
What is the oxidation state of osmium in \[7B\] and \[7C\], respectively?
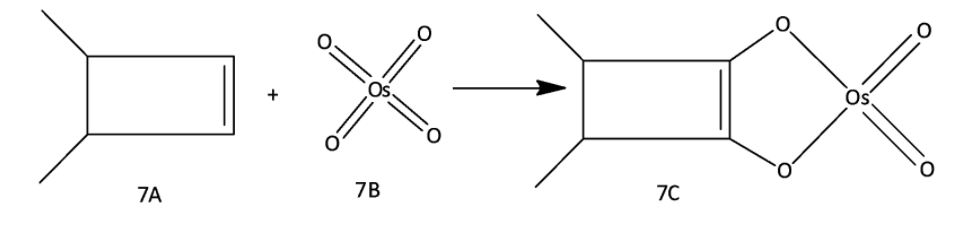
A. \[6,8\]
B. \[8,6\]
C. \[6,6\]
D. \[8,8\]

Answer
504.9k+ views
Hint: We need to know that the oxidation – reduction reaction is also known as redox reaction. This is a type of chemical reaction that undergoes the transfer of electrons between two species. During a chemical reaction, the oxidation state of an atom, molecule or ion may change. It may increase or decrease the oxidation number by losing or gaining the electrons. If the substance has stronger electron affinity, it has the greater oxidizing power. Hence, the weakest oxidizing agent does not have a strong tendency to accept the electrons.
Complete answer:
The oxidation state of \[7B\] and \[7C\] is not equal to \[6,8\]. Thus the option (A) is incorrect.
The oxidation state of \[7B\] is equal to \[8\] and the oxidation state of \[7C\] is equal to \[6\].
The oxidation state of an atom present in a compound can be explained on the basis of electronegativity. If two atoms are present in a compound, one atom should have higher electronegativity than the other. Then the bond will break towards the highly electronegative compound and that compound attains the negative charge (anion) and the low electronegative compound attains the positive charge (cation).
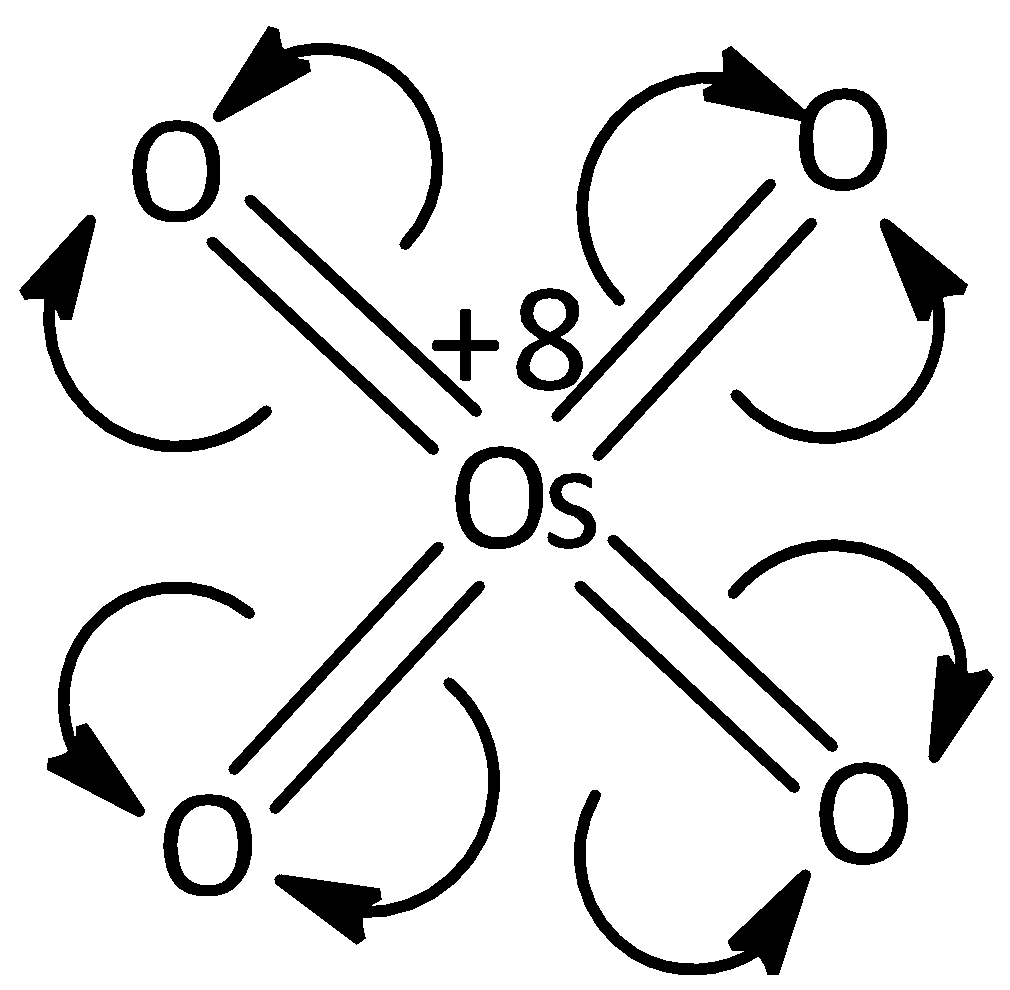
In the case of oxygen and osmium, the oxygen is more electronegative than osmium. In \[7B\] the osmium is bonded with four oxygen bonds by double bond. Hence, each bond will break and it moves towards oxygen. Then each oxygen becomes a negative charge and osmium attains a positive charge. Hence, total positive charge is equal to \[ + 8\]. Thus the oxidation state of osmium in \[7B\] is equal to \[ + 8\]. Let’s see the structure,
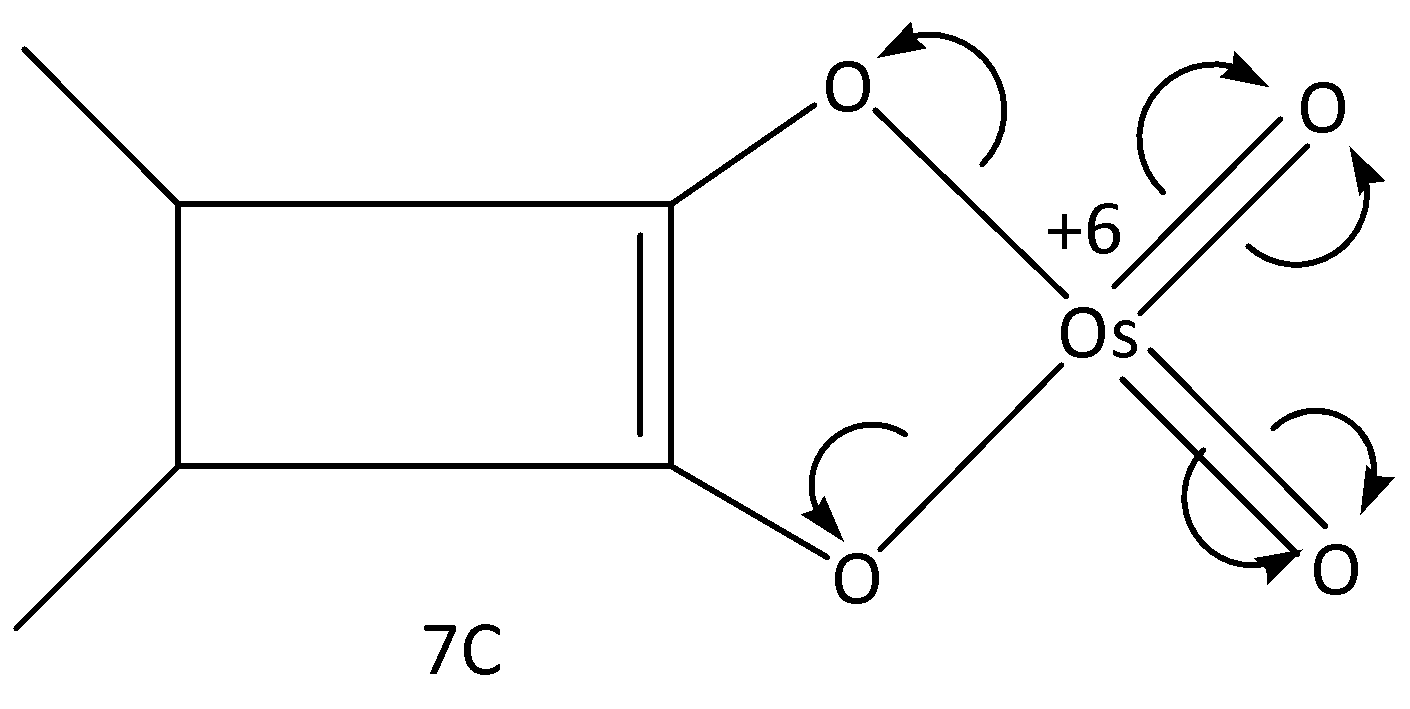
In the case of \[7C\], the osmium attains \[ + 6\] charge. Let’s see the structure;
Hence, option (B) is correct.
The oxidation state of \[7B\] is not equal to\[ + 6\]. Hence, option (C) is incorrect.
The oxidation state of \[7C\] is not equal to\[ + 8\]. Hence, option (D) is incorrect.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
