
On an isothermal process, there are two points A and B at which pressures and volumes are \[\left( {2{P_0},{V_0}} \right)\] and \[\left( {2{P_0},{V_0}} \right)\] respectively. If A and B are connected by a straight line, find the pressure at a POINT on this straight line at which temperature is maximum
A $\dfrac{{4{P_0}}}{3}$
B $\dfrac{{5{P_0}}}{3}$
C $\dfrac{{3{P_0}}}{2}$
D $\dfrac{{7{P_0}}}{5}$
Answer
583.5k+ views
Hint: This question is based on a thermodynamic process called isothermal process. We have to know about the isothermal process. In this process, the temperature throughout the thermodynamic process remains constant. We use the isothermal expression and P-V diagram to find the pressure and volume at which the temperature is maximum.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the isothermal is the contact temperature process. So ,only changes occur in volume and pressure throughout the process.
Now, consider the P-V diagram on which two points A and B lie on it.
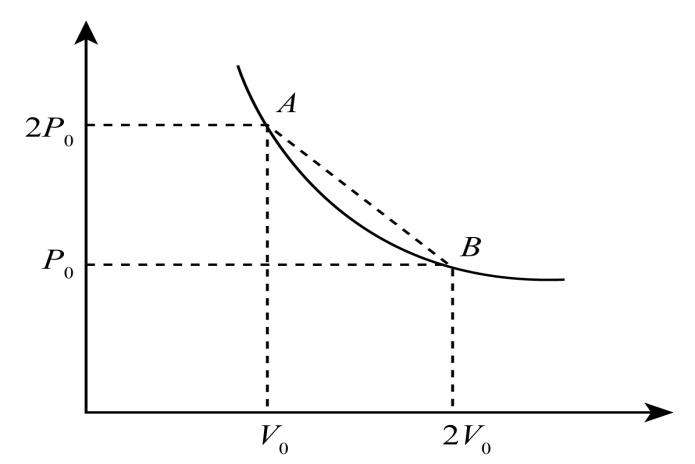
Here, in point A the pressure is $2{P_0}$ and volume is ${v_0}$ and in point B, the pressure is ${P_0}$ and volume is $2{v_0}$. We have to find the pressure on a straight line where the temperature is maximum.
From the given diagram, there is a straight line that follows the straight line equation $y = mx + c$.
Therefore, it can written as,
$P = mv + c........\left( {\rm{i}} \right)$
Here, $m$ is the slope.
Now, we have to calculate the slope of the line.
Therefore,
$m = - \left( {\dfrac{{2{P_0} - {P_0}}}{{2{V_0} - {V_0}}}} \right)$
Now, substitute the value in equation (i) we get,
$
P = \left( {\dfrac{{2{P_0} - {P_0}}}{{2{V_0} - {V_0}}}} \right)v + c\\
\implies P = - \dfrac{{{P_0}}}{{{V_0}}} \times V + c............\left( {{\rm{ii}}} \right)
$
We have to satisfy the equation by substitute the value $\left( {2{P_0},{V_0}} \right)$ we get,
$
2{P_0} = - \dfrac{{{P_0}}}{{{V_0}}} \times {V_0} + c\\
\implies c = 3{P_0}
$
Substitute this value in equation (ii) we get,
$
P = - \dfrac{{{P_0}}}{{{V_0}}} \times V + 3{P_0}\\
\implies {V_0}P + {P_0}V = 3{P_0}{V_0}.......\left( {{\rm{iii}}} \right)
$
Now, by using the ideal gas equation,
$
PV = nRT\\
\implies V = \dfrac{{nRT}}{P}
$
Substitute this value in equation (iii) we get,
$
{V_0}P + {P_0}\left( {\dfrac{{nRT}}{P}} \right) = 3{P_0}{V_0}\\
\implies T = \dfrac{{3{P_0}{V_0}P - {V_0}{P^2}}}{{{P_0}nR}}........\left( {{\rm{iv}}} \right)
$
It is given in question that we have to find the pressure at maximum temperature.
Therefore,
$
\dfrac{{dT}}{{dP}} = 0\\
\implies \dfrac{{3{P_0}{V_0} - 2{V_0}P}}{{{P_0}nR}} = 0\\
\therefore P = \dfrac{3}{2}{P_0}
$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
In this question, we have to know the isothermal process. And with the help of P-V diagram we can find the maximum temperature. Using symmetry, the maximum temperature is at the midpoint of the point A and B.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the isothermal is the contact temperature process. So ,only changes occur in volume and pressure throughout the process.
Now, consider the P-V diagram on which two points A and B lie on it.

Here, in point A the pressure is $2{P_0}$ and volume is ${v_0}$ and in point B, the pressure is ${P_0}$ and volume is $2{v_0}$. We have to find the pressure on a straight line where the temperature is maximum.
From the given diagram, there is a straight line that follows the straight line equation $y = mx + c$.
Therefore, it can written as,
$P = mv + c........\left( {\rm{i}} \right)$
Here, $m$ is the slope.
Now, we have to calculate the slope of the line.
Therefore,
$m = - \left( {\dfrac{{2{P_0} - {P_0}}}{{2{V_0} - {V_0}}}} \right)$
Now, substitute the value in equation (i) we get,
$
P = \left( {\dfrac{{2{P_0} - {P_0}}}{{2{V_0} - {V_0}}}} \right)v + c\\
\implies P = - \dfrac{{{P_0}}}{{{V_0}}} \times V + c............\left( {{\rm{ii}}} \right)
$
We have to satisfy the equation by substitute the value $\left( {2{P_0},{V_0}} \right)$ we get,
$
2{P_0} = - \dfrac{{{P_0}}}{{{V_0}}} \times {V_0} + c\\
\implies c = 3{P_0}
$
Substitute this value in equation (ii) we get,
$
P = - \dfrac{{{P_0}}}{{{V_0}}} \times V + 3{P_0}\\
\implies {V_0}P + {P_0}V = 3{P_0}{V_0}.......\left( {{\rm{iii}}} \right)
$
Now, by using the ideal gas equation,
$
PV = nRT\\
\implies V = \dfrac{{nRT}}{P}
$
Substitute this value in equation (iii) we get,
$
{V_0}P + {P_0}\left( {\dfrac{{nRT}}{P}} \right) = 3{P_0}{V_0}\\
\implies T = \dfrac{{3{P_0}{V_0}P - {V_0}{P^2}}}{{{P_0}nR}}........\left( {{\rm{iv}}} \right)
$
It is given in question that we have to find the pressure at maximum temperature.
Therefore,
$
\dfrac{{dT}}{{dP}} = 0\\
\implies \dfrac{{3{P_0}{V_0} - 2{V_0}P}}{{{P_0}nR}} = 0\\
\therefore P = \dfrac{3}{2}{P_0}
$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
In this question, we have to know the isothermal process. And with the help of P-V diagram we can find the maximum temperature. Using symmetry, the maximum temperature is at the midpoint of the point A and B.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




