
What is the nucleon number of an atom?
(A) The number of neutrons.
(B) The number of protons.
(C) The total number of protons and neutrons.
(D) The total number of protons and electrons.
Answer
584.7k+ views
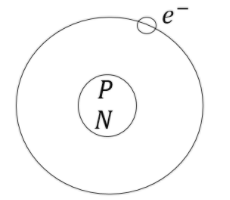
Hint: The fundamental particles of an atom are election, proton and neutron. Protons and neutrons are present in nucleus and electrons are revolving around the nucleus.
Complete answer:
The atom consists of protons, electrons and neutrons. Protons and neutrons are present in nucleus and electrons revolving around nucleus. Electrons have negligible mass compared to protons and neutrons. Therefore, the mass of an atom is due to the mass of protons and neutrons.
Therefore, the total number of protons and neutrons is called the nucleon number.
This is also known as mass number.
We can explain the nucleon number of an element by following an example.
The atomic number (Z) of carbon is 6.
Mass number (A) of carbon is 12.
Atomic number is the number of electrons or protons present in an atom of an element.
Mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons present in an atom of an element.
$\therefore $ Nucleon number of C-atoms is 12.
Similarly, we can calculate the nucleon number of a chlorine atom.
Mass number of chlorine 35.
$\therefore $ Nucleon number of chlorine is 35.
Isotopes are different atoms of the same element having the same atomic number and different mass number.
$\therefore $ We can say that isotopes have different nucleon numbers.
So from the above discussion the correct answer is (C).
Note: The mass of an atom is concentrated at the nucleus because the mass of atom is due to proton and neutron and they are present in the nucleus.
Mass of the electron is negligible; it is revolving around the nucleus.
An atom is neutral as a whole therefore number protons (positive charge) and number of electrons (negative charge) are the same.

Complete answer:
The atom consists of protons, electrons and neutrons. Protons and neutrons are present in nucleus and electrons revolving around nucleus. Electrons have negligible mass compared to protons and neutrons. Therefore, the mass of an atom is due to the mass of protons and neutrons.
Therefore, the total number of protons and neutrons is called the nucleon number.
This is also known as mass number.
We can explain the nucleon number of an element by following an example.
The atomic number (Z) of carbon is 6.
Mass number (A) of carbon is 12.
Atomic number is the number of electrons or protons present in an atom of an element.
Mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons present in an atom of an element.
$\therefore $ Nucleon number of C-atoms is 12.
Similarly, we can calculate the nucleon number of a chlorine atom.
Mass number of chlorine 35.
$\therefore $ Nucleon number of chlorine is 35.
Isotopes are different atoms of the same element having the same atomic number and different mass number.
$\therefore $ We can say that isotopes have different nucleon numbers.
So from the above discussion the correct answer is (C).
Note: The mass of an atom is concentrated at the nucleus because the mass of atom is due to proton and neutron and they are present in the nucleus.
Mass of the electron is negligible; it is revolving around the nucleus.
An atom is neutral as a whole therefore number protons (positive charge) and number of electrons (negative charge) are the same.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




