
Out of (ref. image), which is an example of a benzylic halide?
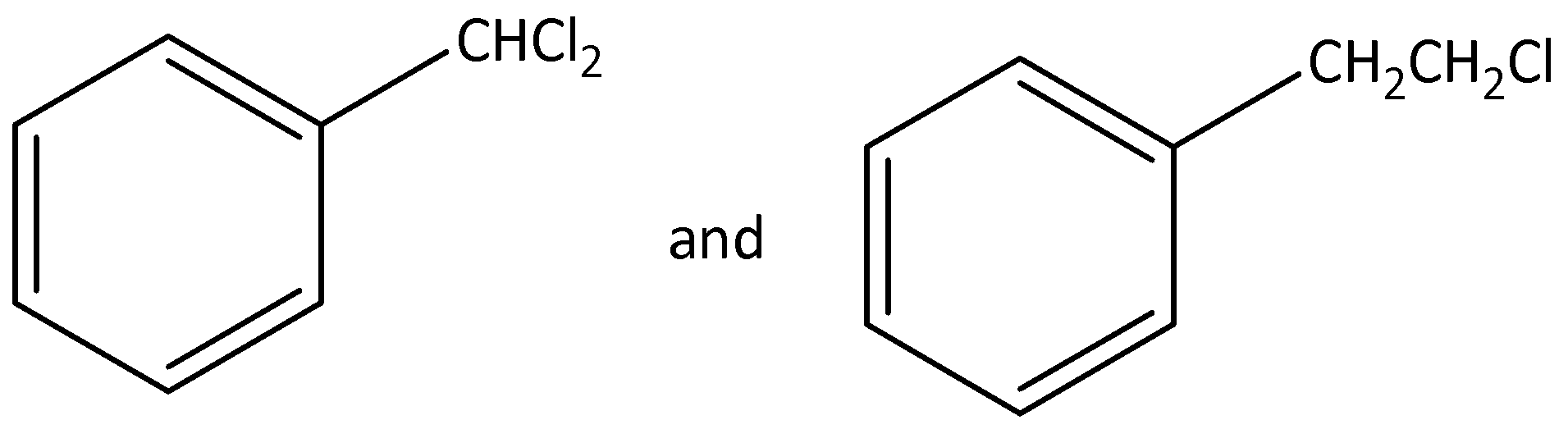

Answer
560.7k+ views
Hint: We have to remember that the benzene is a six membered ring cyclic carbon atom. Benzene is an aromatic compound. The molecular formula of the benzene is ${C_6}{H_6}$ . In benzene, alternate double bonds are present in six membered rings. Due to this delocalisation of pi electrons in benzene, it forms an aromatic compound.
There are 6 pi electrons in benzene, the one more reason it is considered as an aromatic compound.
