
When the object is located beyond 2F for converging lens the image produced is
A. Between F and 2F
B. Enlarged
C. Virtual
D. Diminished
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: We will use the lens formula and the formula for magnification to derive a relation between the position of the image and position of the object. And from the relation we will deduce where the image will be formed and whether it would be enlarged, diminished or of the same size when compared to the size of the object.
Formula Used:
Lens formula
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Magnification of image from a lens
$M=\dfrac{v}{u}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
First, we have the lens formula which gives us the relation between the focal length of the lens, distance of object from the centre of the lens and distance of image from the centre of the lens. Using this we will write the distance of the image formed in terms of the focal length and the distance of the object.
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{f}+\dfrac{1}{u} \\
& \Rightarrow v={{\left( \dfrac{1}{f}+\dfrac{1}{u} \right)}^{-1}}=\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{1}{f}+\dfrac{1}{u}}=\dfrac{fu}{f+u} \\
\end{align}\]
As the object is placed on the left side of the mirror, its length will be negative. And the focal length of the converging lens or the convex lens is positive. Hence, for $|u|>2F$, the term in the denominator will be a negative number greater than f in magnitude. And the ratio $\dfrac{u}{f+u}$will be less than 2. So, the value of v will be less than 2F and will be F when the object is at infinity. So, the image will be formed between F and 2F. Also, since the ratio of v and u is less than 1, the image will be diminished.
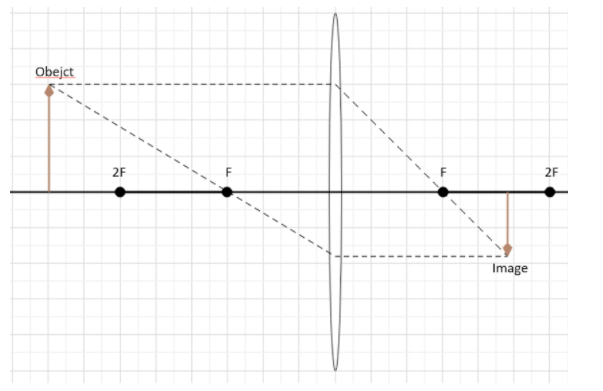
Hence, the correct options are A, i.e. Between F and 2F and D, i.e. Diminished.
Note: Alternatively, we can also find where the image will be formed for the two extreme values of the position of the object i.e. 2F and infinity. Using the results, we can deduce that the image will always be between them for the given condition as the formula for the distance of image is continuous.
Formula Used:
Lens formula
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Magnification of image from a lens
$M=\dfrac{v}{u}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
First, we have the lens formula which gives us the relation between the focal length of the lens, distance of object from the centre of the lens and distance of image from the centre of the lens. Using this we will write the distance of the image formed in terms of the focal length and the distance of the object.
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{f}+\dfrac{1}{u} \\
& \Rightarrow v={{\left( \dfrac{1}{f}+\dfrac{1}{u} \right)}^{-1}}=\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{1}{f}+\dfrac{1}{u}}=\dfrac{fu}{f+u} \\
\end{align}\]
As the object is placed on the left side of the mirror, its length will be negative. And the focal length of the converging lens or the convex lens is positive. Hence, for $|u|>2F$, the term in the denominator will be a negative number greater than f in magnitude. And the ratio $\dfrac{u}{f+u}$will be less than 2. So, the value of v will be less than 2F and will be F when the object is at infinity. So, the image will be formed between F and 2F. Also, since the ratio of v and u is less than 1, the image will be diminished.

Hence, the correct options are A, i.e. Between F and 2F and D, i.e. Diminished.
Note: Alternatively, we can also find where the image will be formed for the two extreme values of the position of the object i.e. 2F and infinity. Using the results, we can deduce that the image will always be between them for the given condition as the formula for the distance of image is continuous.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




