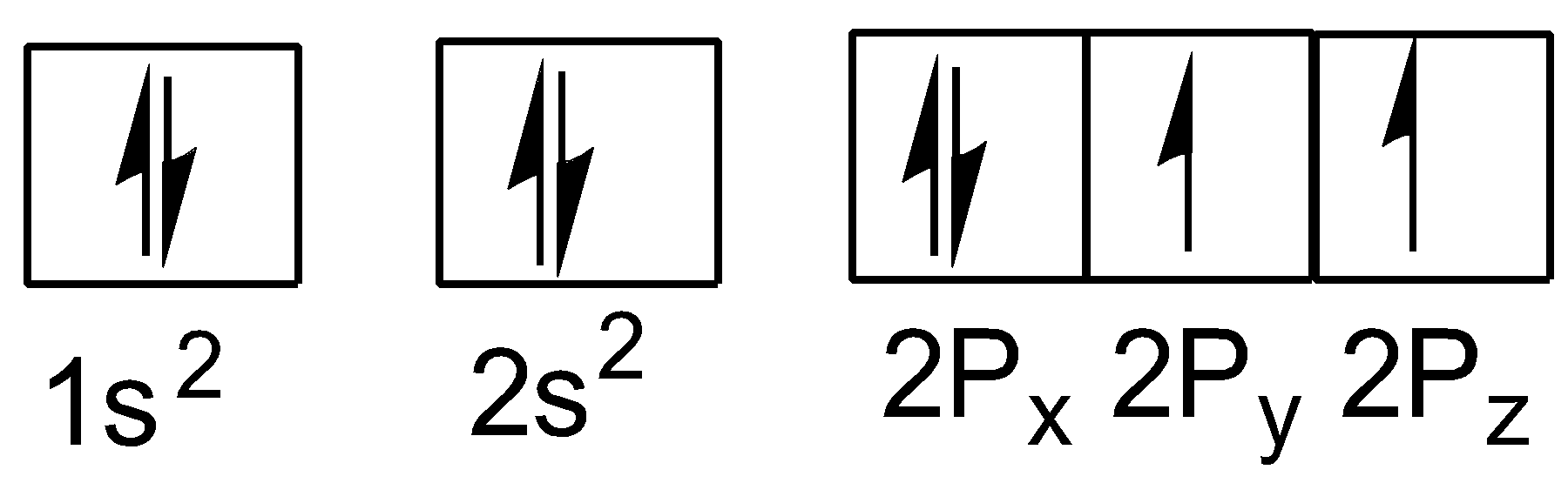
As each oxygen atom has light electron so, the electronic configuration of oxygen molecule is:
${O_2} \to 1{S^2}{\sigma ^*}1{S^2}\sigma 2{S^2}{\sigma ^*}2{S^2}\pi 2{P_2}^2\pi 2{P_x}^2 = \pi 2P{y^2}$
${\pi ^*}2P{x^1} = {\pi ^*}2P{y^1}$
The bond – order of ${O_2}$ is two.
$\operatorname{Bond} order{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{N_b} - {N_a}}}{2} = \dfrac{{8 - 4}}{2} = 2$
Bond – order shows the number of electrons present in anti – bonding molecular orbitals.
${O_2}$Has two bonds, one is sigma bond and other is pi-bonded.
