
Opposite angles of a Rhombus are
$A$- Complementary
$B$- Equal
$C$- Supplementary
$D$- Never Equal
Answer
570.6k+ views
Hint: In order to solve such a type of question, the student must have an idea about the properties of geometric figures. The properties which student should be aware of for rhombus are as follows
> All sides of the Rhombus are equal.
> Opposite Sides of Rhombus are parallel.
> Diagonals bisect each other at Right Angles.
> Diagonals bisect the angles of the Rhombus.
Complete answer:
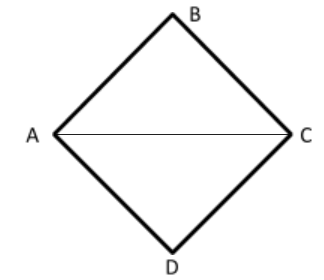
In the given figure ABCD is a Rhombus with Diagonal AC
We know from the properties of Rhombus that BC$||$AD, AC is a transversal, Since opposite sides of Rhombus are Parallel
So, $\angle ACB = \angle CAD......(1)$- Alternate Interior Angles are equal
Similarly we can say $\angle BAC = \angle ACD......(2)$
In $\vartriangle ABC\& \vartriangle ACD$, we have
$\angle ACB = \angle CAD$
$\angle BAC = \angle ACD$
Side AC is Common.
SO both the triangles are congruent by the Rule ASA
$\therefore \vartriangle ACB \cong \vartriangle ACD$
Thus We can say that $\angle ABC = \angle ADC.......(3)$
Adding Equation $1\& 2$ we get
$\begin{gathered}
\angle ACB + \angle ACD = \angle CAD + \angle BAC \\
OR,\angle BCD = \angle BAC...........(4) \\
\end{gathered} $
So, from equation $3\& 4$, we can say that the opposite angles of rhombus are equal.
Hence Proved.
Answer to this question is Option $B$- Equal
Note: Though the property is asked directly in this question, it is always necessary to know how to prove it because most of the times the questions asked are about the proof. So the students should not rely on only learning the property but rather know how to prove the property.
> All sides of the Rhombus are equal.
> Opposite Sides of Rhombus are parallel.
> Diagonals bisect each other at Right Angles.
> Diagonals bisect the angles of the Rhombus.
Complete answer:

In the given figure ABCD is a Rhombus with Diagonal AC
We know from the properties of Rhombus that BC$||$AD, AC is a transversal, Since opposite sides of Rhombus are Parallel
So, $\angle ACB = \angle CAD......(1)$- Alternate Interior Angles are equal
Similarly we can say $\angle BAC = \angle ACD......(2)$
In $\vartriangle ABC\& \vartriangle ACD$, we have
$\angle ACB = \angle CAD$
$\angle BAC = \angle ACD$
Side AC is Common.
SO both the triangles are congruent by the Rule ASA
$\therefore \vartriangle ACB \cong \vartriangle ACD$
Thus We can say that $\angle ABC = \angle ADC.......(3)$
Adding Equation $1\& 2$ we get
$\begin{gathered}
\angle ACB + \angle ACD = \angle CAD + \angle BAC \\
OR,\angle BCD = \angle BAC...........(4) \\
\end{gathered} $
So, from equation $3\& 4$, we can say that the opposite angles of rhombus are equal.
Hence Proved.
Answer to this question is Option $B$- Equal
Note: Though the property is asked directly in this question, it is always necessary to know how to prove it because most of the times the questions asked are about the proof. So the students should not rely on only learning the property but rather know how to prove the property.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




