
Net yield of aerobic respiration during Krebs cycle per glucose molecule is
(a) 2 ATP molecules
(b) 8 ATP molecules
(c) 36 ATP molecules
(d) 38 ATP molecules
Answer
540.9k+ views
Hint: The other name of Krebs cycle is called the citric acid cycle. This cycle is used for the formation of energy by the process of aerobic respiration. In this process the oxidation of carbohydrates called acetyl, Co-A occurs.
Complete answer:
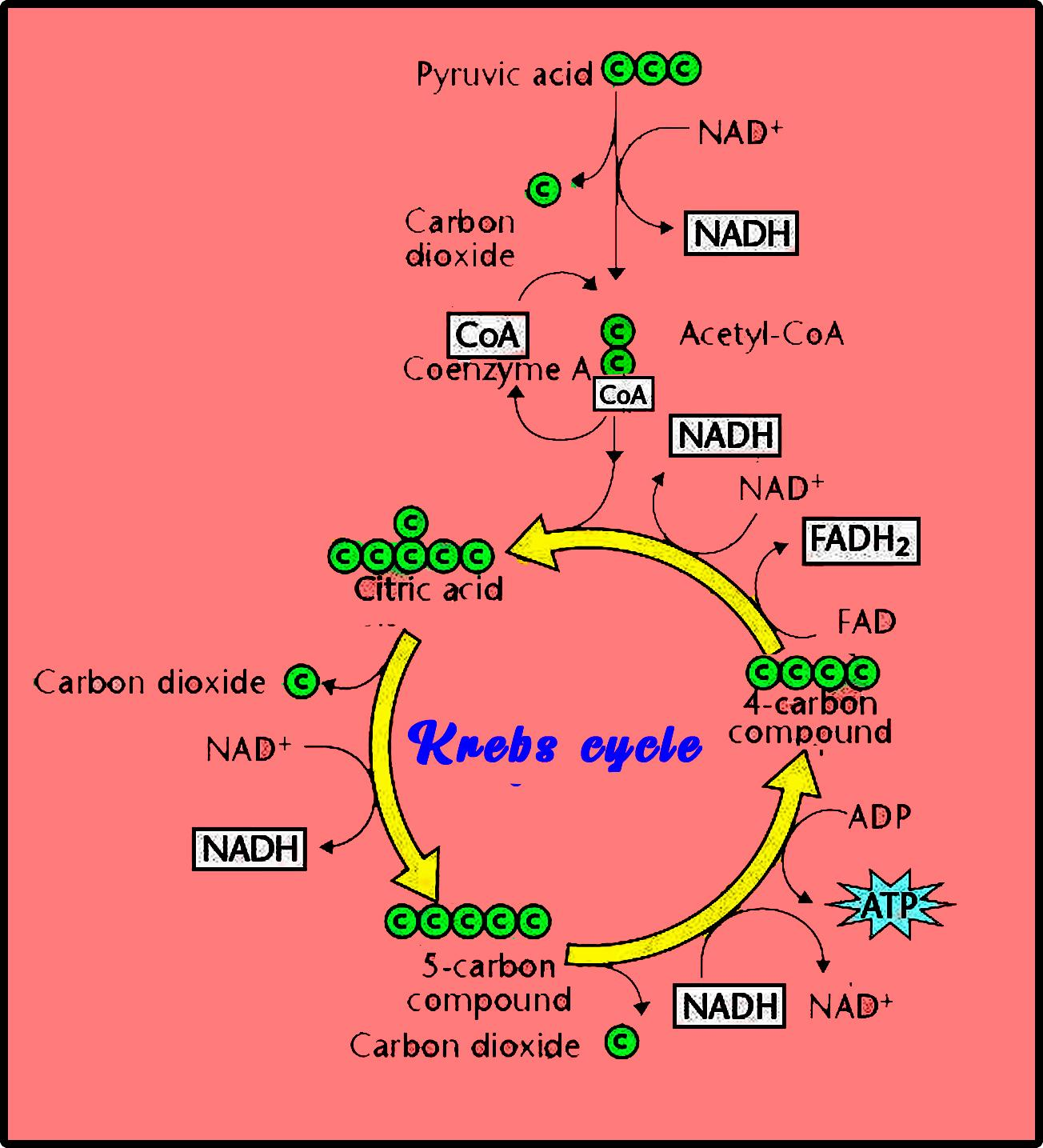
The Krebs cycle takes place in the cell's mitochondria, helps to generate energy, and takes place immediately after glycolysis. The beginning of the cycle occurs when due to acetyl coenzyme A the pyruvic acid is formed, which then forms citric acid when combined along with oxalo acetic acid. During one cycle one ATP is produced and thus for 1 molecules of glucose 2 Krebs cycles are required. Therefore, 2 ATP molecules are produced.
-It is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl Co-A derived from carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
-There are eight enzymes that are required for the reaction of the TCA cycle which oxidizes the acetate molecule to form two acetyls Co-A.
-The pyruvate molecule that is formed in the glycolysis by the reduction of glucose is broken into acetyl-CoA which then enters into the Krebs cycle to form citrate when combined with oxaloacetate.
-There are 15 ATO molecules formed by one pyruvate molecule while 30 ATP molecules are formed by two pyruvate molecules.
-The Krebs cycle takes place in the mitochondria most due to its historic past as it is believed that the mitochondria have an origin of an independent, energy-producing organism, which was taken as a means for the energy exchange.
-In the case of prokaryotic cells, the TCA cycle occurs in the cytosol unlike eukaryotic cells that occur in the inner mitochondrial membrane because in prokaryotic cells mitochondria remains absent.
So, the correct answer is ‘2 ATP molecules’.
Note:
The citric acid cycle is also referred to as the TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle). It is a series of reactions used by all aerobic species to generate accumulated energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA obtained from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. In addition, the cycle produces precursors of some amino acids, as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in various other reactions.
Complete answer:
The Krebs cycle takes place in the cell's mitochondria, helps to generate energy, and takes place immediately after glycolysis. The beginning of the cycle occurs when due to acetyl coenzyme A the pyruvic acid is formed, which then forms citric acid when combined along with oxalo acetic acid. During one cycle one ATP is produced and thus for 1 molecules of glucose 2 Krebs cycles are required. Therefore, 2 ATP molecules are produced.
-It is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl Co-A derived from carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
-There are eight enzymes that are required for the reaction of the TCA cycle which oxidizes the acetate molecule to form two acetyls Co-A.
-The pyruvate molecule that is formed in the glycolysis by the reduction of glucose is broken into acetyl-CoA which then enters into the Krebs cycle to form citrate when combined with oxaloacetate.
-There are 15 ATO molecules formed by one pyruvate molecule while 30 ATP molecules are formed by two pyruvate molecules.
-The Krebs cycle takes place in the mitochondria most due to its historic past as it is believed that the mitochondria have an origin of an independent, energy-producing organism, which was taken as a means for the energy exchange.
-In the case of prokaryotic cells, the TCA cycle occurs in the cytosol unlike eukaryotic cells that occur in the inner mitochondrial membrane because in prokaryotic cells mitochondria remains absent.
So, the correct answer is ‘2 ATP molecules’.

Note:
The citric acid cycle is also referred to as the TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle). It is a series of reactions used by all aerobic species to generate accumulated energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA obtained from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. In addition, the cycle produces precursors of some amino acids, as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in various other reactions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