The energy diagram of ${O_2}$molecule is:
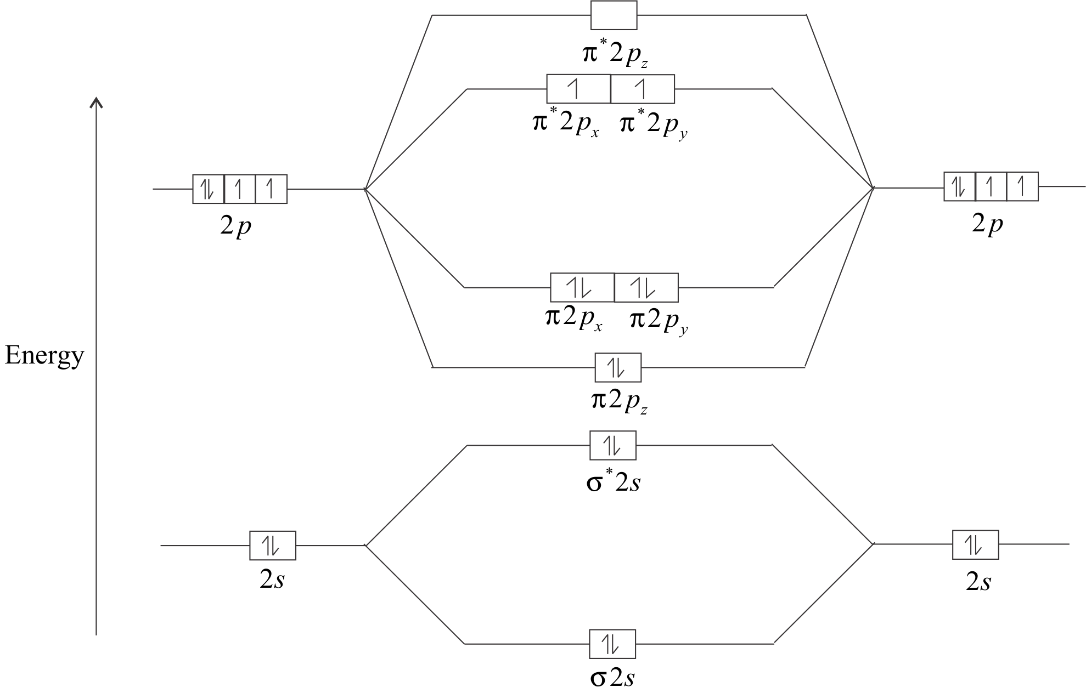
The electrons in ${\pi ^*}2Px$ and ${\pi ^*}2Py$ remain unpaired. So, there are two unpaired electrons in ${O_2}$. Hence, it is paramagnetic in nature with two unpaired electrons.
So, the correct answer is Option C .
Additional information:
The molecular theory or MOT is based on chemical bonding and it was developed by F. Hund and R.S. Mulliken. It describes the structure and the properties of different molecules. The molecular orbital theory proved to be good as compared to valence bond theory because valence bond theory failed to explain how the molecules contain two or more than two equivalent bonds if in case their bond order lies in between single and double bonds.
Note: The molecular orbital theory can explain the existence of molecules on the basis of bond order, this holds good for diatomic molecules but not for the polyatomic molecules. Also, only with the help of molecular orbital theory one cannot describe the geometry and shape of the molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
The electronic configuration of oxygen (atomic number$z = 8$ ) in the ground state is:

As each oxygen atom has light electron so, the electronic configuration of oxygen molecule is:
${O_2} \to 1{S^2}{\sigma ^*}1{S^2}\sigma 2{S^2}{\sigma ^*}2{S^2}\pi 2{P_2}^2\pi 2{P_x}^2 = \pi 2P{y^2}$
${\pi ^*}2P{x^1} = {\pi ^*}2P{y^1}$
The bond – order of ${O_2}$ is two.
$\operatorname{Bond} order{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{N_b} - {N_a}}}{2} = \dfrac{{8 - 4}}{2} = 2$
Bond – order shows the number of electrons present in anti – bonding molecular orbitals.
${O_2}$Has two bonds, one is sigma bond and other is pi-bonded.
The energy diagram of ${O_2}$molecule is:

The electrons in ${\pi ^*}2Px$ and ${\pi ^*}2Py$ remain unpaired. So, there are two unpaired electrons in ${O_2}$. Hence, it is paramagnetic in nature with two unpaired electrons.
So, the correct answer is Option C .
Additional information:
The molecular theory or MOT is based on chemical bonding and it was developed by F. Hund and R.S. Mulliken. It describes the structure and the properties of different molecules. The molecular orbital theory proved to be good as compared to valence bond theory because valence bond theory failed to explain how the molecules contain two or more than two equivalent bonds if in case their bond order lies in between single and double bonds.
Note: The molecular orbital theory can explain the existence of molecules on the basis of bond order, this holds good for diatomic molecules but not for the polyatomic molecules. Also, only with the help of molecular orbital theory one cannot describe the geometry and shape of the molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




