
Nitration of phenol is an example of:
(a)- Nucleophilic addition
(b)- Nucleophilic substitution
(c)- Electrophilic substitution
(d)- Electrophilic addition
Answer
537.5k+ views
Hint: When nitric acid reacts with phenol either nitrophenol or picric acid is formed based on the reactants taken. Nitro molecule ($N{{O}_{2}}$) is an electrophile. The nitro group is attached to the phenol by removing the hydrogen atom.
Complete step by step answer:
Phenols undergo an Electrophilic substitution reaction. An example of an Electrophilic substitution reaction is the nitration of phenol.
There are 2 processes of nitration of phenol:
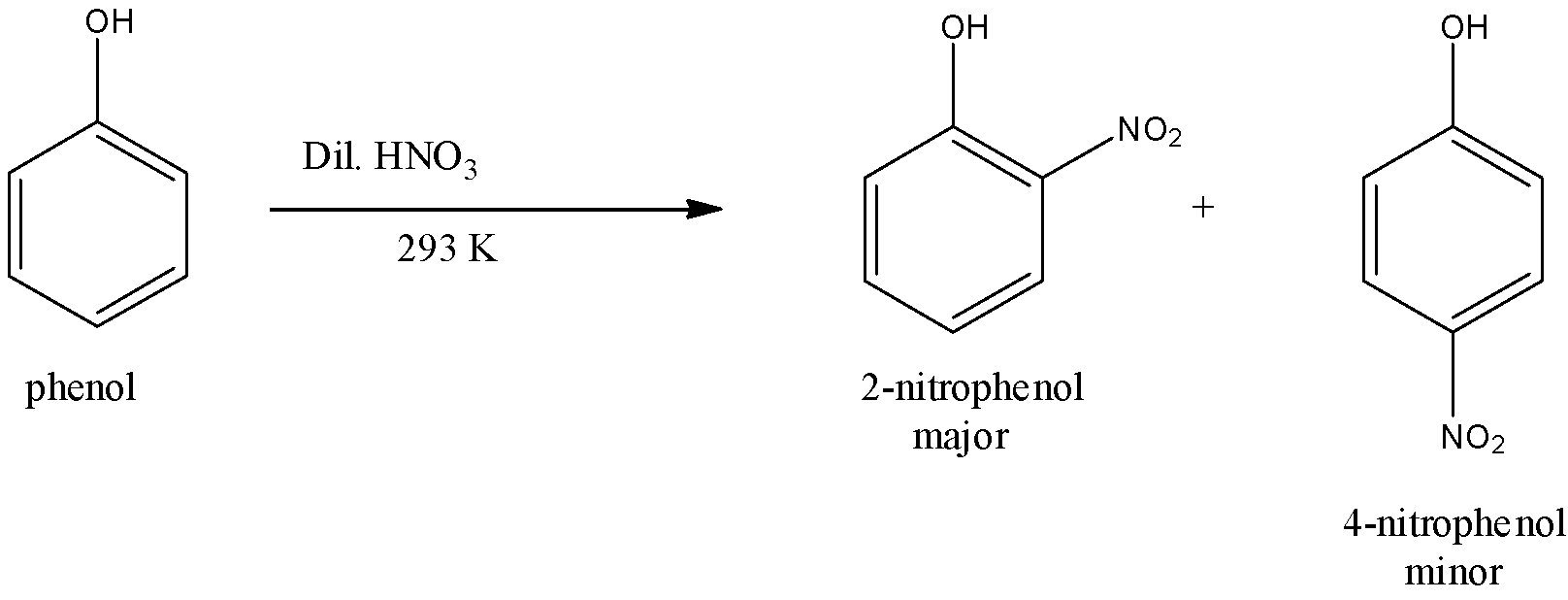
(i)- With dilute nitric acid: When dilute nitric acid at 293 K is used, phenols give mononitrophenols i.e., a mixture of 2-nitrophenol and 4-nitrophenol. Nitro molecule ($N{{O}_{2}}$) is an electrophile. The nitro group is attached to the phenol by removing the hydrogen atom. However, 