
Why is the nucleus called the brain of the cell?
Answer
496.5k+ views
Hint: A cell is a structural and functional unit of life. And it is the smallest structural (microscopic) unit of living matter and makes up all living things.
Complete answer:
In eukaryotic cells, the nucleus is an organelle. The majority of the cell's genetic material is contained within its totally encased nuclear membrane. Chromosomes are formed from this material, which is structured as DNA molecules and a variety of proteins.
The nucleus of a cell is located in the middle of the cytoplasm, which is the liquid that fills the cell. The nucleus, on the other hand, may not be located at the centre of the cell. The nucleus, which takes up roughly 10% of the cell's volume, is normally found in the cell's centre.
The component of a nucleus contains the cell's DNA which controls the ribosome and protein production.
The nucleus directs and regulates the cell's functions (such as development and metabolism) and houses the genes, which hold the cell's genetic information.
Hence, due to these functions of a nucleus it is called the brain of the cell.
Note:
A cell is made up of three parts that are the cell membrane, the nucleus, and the cytoplasm, which sits between these two parts. The cytoplasm contains elaborate arrangements of fine fibres as well as hundreds, if not thousands, of tiny yet unique structures known as organelles. They support the body's structure, absorb nutrients from meals, transform those nutrients to energy, and perform specialised functions. Cells also contain the body's genetic material and have the ability to replicate them.
Image of a Nucleus is as follows:
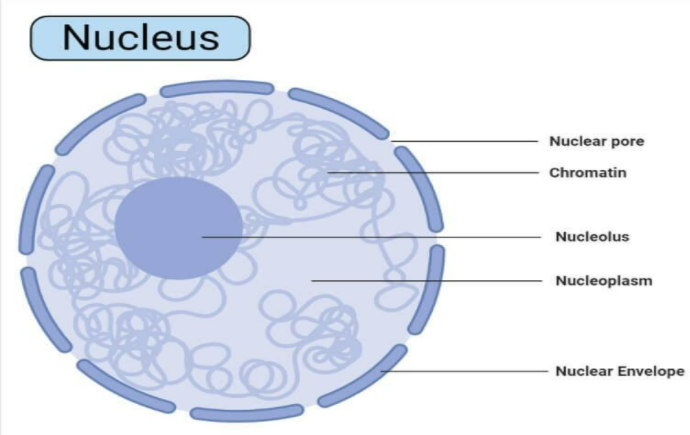
Complete answer:
In eukaryotic cells, the nucleus is an organelle. The majority of the cell's genetic material is contained within its totally encased nuclear membrane. Chromosomes are formed from this material, which is structured as DNA molecules and a variety of proteins.
The nucleus of a cell is located in the middle of the cytoplasm, which is the liquid that fills the cell. The nucleus, on the other hand, may not be located at the centre of the cell. The nucleus, which takes up roughly 10% of the cell's volume, is normally found in the cell's centre.
The component of a nucleus contains the cell's DNA which controls the ribosome and protein production.
The nucleus directs and regulates the cell's functions (such as development and metabolism) and houses the genes, which hold the cell's genetic information.
Hence, due to these functions of a nucleus it is called the brain of the cell.
Note:
A cell is made up of three parts that are the cell membrane, the nucleus, and the cytoplasm, which sits between these two parts. The cytoplasm contains elaborate arrangements of fine fibres as well as hundreds, if not thousands, of tiny yet unique structures known as organelles. They support the body's structure, absorb nutrients from meals, transform those nutrients to energy, and perform specialised functions. Cells also contain the body's genetic material and have the ability to replicate them.
Image of a Nucleus is as follows:

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




