
Observe any one flower and its various parts and describe it in your own words.
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: In plants, flowers aid in reproduction. There are four parts of a typical angiosperm flower, which play an important role in reproduction. The flower here is an almond flower.
Complete answer:
The reproductive unit of any angiosperm can be described as a flower. Flowers in angiosperms carry out sexual reproduction. An attractively modified stem with a condensed axis is usually a typical flower. There are four distinct sections of a flower-calyx, corolla, androecium, and gynoecium. The androecium and gynoecium sections contain a flower's male and female reproductive organs, respectively.
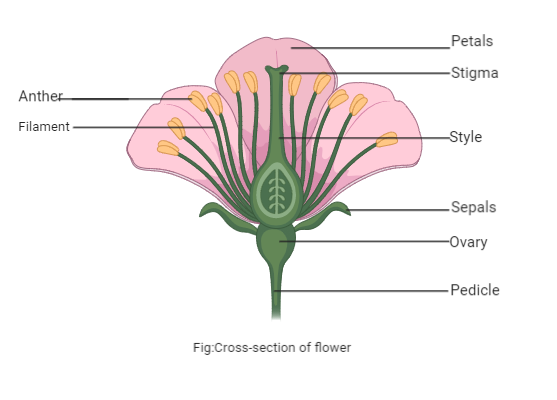
The following are the elements of a flower:
1. Androecium: Androecium (male reproductive organ) is made up of stamen whorls. The filament (long and slender stalk) and anther (bilobed structure) are composed of the stamen. Bilobed is a typical anther, which includes the grains of pollen.
2. Gynoecium: The innermost section or whorl of a flower is the gynoecium. It consists of pistils, the reproductive organs of flowers that are female. There are three parts of a pistil: the stigma, the style, and the ovary.
a. Style-It connects the ovary with the stigma.
b. Stigma-For the pollen seeds, it serves as a receptacle.
c.Ovary-The extended basal portion on which the style rests. Each ovary carries one or more ovules attached to the cushion-like placenta. Ovules grow into seeds and ovaries into a fruit after fertilization.
3. Calyx (sepal-bearing accessory organ)- The calyx is the outermost whorl of a flower. They include sepals primarily. They are green and leaf-like structures that during the initial stage or bud process cover and protect the flowers and also attract pollinating insects. When the sepals in a flower arrangement are apart, they are called polysepalous, while they are called gamopetalous when fused.
4. Corolla- A layer that is located within the calyx is the corolla of a flower. It includes beautifully, attractively colored petals and a flower's brightly coloured whorl. Such petals help to seduce and attract insects for pollination. They are called polypetalous flowers when the petals are free in a flower, while the flowers with fused petals are called gamopetalous flowers. The individual corolla unit is made up of petals. As they are brightly coloured, the inner vital organs (i.e., stamens and carpels) are surrounded by petals and attract pollinators.
Note: Depending on whether the plant is a monocot or dicot, the number of sepals and petals varies. The number of petals in monocots is normally three or more than three, while the number of petals in dicots is four or more. The calyx and corolla, together, are recognized as the perianth. The male reproductive structures are found in the third whorl and are known as the androecium. If all four whorls are present in a flower, the flower is defined as complete, while the flower is known as incomplete if any of these four parts are missing.
Complete answer:
The reproductive unit of any angiosperm can be described as a flower. Flowers in angiosperms carry out sexual reproduction. An attractively modified stem with a condensed axis is usually a typical flower. There are four distinct sections of a flower-calyx, corolla, androecium, and gynoecium. The androecium and gynoecium sections contain a flower's male and female reproductive organs, respectively.

The following are the elements of a flower:
1. Androecium: Androecium (male reproductive organ) is made up of stamen whorls. The filament (long and slender stalk) and anther (bilobed structure) are composed of the stamen. Bilobed is a typical anther, which includes the grains of pollen.
2. Gynoecium: The innermost section or whorl of a flower is the gynoecium. It consists of pistils, the reproductive organs of flowers that are female. There are three parts of a pistil: the stigma, the style, and the ovary.
a. Style-It connects the ovary with the stigma.
b. Stigma-For the pollen seeds, it serves as a receptacle.
c.Ovary-The extended basal portion on which the style rests. Each ovary carries one or more ovules attached to the cushion-like placenta. Ovules grow into seeds and ovaries into a fruit after fertilization.
3. Calyx (sepal-bearing accessory organ)- The calyx is the outermost whorl of a flower. They include sepals primarily. They are green and leaf-like structures that during the initial stage or bud process cover and protect the flowers and also attract pollinating insects. When the sepals in a flower arrangement are apart, they are called polysepalous, while they are called gamopetalous when fused.
4. Corolla- A layer that is located within the calyx is the corolla of a flower. It includes beautifully, attractively colored petals and a flower's brightly coloured whorl. Such petals help to seduce and attract insects for pollination. They are called polypetalous flowers when the petals are free in a flower, while the flowers with fused petals are called gamopetalous flowers. The individual corolla unit is made up of petals. As they are brightly coloured, the inner vital organs (i.e., stamens and carpels) are surrounded by petals and attract pollinators.
Note: Depending on whether the plant is a monocot or dicot, the number of sepals and petals varies. The number of petals in monocots is normally three or more than three, while the number of petals in dicots is four or more. The calyx and corolla, together, are recognized as the perianth. The male reproductive structures are found in the third whorl and are known as the androecium. If all four whorls are present in a flower, the flower is defined as complete, while the flower is known as incomplete if any of these four parts are missing.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