2-nitrophenol predominates over 4-nitrophenol probably due to the stabilization of the transition state leading to the formation of 2-nitrophenol due to the intramolecular H-bonding. The reaction is given below:
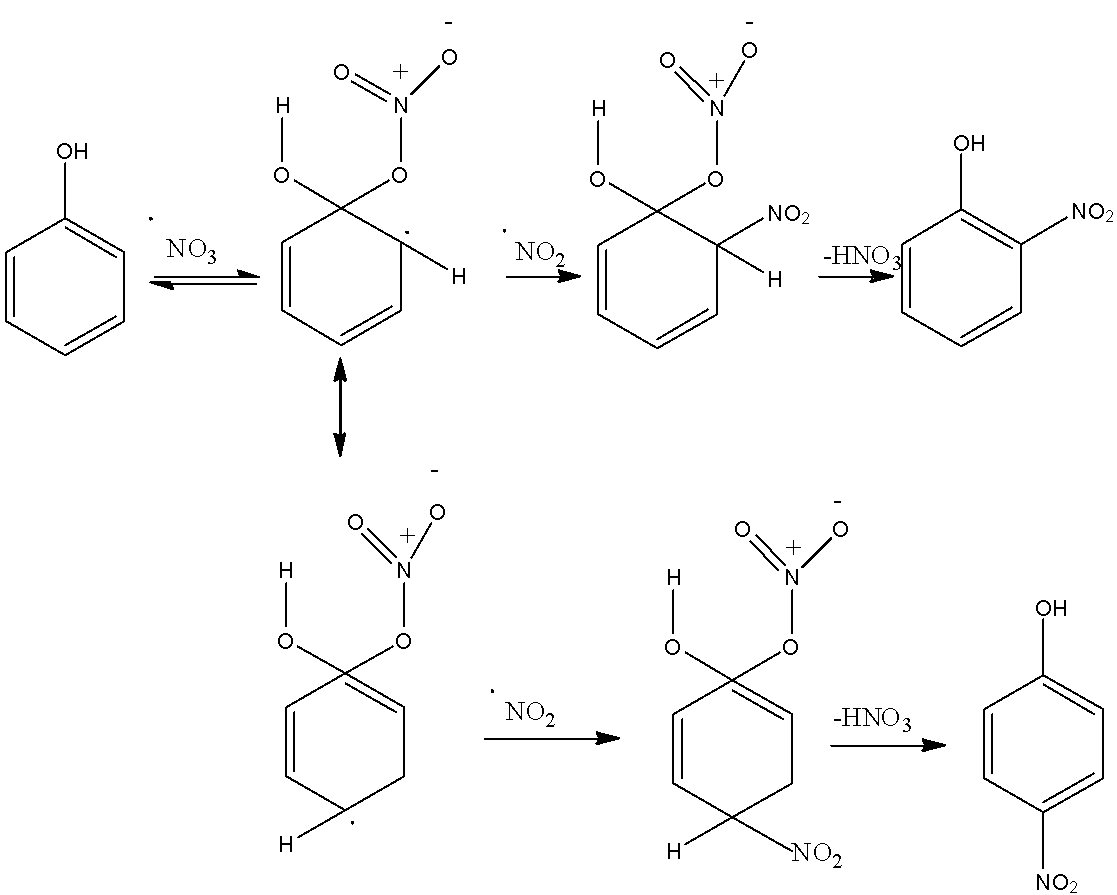
The mechanism of nitration is given below:
The intramolecular hydrogen bonding of 2-nitrophenol is given below:
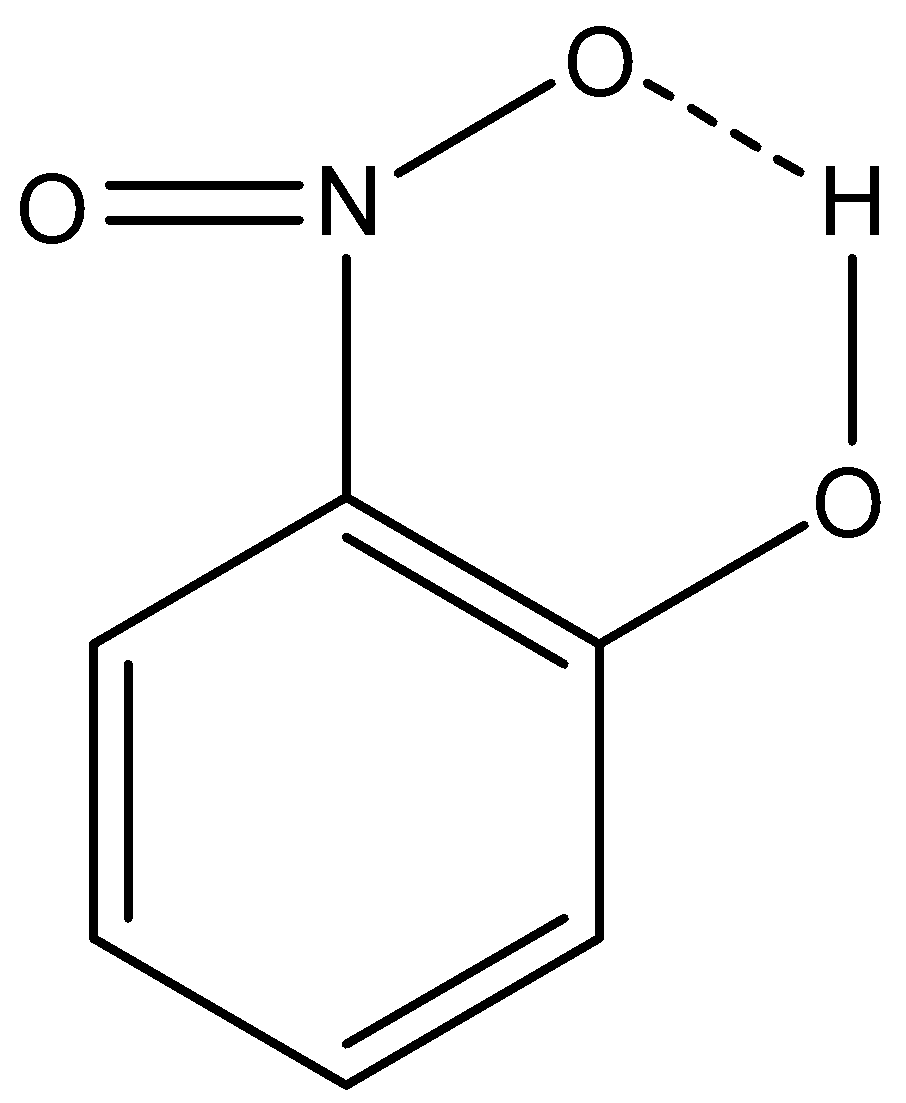
This intramolecular hydrogen bonding is not possible in 4-nitrophenol.
