
Obtain an expression for magnetic flux density B at the center of a circular coil of radius R, having N turns and carrying a current $I$.
Answer
595.8k+ views
Hint: This problem is based on the application of Biot-savart’s law. This law is used to determine the strength of the magnetic field at any point due to a current-carrying conductor. Biot-savart’s law for the magnetic field obeys inverse square law and the superposition principle.
Complete step by step answer:
Consider a circular coil or a circular loop of radius R, carrying current I. The circular coil consists of a large number of current elements of length $dl$. Let the current element (AB) $Id\vec l$.
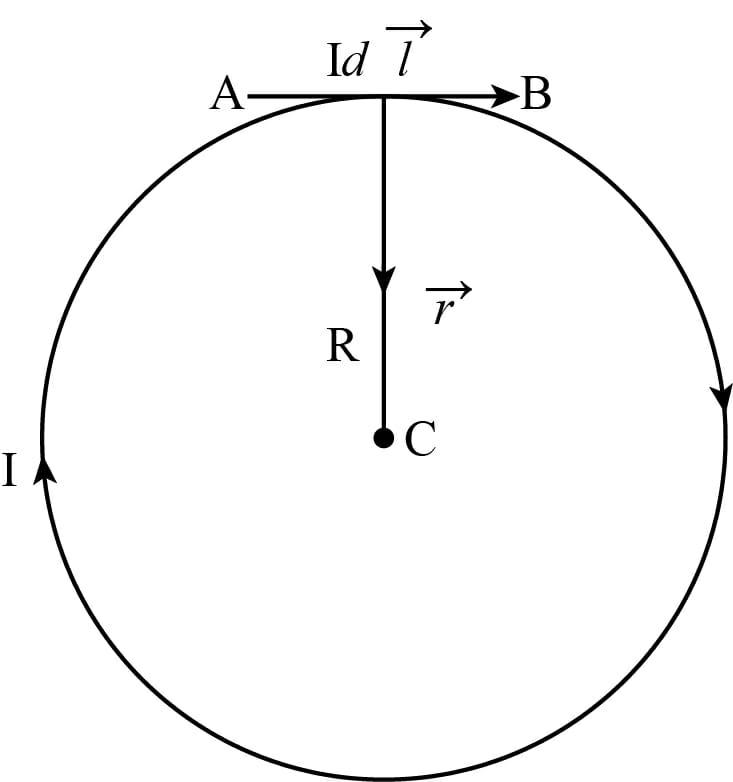
AS per Biot-savart’s law, the magnetic field at point C due to current element AB.
$ \Rightarrow d\vec B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{{Id\vec l \times r}}{{{R^2}}}$
Since the angle between $d\vec l$ and $\hat r$ is $90^\circ $, so
$d\vec l \times \hat r = dl\sin 90^\circ $
\[ \Rightarrow d\vec l \times \hat r = dl\]
Simplifying the above equation, it gives us,
$db = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{{Idl}}{{{R^2}}}$
Therefore, the magnetic flux at the center of a current-carrying loop
\[B = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I}}{{4\pi }} \times \dfrac{1}{{{R^2}}}\oint {dl} \]
$ \Rightarrow B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi {R^2}}}2\pi R$
$ \Rightarrow B = \left( {\dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }}} \right)\dfrac{{2\pi I}}{R}$
However, if the direction of the magnetic field at the center of the current-carrying loop is perpendicular to the plane of the loop and in the upward direction if the current in the loop passes anticlockwise. If a coil has N turns, then the magnetic field at the current coil its center is given by
$ \Rightarrow B = \left( {\dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{{4\pi }}} \right)\dfrac{{N \times 2\pi I}}{R}$
$ \Rightarrow B = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}NI}}{{2R}}$
Therefore, An expression for magnetic flux density B at the center of a circular coil of radius R, having N turns and carrying a current $I$ is given by $B = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}NI}}{{2R}}$.
Note:
Here $db$ is the magnetic field, ${\mu _o}$ is the absolute permeability and $dl$ is the small element length. Here the current element is a vector quantity whose magnitude equal to the product of current and length of a small element having a direction to the flow of current i.e. $Id\vec l$.
Complete step by step answer:
Consider a circular coil or a circular loop of radius R, carrying current I. The circular coil consists of a large number of current elements of length $dl$. Let the current element (AB) $Id\vec l$.

AS per Biot-savart’s law, the magnetic field at point C due to current element AB.
$ \Rightarrow d\vec B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{{Id\vec l \times r}}{{{R^2}}}$
Since the angle between $d\vec l$ and $\hat r$ is $90^\circ $, so
$d\vec l \times \hat r = dl\sin 90^\circ $
\[ \Rightarrow d\vec l \times \hat r = dl\]
Simplifying the above equation, it gives us,
$db = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{{Idl}}{{{R^2}}}$
Therefore, the magnetic flux at the center of a current-carrying loop
\[B = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I}}{{4\pi }} \times \dfrac{1}{{{R^2}}}\oint {dl} \]
$ \Rightarrow B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi {R^2}}}2\pi R$
$ \Rightarrow B = \left( {\dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }}} \right)\dfrac{{2\pi I}}{R}$
However, if the direction of the magnetic field at the center of the current-carrying loop is perpendicular to the plane of the loop and in the upward direction if the current in the loop passes anticlockwise. If a coil has N turns, then the magnetic field at the current coil its center is given by
$ \Rightarrow B = \left( {\dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{{4\pi }}} \right)\dfrac{{N \times 2\pi I}}{R}$
$ \Rightarrow B = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}NI}}{{2R}}$
Therefore, An expression for magnetic flux density B at the center of a circular coil of radius R, having N turns and carrying a current $I$ is given by $B = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}NI}}{{2R}}$.
Note:
Here $db$ is the magnetic field, ${\mu _o}$ is the absolute permeability and $dl$ is the small element length. Here the current element is a vector quantity whose magnitude equal to the product of current and length of a small element having a direction to the flow of current i.e. $Id\vec l$.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




