
Normal at P(2,4) to $ {{y}^{2}}=8x $ meets the parabola at Q. Then the equation of circle on normal chord PQ as diameter is
\[\begin{align}
& A.{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-20x+8y-12=0 \\
& B.{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-10x+4y-8=0 \\
& C.{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-12x+6y-15=0 \\
& D.{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-10x+8y-12=0 \\
\end{align}\]
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: For solving this question, we will first draw a rough diagram and then we will find coordinates of Q using the given information. PQ will act as a diameter to the circle, so we will use the equation of a circle when endpoints of diameter is given to find the required equation. We will use the following formulas,
(I) Slope of a normal to any equation y = f(x) is given by $ m=\dfrac{-1}{\dfrac{dy}{dx}}=\dfrac{-dy}{dx} $ .
(II) Quadratic formula for any equation $ a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c $ is given by $ x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a} $ .
(III) Equation of circle, if diameter of the circle has end points $ \left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\text{ and }\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right) $ is given by,
$ \left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)\left( x-{{x}_{2}} \right)+\left( y-{{y}_{1}} \right)\left( y-{{y}_{2}} \right)=0 $ .
(IV) Equation of line with one point $ \left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right) $ and slope m is equal to $ \left( y-{{y}_{1}} \right)=m\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right) $ .
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first draw a rough diagram according to our question given,
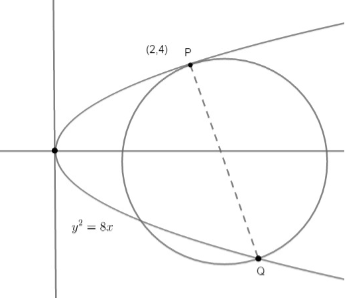
Here the equation of a parabola is $ {{y}^{2}}=8x $ .
Normal at P(2,4) meets the parabola again at Q. We need to find the equation of a circle, such that PQ is the diameter. For this, we need to find the coordinates of Q. Let us first find the slope of the normal. We know that, slope of the normal on y = f(x) is given by $ m=\dfrac{-1}{\dfrac{dy}{dx}}=\dfrac{-dy}{dx} $ so, differentiating $ {{y}^{2}}=8x $ with respect to x, we get, $ 2y\dfrac{dy}{dx}=8 $ .
Rearranging $ \dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{8}{2y} $ at point P(2,4) $ \dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{8}{2\left( 4 \right)}=\dfrac{8}{8}=1 $ .
So slope of the normal becomes, $ m=\dfrac{-1}{\dfrac{dy}{dx}}=\dfrac{-1}{1}=-1 $ .
Now let us find the equation of normal.
We know, equation of line having a point $ \left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right) $ and slope m is given by $ \left( y-{{y}_{1}} \right)=m\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right) $ .
So here our point is P(2,4) and slope m is -1.
Therefore, equation of normal is
\[\begin{align}
& \left( y-4 \right)=-1\left( x-2 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y-4=-x+2 \\
& \Rightarrow y+x=2+4 \\
& \Rightarrow x+y-6=0\cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 2 \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Now equation of parabola and equation of normal meets each other at two points P and Q. So let us find the coordinates of PQ using this, from equation (2) x = 6-y.
Putting it in equation (1) we get,
$ \begin{align}
& {{y}^{2}}=8\left( 6-y \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}=48-8y \\
\end{align} $
Rearranging we get,
\[{{y}^{2}}+8y-48=0\].
Which is a quadratic equation.
Lets solve it using quadratic formula which is given by $ x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a} $ for equation $ a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c $
So,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-8\pm \sqrt{{{\left( 8 \right)}^{2}}-4\left( 1 \right)\left( 48 \right)}}{2\left( 1 \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-8\pm \sqrt{64+192}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-8\pm \sqrt{256}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-8\pm 16}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-8-16}{2}\text{ and }y=\dfrac{-8+16}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-24}{2}\text{ and }y=\dfrac{8}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow y=-12\text{ and }y=4 \\
\end{align}\]
For y = 4, we will get the point P which we already know. So let us find point Q using y = -12. Putting y = -12 in equation (2) we get,
\[\begin{align}
& x+\left( -12 \right)-6=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=6+12 \\
& \Rightarrow x=18 \\
\end{align}\]
Hence point Q is (18,-12).
Now we need to find the equation of circle having diameter PQ where P has coordinate (2,4) and Q has coordinates (18,-12).
We know that equation of circles having end points of diameter as $ \left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\text{ and }\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right) $ is given as,
$ \left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)\left( x-{{x}_{2}} \right)+\left( y-{{y}_{1}} \right)\left( y-{{y}_{2}} \right)=0 $ .
Putting $ \left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right) $ as (2,4) and $ \left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right) $ as (18,-12), we get,
Equation of circle is $ \begin{align}
& \left( x-2 \right)\left( x-18 \right)+\left( y-4 \right)\left( y-\left( -12 \right) \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \left( x-2 \right)\left( x-18 \right)+\left( y-4 \right)\left( y+12 \right)=0 \\
\end{align} $ .