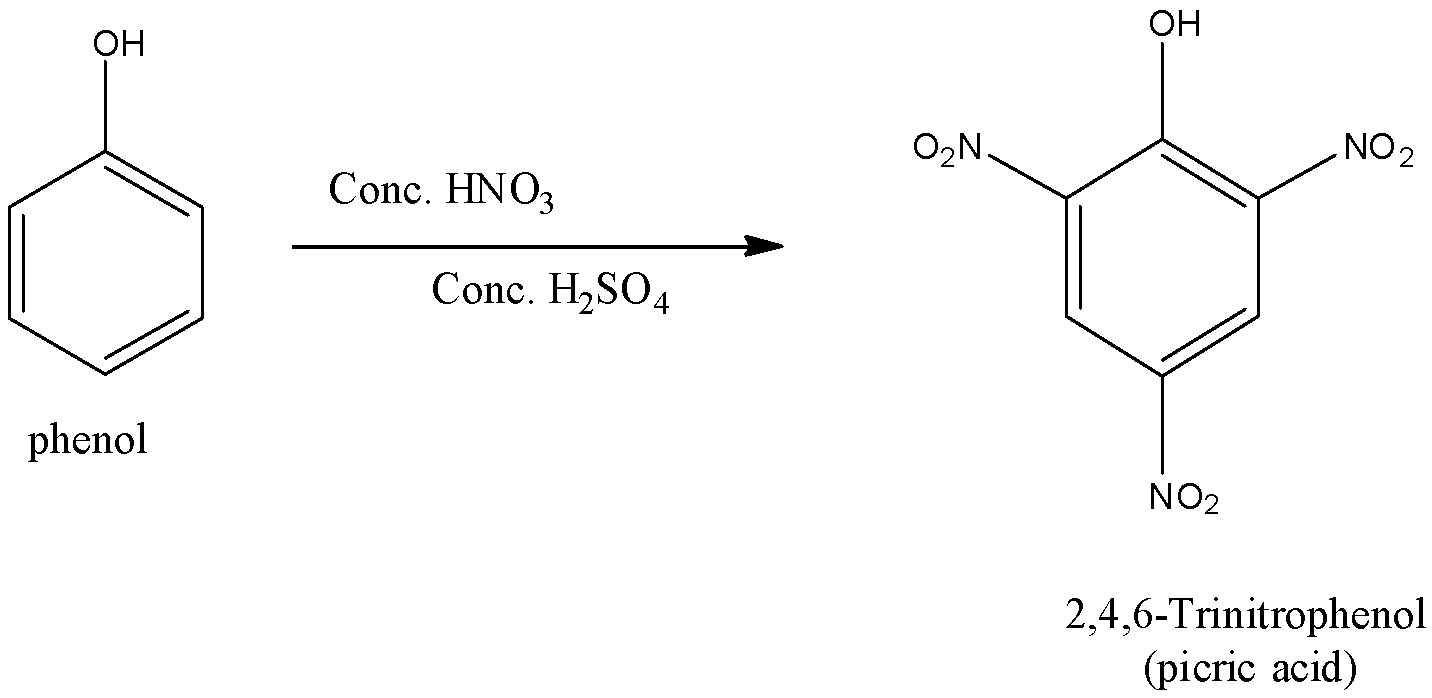
(ii)- With concentrated nitric acid: When the phenol is reacted with concentrated nitric acid in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid gives a trisubstituted phenol called 2,4,6-Trinitrphenol or it is commonly called picric acid. The yield is poor since most of the phenol is oxidized by concentrated nitric acid. The reaction is given below:
So, the correct answer is an option (c)- Electrophilic substitution.
