
When an object is placed at a distance of 50cm from a concave spherical mirror, the magnification produced is \[-\dfrac{1}{2}\]. Where should the object be placed to get a magnification of \[-\dfrac{1}{5}\]?
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: A concave mirror of certain focal length is used to get a magnification of \[-\dfrac{1}{2}\] when placed at 50cm from the mirror. We can find the focal length using the mirror formula and hence, find the object distance to get the magnification of \[-\dfrac{1}{5}\].
Complete answer:
We are given a concave mirror of focal length ‘f’ which produces an image of magnification \[-\dfrac{1}{2}\] when an object is placed 50cm from its reflecting surface. We can easily find the focal length using the mirror formula and magnification formula for reflecting surfaces.
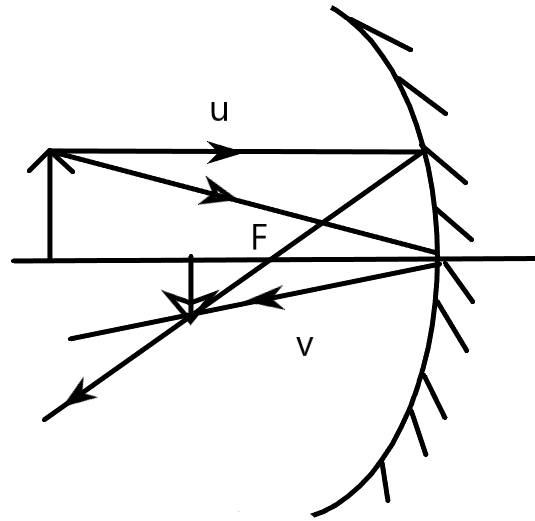
The mirror formula as we know is given by –
\[\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}\]
Where, f is the focal length of the concave mirror,
v is the image distance from the reflecting surface,
u is the object distance from the reflecting surface.
Here,
\[u=-50cm\]
Now, we can employ the formula to find the magnification in terms of image distance and object distance to find the image distance ‘v’.
\[\begin{align}
& \text{also,} \\
& \text{magnification, }m=\dfrac{v}{u} \\
& \text{given,} \\
& m=-\dfrac{1}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }\dfrac{v}{u}=-\dfrac{1}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }v=-\dfrac{u}{2}=-25cm \\
\end{align}\]
Now we can apply these in the mirror formula to get the focal length of the concave mirror as –
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }f=\dfrac{uv}{u+v} \\
& u=-50cm\text{ and }v=-25cm \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }f=\dfrac{-50\times -25}{-50+-25}=\dfrac{-50}{3}cm \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let us find the object distance to get an image of magnification \[-\dfrac{1}{5}\] with a focal length of \[\dfrac{-50}{3}cm\].
\[\begin{align}
& \text{given,} \\
& m'=-\dfrac{1}{5} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ -}\dfrac{v}{u}=-\dfrac{1}{5} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ u}=5v \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we can apply the mirror formula to find the object distance ‘u’
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }f=\dfrac{uv}{u+v} \\
& u=5v \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }\dfrac{-50}{3}=\dfrac{5v.v}{5v+v} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }\dfrac{5v}{6}=\dfrac{-50}{3} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }v=-20cm \\
& \text{but, } \\
& u=5v \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }u=-100cm \\
\end{align}\]
We got the object distance for the image to have a magnification of \[-\dfrac{1}{5}\] to be 100cm from the mirror to the left.
Note:
We should be careful while considering the sign conventions in the mirror formula and the magnification. We have to consider the signs for a variable which is known to have a negative direction as that of the object distance always has. Errors can be severe if we avoid them.
Complete answer:
We are given a concave mirror of focal length ‘f’ which produces an image of magnification \[-\dfrac{1}{2}\] when an object is placed 50cm from its reflecting surface. We can easily find the focal length using the mirror formula and magnification formula for reflecting surfaces.

The mirror formula as we know is given by –
\[\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}\]
Where, f is the focal length of the concave mirror,
v is the image distance from the reflecting surface,
u is the object distance from the reflecting surface.
Here,
\[u=-50cm\]
Now, we can employ the formula to find the magnification in terms of image distance and object distance to find the image distance ‘v’.
\[\begin{align}
& \text{also,} \\
& \text{magnification, }m=\dfrac{v}{u} \\
& \text{given,} \\
& m=-\dfrac{1}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }\dfrac{v}{u}=-\dfrac{1}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }v=-\dfrac{u}{2}=-25cm \\
\end{align}\]
Now we can apply these in the mirror formula to get the focal length of the concave mirror as –
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }f=\dfrac{uv}{u+v} \\
& u=-50cm\text{ and }v=-25cm \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }f=\dfrac{-50\times -25}{-50+-25}=\dfrac{-50}{3}cm \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let us find the object distance to get an image of magnification \[-\dfrac{1}{5}\] with a focal length of \[\dfrac{-50}{3}cm\].
\[\begin{align}
& \text{given,} \\
& m'=-\dfrac{1}{5} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ -}\dfrac{v}{u}=-\dfrac{1}{5} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ u}=5v \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we can apply the mirror formula to find the object distance ‘u’
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }f=\dfrac{uv}{u+v} \\
& u=5v \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }\dfrac{-50}{3}=\dfrac{5v.v}{5v+v} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }\dfrac{5v}{6}=\dfrac{-50}{3} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }v=-20cm \\
& \text{but, } \\
& u=5v \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }u=-100cm \\
\end{align}\]
We got the object distance for the image to have a magnification of \[-\dfrac{1}{5}\] to be 100cm from the mirror to the left.
Note:
We should be careful while considering the sign conventions in the mirror formula and the magnification. We have to consider the signs for a variable which is known to have a negative direction as that of the object distance always has. Errors can be severe if we avoid them.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