Complete step by step answer:
We need to know that the benzylic halide means one more or more halogen atom bonded to a carbon atom, that carbon atom is attached to any carbon atom in the benzene ring.
According to below figure
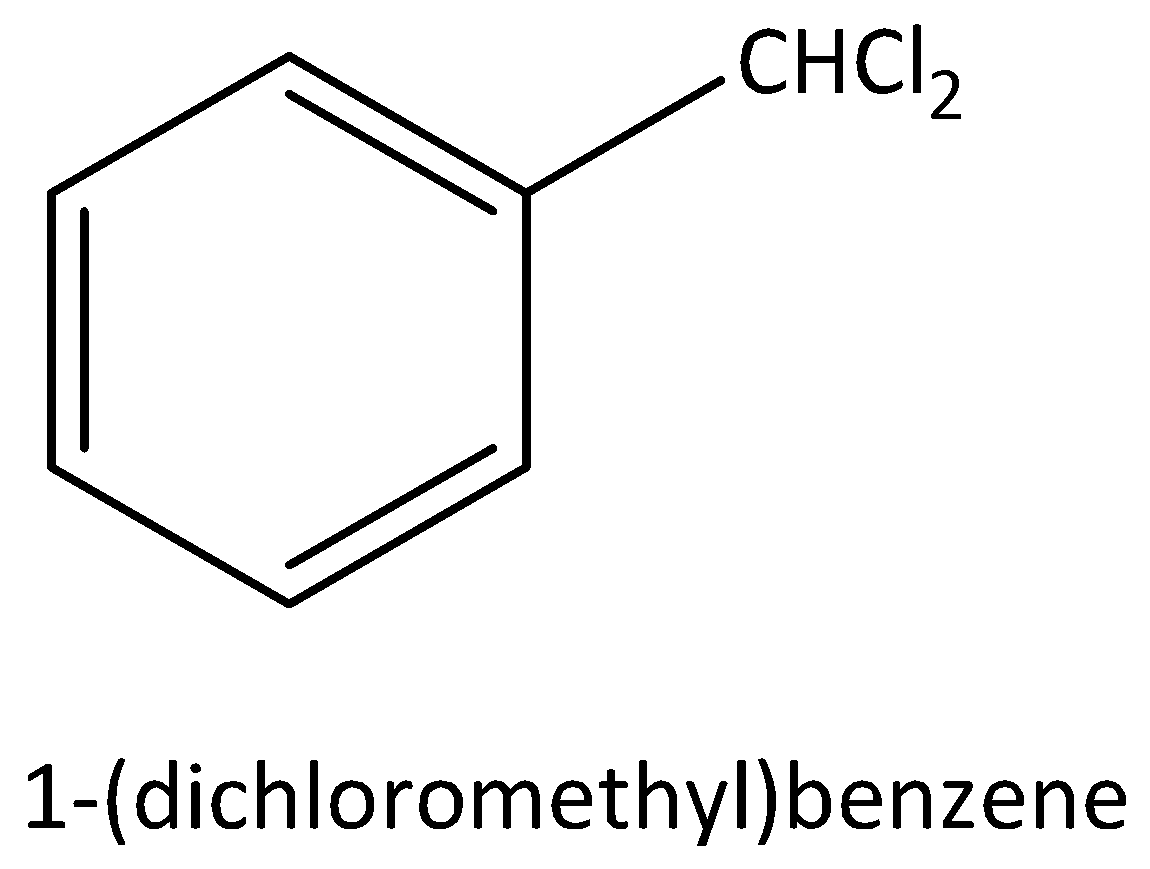
The molecular formula of this figure ${C_7}{H_6}C{l_2}$ .
In this molecule two chlorine atoms are bonded to carbon, that carbon is attached to any carbon atom in the benzene ring.
Hence, this molecule is a good example for benzylic halide.