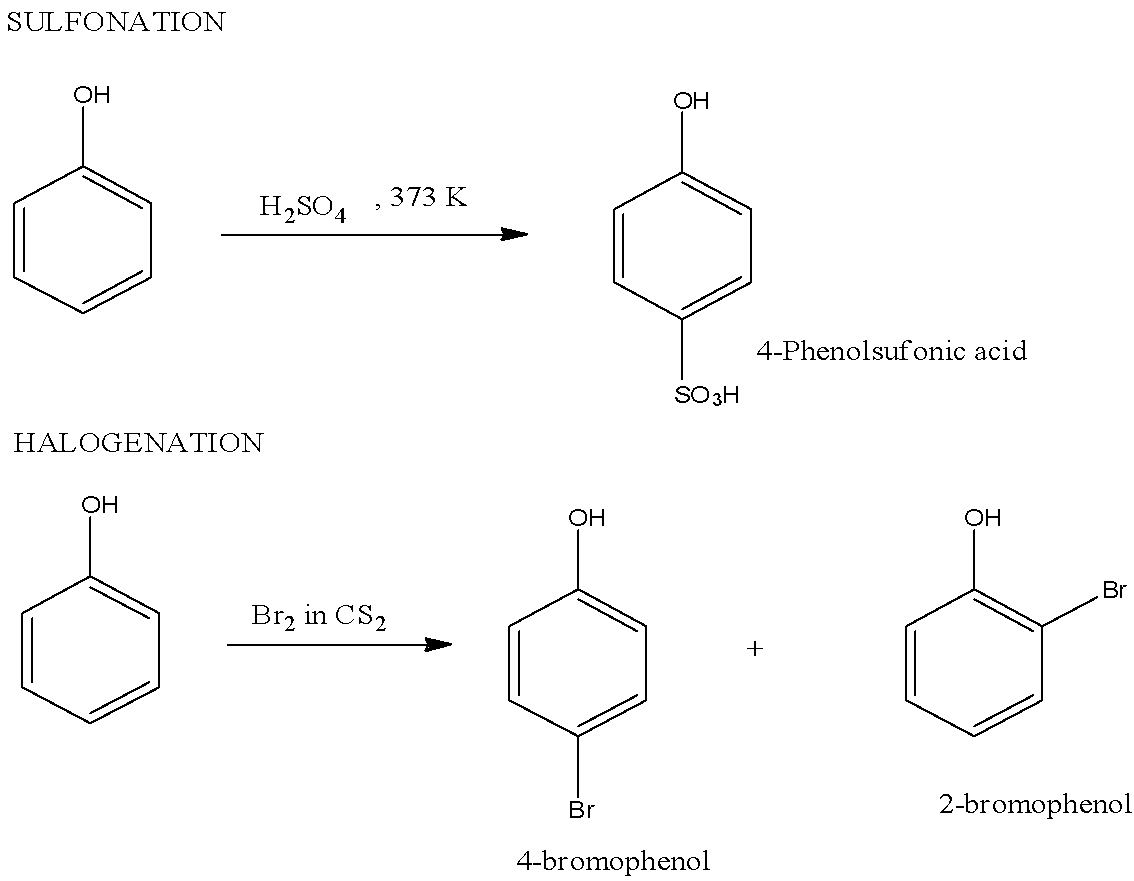
Note: Other examples of Electrophilic substitution reactions of phenol are halogenations in which halophenols are formed, sulfonation in which 4-Phenolsulfonic acid is formed, etc. The reaction of halogenations and sulfonation is given below:
Complete step by step answer:
Phenols undergo an Electrophilic substitution reaction. An example of an Electrophilic substitution reaction is the nitration of phenol.
There are 2 processes of nitration of phenol:
(i)- With dilute nitric acid: When dilute nitric acid at 293 K is used, phenols give mononitrophenols i.e., a mixture of 2-nitrophenol and 4-nitrophenol. Nitro molecule ($N{{O}_{2}}$) is an electrophile. The nitro group is attached to the phenol by removing the hydrogen atom. However, 2-nitrophenol predominates over 4-nitrophenol probably due to the stabilization of the transition state leading to the formation of 2-nitrophenol due to the intramolecular H-bonding. The reaction is given below:

The mechanism of nitration is given below:

The intramolecular hydrogen bonding of 2-nitrophenol is given below:

This intramolecular hydrogen bonding is not possible in 4-nitrophenol.
(ii)- With concentrated nitric acid: When the phenol is reacted with concentrated nitric acid in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid gives a trisubstituted phenol called 2,4,6-Trinitrphenol or it is commonly called picric acid. The yield is poor since most of the phenol is oxidized by concentrated nitric acid. The reaction is given below:

So, the correct answer is an option (c)- Electrophilic substitution.
Note: Other examples of Electrophilic substitution reactions of phenol are halogenations in which halophenols are formed, sulfonation in which 4-Phenolsulfonic acid is formed, etc. The reaction of halogenations and sulfonation is given below:

Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