Opening the brackets and simplifying we get,
$ \begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}-2x-18x+36+{{y}^{2}}-4y+12y-48=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-20x+{{y}^{2}}+8y-12=0 \\
\end{align} $
Rearranging the terms we get,
$ {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-20x+8y-12=0 $ .
Which is our required equation of the circle.
Hence option A is the correct answer.
Note:
Students should take care of the signs while solving the equation. We can find the intersection of two curves by just solving them which we have done for line and parabola to find P and Q. Keep in mind all the general equations. Try to draw diagrams for better understanding.
(I) Slope of a normal to any equation y = f(x) is given by $ m=\dfrac{-1}{\dfrac{dy}{dx}}=\dfrac{-dy}{dx} $ .
(II) Quadratic formula for any equation $ a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c $ is given by $ x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a} $ .
(III) Equation of circle, if diameter of the circle has end points $ \left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\text{ and }\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right) $ is given by,
$ \left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)\left( x-{{x}_{2}} \right)+\left( y-{{y}_{1}} \right)\left( y-{{y}_{2}} \right)=0 $ .
(IV) Equation of line with one point $ \left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right) $ and slope m is equal to $ \left( y-{{y}_{1}} \right)=m\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right) $ .
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first draw a rough diagram according to our question given,

Here the equation of a parabola is $ {{y}^{2}}=8x $ .
Normal at P(2,4) meets the parabola again at Q. We need to find the equation of a circle, such that PQ is the diameter. For this, we need to find the coordinates of Q. Let us first find the slope of the normal. We know that, slope of the normal on y = f(x) is given by $ m=\dfrac{-1}{\dfrac{dy}{dx}}=\dfrac{-dy}{dx} $ so, differentiating $ {{y}^{2}}=8x $ with respect to x, we get, $ 2y\dfrac{dy}{dx}=8 $ .
Rearranging $ \dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{8}{2y} $ at point P(2,4) $ \dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{8}{2\left( 4 \right)}=\dfrac{8}{8}=1 $ .
So slope of the normal becomes, $ m=\dfrac{-1}{\dfrac{dy}{dx}}=\dfrac{-1}{1}=-1 $ .
Now let us find the equation of normal.
We know, equation of line having a point $ \left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right) $ and slope m is given by $ \left( y-{{y}_{1}} \right)=m\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right) $ .
So here our point is P(2,4) and slope m is -1.
Therefore, equation of normal is
\[\begin{align}
& \left( y-4 \right)=-1\left( x-2 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y-4=-x+2 \\
& \Rightarrow y+x=2+4 \\
& \Rightarrow x+y-6=0\cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 2 \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Now equation of parabola and equation of normal meets each other at two points P and Q. So let us find the coordinates of PQ using this, from equation (2) x = 6-y.
Putting it in equation (1) we get,
$ \begin{align}
& {{y}^{2}}=8\left( 6-y \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}=48-8y \\
\end{align} $
Rearranging we get,
\[{{y}^{2}}+8y-48=0\].
Which is a quadratic equation.
Lets solve it using quadratic formula which is given by $ x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a} $ for equation $ a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c $
So,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-8\pm \sqrt{{{\left( 8 \right)}^{2}}-4\left( 1 \right)\left( 48 \right)}}{2\left( 1 \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-8\pm \sqrt{64+192}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-8\pm \sqrt{256}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-8\pm 16}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-8-16}{2}\text{ and }y=\dfrac{-8+16}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-24}{2}\text{ and }y=\dfrac{8}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow y=-12\text{ and }y=4 \\
\end{align}\]
For y = 4, we will get the point P which we already know. So let us find point Q using y = -12. Putting y = -12 in equation (2) we get,
\[\begin{align}
& x+\left( -12 \right)-6=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=6+12 \\
& \Rightarrow x=18 \\
\end{align}\]
Hence point Q is (18,-12).
Now we need to find the equation of circle having diameter PQ where P has coordinate (2,4) and Q has coordinates (18,-12).
We know that equation of circles having end points of diameter as $ \left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\text{ and }\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right) $ is given as,
$ \left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)\left( x-{{x}_{2}} \right)+\left( y-{{y}_{1}} \right)\left( y-{{y}_{2}} \right)=0 $ .
Putting $ \left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right) $ as (2,4) and $ \left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right) $ as (18,-12), we get,
Equation of circle is $ \begin{align}
& \left( x-2 \right)\left( x-18 \right)+\left( y-4 \right)\left( y-\left( -12 \right) \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \left( x-2 \right)\left( x-18 \right)+\left( y-4 \right)\left( y+12 \right)=0 \\
\end{align} $ .
Opening the brackets and simplifying we get,
$ \begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}-2x-18x+36+{{y}^{2}}-4y+12y-48=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-20x+{{y}^{2}}+8y-12=0 \\
\end{align} $
Rearranging the terms we get,
$ {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-20x+8y-12=0 $ .
Which is our required equation of the circle.
Hence option A is the correct answer.
Note:
Students should take care of the signs while solving the equation. We can find the intersection of two curves by just solving them which we have done for line and parabola to find P and Q. Keep in mind all the general equations. Try to draw diagrams for better understanding.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