The IUPAC name of this molecule is 1-(dichloromethyl) benzene.
This is an aromatic compound.
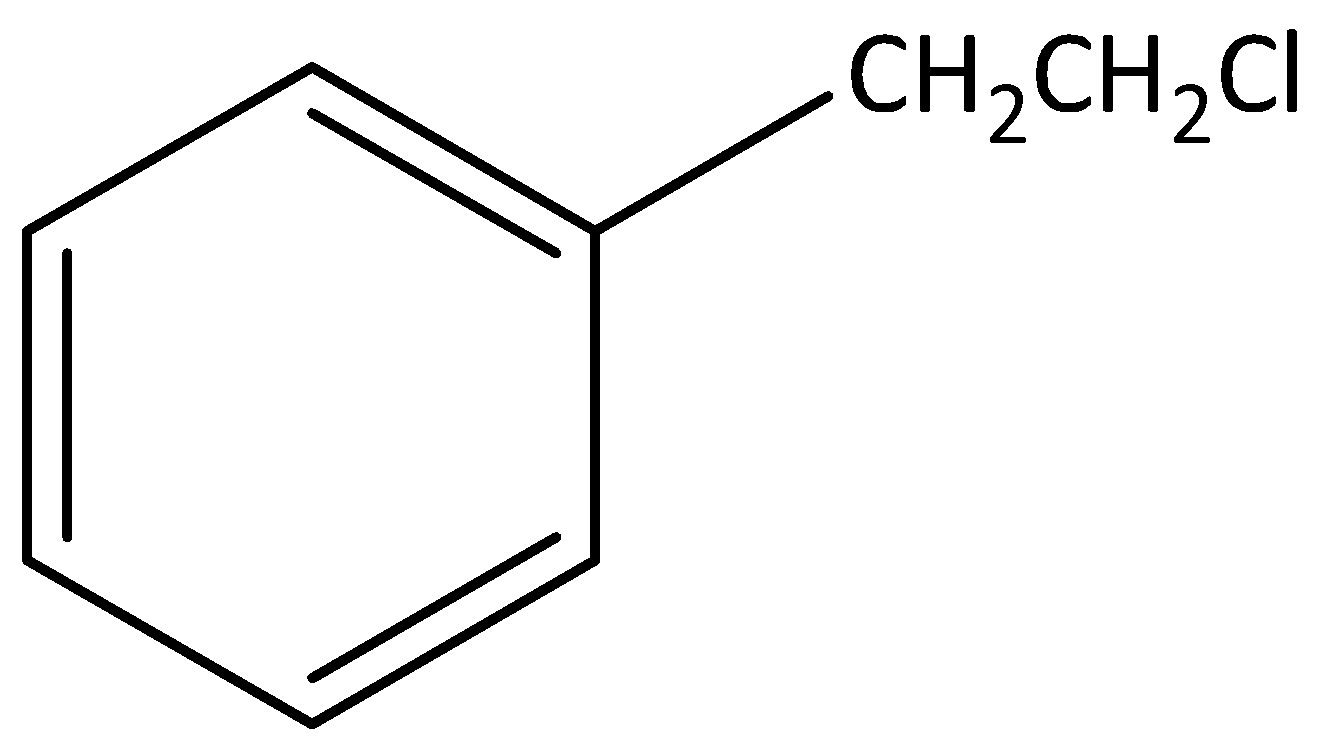
According to below figure
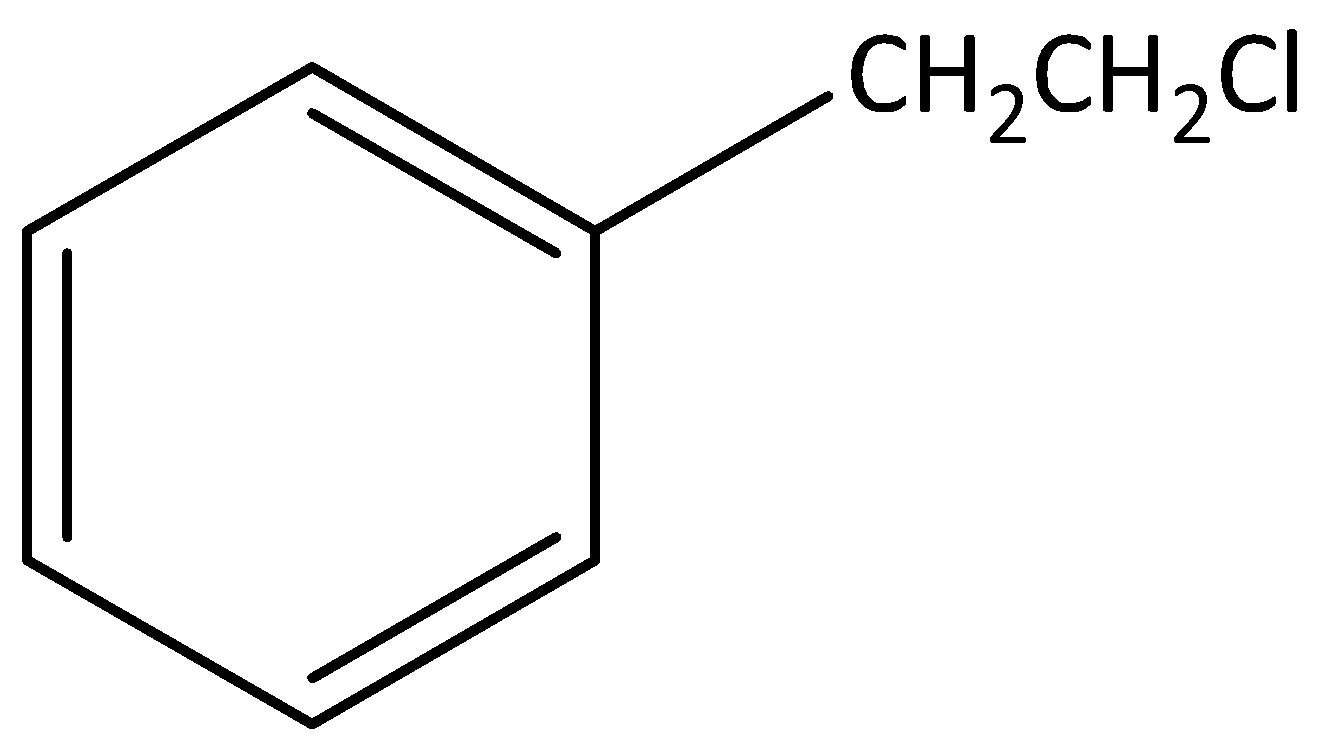
The molecular formula of this figure ${C_8}{H_{10}}C{l_1}$ .
In this molecule one chlorine atom is bonded to carbon, that carbon is not attached to any carbon atom in the benzene ring.
Hence, this molecule is not an example for benzylic halide.
The IUPAC name of this molecule is 1-(2-chloroethyl) benzene.
This is an aromatic compound.
