
Optically active dimethylcyclobutane is:
(A) $ cis-1,2-dimethyl\;cyclobutane $
(B) $ trans-1,2-dimethyl\;cyclobutane $
(C) $ cis-1,3-dimethyl\;cyclobutane $
(D) $ trans-1,3-dimethyl\;cyclobutane $
Answer
534.3k+ views
Hint: An optically active compound has the ability to rotate the plane of oscillation of polarised light. For a compound to be optically active, the molecules should be asymmetric or at least one carbon should be chiral. An asymmetric compound does not contain any point or axis of symmetry about which the molecule will be symmetric. A compound whose image cannot be superimposed is known as a chiral compound.
Complete answer:
An optically active compound is the compound that rotates the plane of polarized light, hence also known as polarizer.
To check whether the compound is optically active, we need to check if the compound is asymmetric as well as chiral.
For an asymmetric compound, it is not possible to find a point or an axis around which the compound is symmetric, meaning the sections on both sides of the point or axis are similar.
An asymmetric compound for hydrocarbons, can also be defined as the compound where all four valencies of carbon are satisfied by different groups.
A chiral compound is a compound whose mirror image taken from any of the axes is not superimposable on the original compound.
To find the optically active isomer of dimethylcyclobutane, let us draw the structures of all the given isomers.
$ cis-1,2-dimethyl\;cyclobutane $
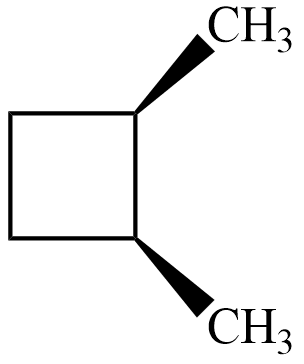
$ trans-1,2-dimethyl\;cyclobutane $
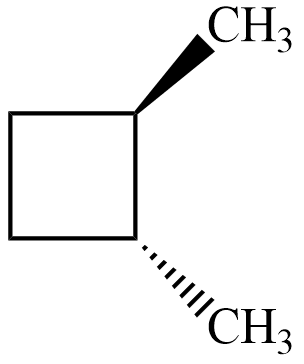
$ cis-1,3-dimethyl\;cyclobutane $
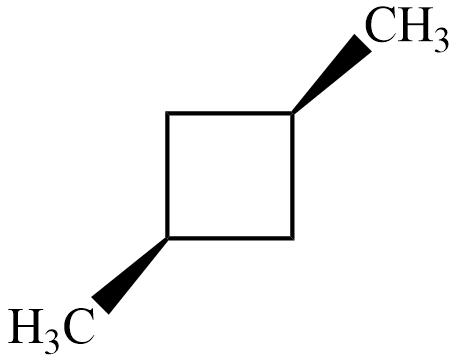
$ trans-1,3-dimethyl\;cyclobutane $

