
Number substituted cycloalkenes in the way that gives the carbon atoms of the double bond 1 and 2 positions and that also gives the substituent groups the lower number at the first point of difference. With substituted cycloalkenes it is not necessary to specify the position of the double bond since it will always begin with $C_1$ and $C_2$ . The examples shown here illustrate the application of these rules:

Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: We are given two compounds both the compounds are cyclic in nature and contain double bonds thus, they are cycloalkenes. To solve this we must know the rules of nomenclature of cycloalkenes. Recall the most important rule for the numbering of carbon atoms involved in double bonds and the numbering of the substituents.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The rules for the IUPAC nomenclature of cycloalkenes are as follows:
-Name the parent hydrocarbon depending on the total number of carbon atoms with the suffix –ene.
-Number the carbon atoms such that the double bonded carbon atoms get the numbers 1 and 2. And the first substituent has the lowest possible number.
-Write the full name number of the substituents according to their positions in an alphabetical order.
-The name indicates the double bond by the number of the first carbon.
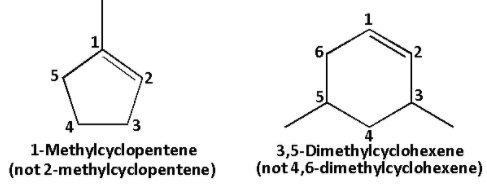
We are given two compounds as follows:
Consider the first compound: The compound is cyclic in nature. It contains 5 carbons. Thus, it is cyclopentene. The methyl substituent is attached to carbon number 1. Thus, the name is 1-methylcyclopentene.
Consider the second compound: The compound is cyclic in nature. It contains 6 carbons. Thus, it is cyclohexene. The two methyl substituents are attached to carbon number 3 and 5 thus, dimethyl. Thus, the name is 3,5-dimethylcyclohexene.
The number in both the compounds is done in such a way that the double bonded carbons have carbon number 1 and 2 and the substituents have the lowest possible numbers.
Thus, the first compound is named as 1-methylcyclopentene and not 2-methylcyclopentene and the second compound is named as 3,5-dimethylcyclohexene and not 4,6-dimethylcyclohexene.
Note: Remember the rules for naming the cycloalkenes. The important rule to be remembered is that we have to number the carbon atoms in such a way that the double bonded carbon atoms get the numbers 1 and 2. And the first substituent has the lowest possible number.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The rules for the IUPAC nomenclature of cycloalkenes are as follows:
-Name the parent hydrocarbon depending on the total number of carbon atoms with the suffix –ene.
-Number the carbon atoms such that the double bonded carbon atoms get the numbers 1 and 2. And the first substituent has the lowest possible number.
-Write the full name number of the substituents according to their positions in an alphabetical order.
-The name indicates the double bond by the number of the first carbon.

We are given two compounds as follows:
Consider the first compound: The compound is cyclic in nature. It contains 5 carbons. Thus, it is cyclopentene. The methyl substituent is attached to carbon number 1. Thus, the name is 1-methylcyclopentene.
Consider the second compound: The compound is cyclic in nature. It contains 6 carbons. Thus, it is cyclohexene. The two methyl substituents are attached to carbon number 3 and 5 thus, dimethyl. Thus, the name is 3,5-dimethylcyclohexene.
The number in both the compounds is done in such a way that the double bonded carbons have carbon number 1 and 2 and the substituents have the lowest possible numbers.
Thus, the first compound is named as 1-methylcyclopentene and not 2-methylcyclopentene and the second compound is named as 3,5-dimethylcyclohexene and not 4,6-dimethylcyclohexene.
Note: Remember the rules for naming the cycloalkenes. The important rule to be remembered is that we have to number the carbon atoms in such a way that the double bonded carbon atoms get the numbers 1 and 2. And the first substituent has the lowest possible number.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