According to above discussion,
Figure one 1-(dichloromethyl) benzene is benzylic halide
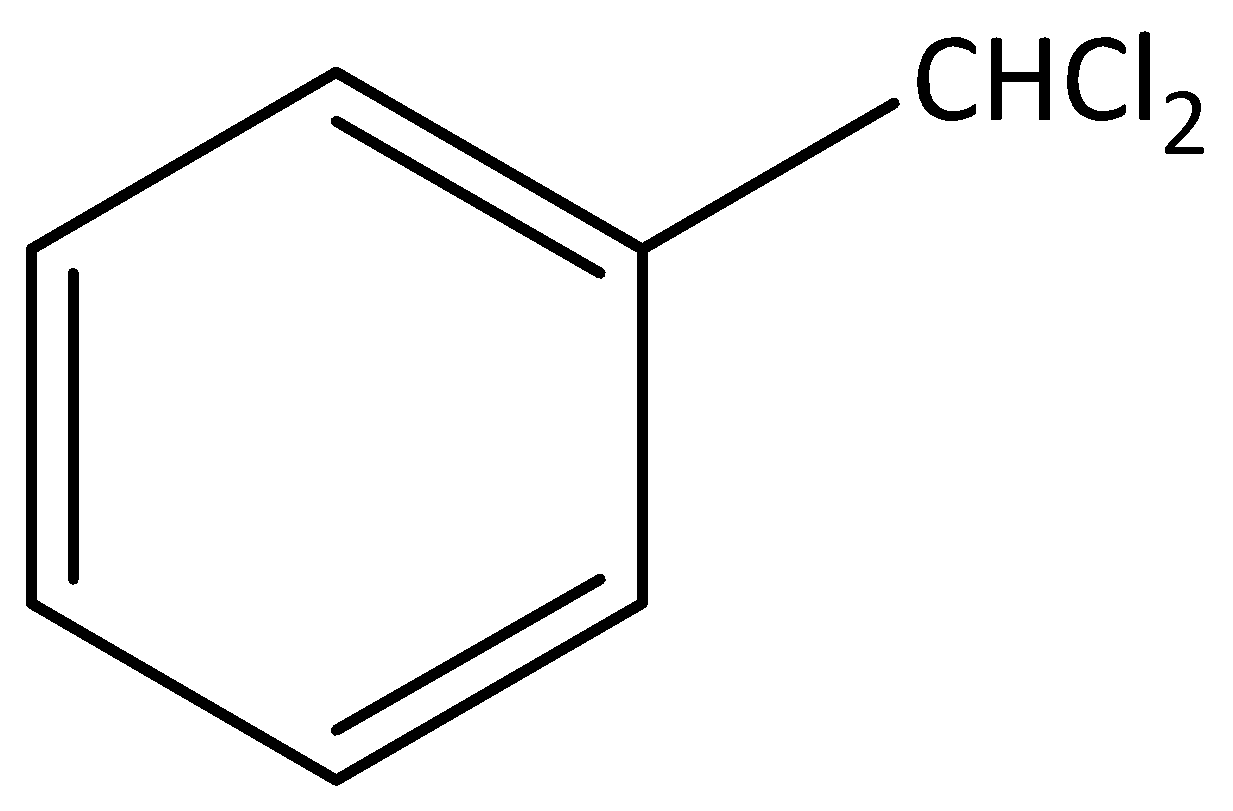
Figure two 1-(2-chloroethyl) benzene is not benzylic halide
Note: Figure one and two are aromatic compounds. Both obey delocalised pi electrons. Resonance structures are also possible in two structures. Both molecules obey $(4n + 2)$ rule.
But one is benzylic halide, another is not benzylic halide. Because of the halogen group bonded carbon is different in both molecules.
There are 6 pi electrons in benzene, the one more reason it is considered as an aromatic compound.
Complete step by step answer:
We need to know that the benzylic halide means one more or more halogen atom bonded to a carbon atom, that carbon atom is attached to any carbon atom in the benzene ring.
According to below figure

The molecular formula of this figure ${C_7}{H_6}C{l_2}$ .
In this molecule two chlorine atoms are bonded to carbon, that carbon is attached to any carbon atom in the benzene ring.
Hence, this molecule is a good example for benzylic halide.
The IUPAC name of this molecule is 1-(dichloromethyl) benzene.
This is an aromatic compound.
According to below figure

The molecular formula of this figure ${C_8}{H_{10}}C{l_1}$ .
In this molecule one chlorine atom is bonded to carbon, that carbon is not attached to any carbon atom in the benzene ring.
Hence, this molecule is not an example for benzylic halide.
The IUPAC name of this molecule is 1-(2-chloroethyl) benzene.
This is an aromatic compound.
According to above discussion,
Figure one 1-(dichloromethyl) benzene is benzylic halide

Figure two 1-(2-chloroethyl) benzene is not benzylic halide

Note: Figure one and two are aromatic compounds. Both obey delocalised pi electrons. Resonance structures are also possible in two structures. Both molecules obey $(4n + 2)$ rule.
But one is benzylic halide, another is not benzylic halide. Because of the halogen group bonded carbon is different in both molecules.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