As we know, the oxidizing agent is also known as oxidant. And the oxidizing agent is a species which has the ability to oxidize other substances. Which means, there is an increase in the oxidation state of the species by removing the electrons. Oxygen, hydrogen peroxide and halogens are the common oxidizing agents. The oxidizing agent will always try to exist in its highest oxidation state due to their strong tendency to accept the electron which undergoes the reduction.
Complete answer:
The oxidation state of \[7B\] and \[7C\] is not equal to \[6,8\]. Thus the option (A) is incorrect.
The oxidation state of \[7B\] is equal to \[8\] and the oxidation state of \[7C\] is equal to \[6\].
The oxidation state of an atom present in a compound can be explained on the basis of electronegativity. If two atoms are present in a compound, one atom should have higher electronegativity than the other. Then the bond will break towards the highly electronegative compound and that compound attains the negative charge (anion) and the low electronegative compound attains the positive charge (cation).
In the case of oxygen and osmium, the oxygen is more electronegative than osmium. In \[7B\] the osmium is bonded with four oxygen bonds by double bond. Hence, each bond will break and it moves towards oxygen. Then each oxygen becomes a negative charge and osmium attains a positive charge. Hence, total positive charge is equal to \[ + 8\]. Thus the oxidation state of osmium in \[7B\] is equal to \[ + 8\]. Let’s see the structure,

In the case of \[7C\], the osmium attains \[ + 6\] charge. Let’s see the structure;

Hence, option (B) is correct.
The oxidation state of \[7B\] is not equal to\[ + 6\]. Hence, option (C) is incorrect.
The oxidation state of \[7C\] is not equal to\[ + 8\]. Hence, option (D) is incorrect.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
As we know, the oxidizing agent is also known as oxidant. And the oxidizing agent is a species which has the ability to oxidize other substances. Which means, there is an increase in the oxidation state of the species by removing the electrons. Oxygen, hydrogen peroxide and halogens are the common oxidizing agents. The oxidizing agent will always try to exist in its highest oxidation state due to their strong tendency to accept the electron which undergoes the reduction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