Now, for both the isomers of , there exists an axis of symmetry as shown below about which the compound is symmetrical
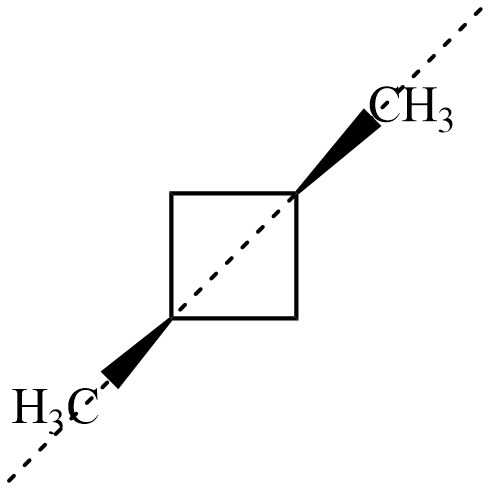
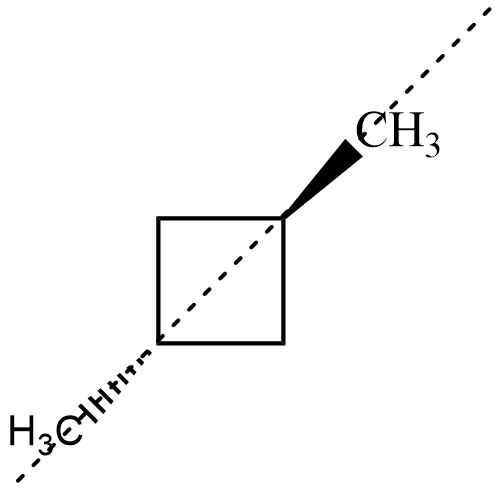
Hence, both isomers of $ 1,3-dimethyl\;cyclobutane $ are not optically active.
Now, for the isomer $ cis-1,2-dimethyl\;cyclobutane $ , there is no plane of symmetry but its mirror image is similar to original and hence superimposable as shown.
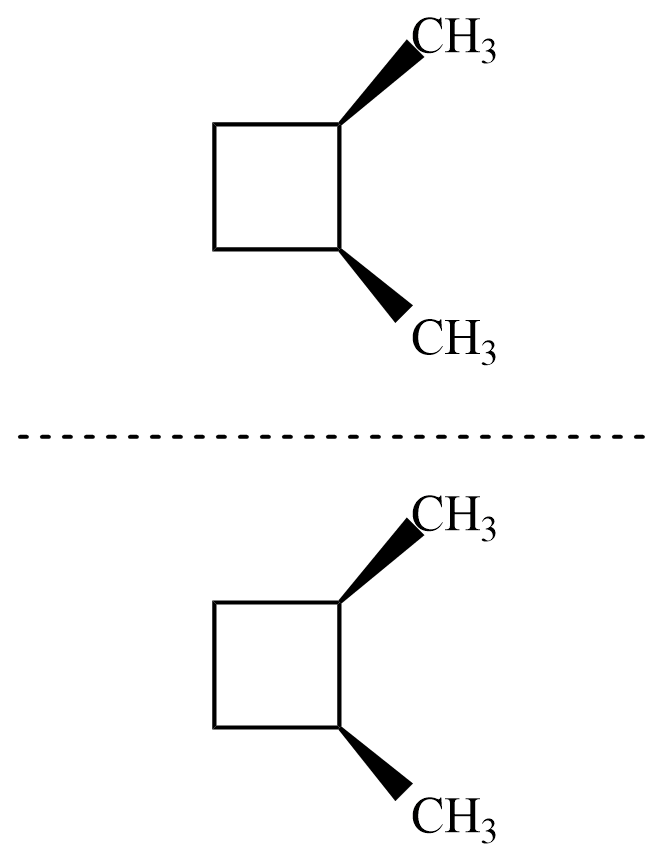
Hence, the isomer is achiral and thus not optically active.
For the isomer $ trans-1,2-dimethylbutane $ , its mirror image is as shown
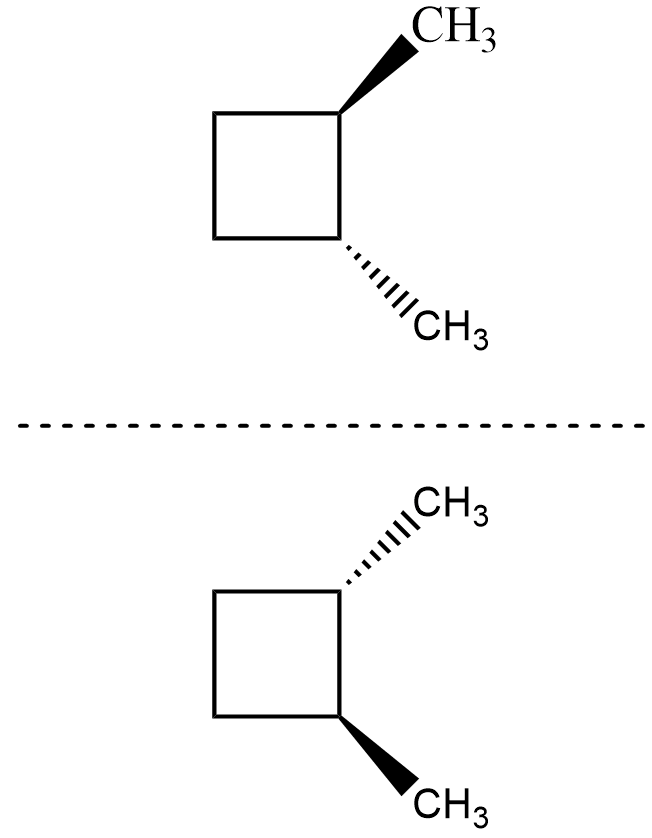
The mirror image is not superimposable on the compound and hence, it is chiral and thus optically active as we cannot find any plane or axis about which it is symmetrical.
Hence, the correct answer is Option $ (B) $ .
Note:
The point to understand here is that even though cyclobutane appears to be a planar compound, due to $ sp^3 $ hybridization, one of the carbons makes an angle of $ 25{}^\circ $ with the plane formed by the other three carbons. Also, we need to remember that for a compound to be optically active, it has to be asymmetric as well as chiral.
Complete answer:
An optically active compound is the compound that rotates the plane of polarized light, hence also known as polarizer.
To check whether the compound is optically active, we need to check if the compound is asymmetric as well as chiral.
For an asymmetric compound, it is not possible to find a point or an axis around which the compound is symmetric, meaning the sections on both sides of the point or axis are similar.
An asymmetric compound for hydrocarbons, can also be defined as the compound where all four valencies of carbon are satisfied by different groups.
A chiral compound is a compound whose mirror image taken from any of the axes is not superimposable on the original compound.
To find the optically active isomer of dimethylcyclobutane, let us draw the structures of all the given isomers.
$ cis-1,2-dimethyl\;cyclobutane $

$ trans-1,2-dimethyl\;cyclobutane $

$ cis-1,3-dimethyl\;cyclobutane $

$ trans-1,3-dimethyl\;cyclobutane $

Now, for both the isomers of , there exists an axis of symmetry as shown below about which the compound is symmetrical


Hence, both isomers of $ 1,3-dimethyl\;cyclobutane $ are not optically active.
Now, for the isomer $ cis-1,2-dimethyl\;cyclobutane $ , there is no plane of symmetry but its mirror image is similar to original and hence superimposable as shown.

Hence, the isomer is achiral and thus not optically active.
For the isomer $ trans-1,2-dimethylbutane $ , its mirror image is as shown

The mirror image is not superimposable on the compound and hence, it is chiral and thus optically active as we cannot find any plane or axis about which it is symmetrical.
Hence, the correct answer is Option $ (B) $ .
Note:
The point to understand here is that even though cyclobutane appears to be a planar compound, due to $ sp^3 $ hybridization, one of the carbons makes an angle of $ 25{}^\circ $ with the plane formed by the other three carbons. Also, we need to remember that for a compound to be optically active, it has to be asymmetric as well as chiral.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




