
n-butane and isobutane are a pair of
A.Chain isomers
B.Position isomers
C.Metamers
D.Functional isomers
Answer
574.2k+ views
Hint: Constitutional or structural isomers are those isomers which differ from each other due to the arrangement of atoms within the molecule. The various structural isomers are chain isomers, position isomers, ring chain isomers, functional isomers, metamers and tautomers.
Complete step by step solution:
Chain isomerism – This type of isomerism occurs due to the difference in nature of the carbon chain (based on whether it is straight or branched) which gives a basic structure to the compound.
Examples: n-pentane, isopentane, neopentane.
Position isomerism – This type of isomerism is exhibited by compounds in which there is a difference in the position of the substituted group or an unsaturated linkage in the same carbon chain.
Examples: $2,2 - {\text{dichloropropane, 1,1 - dichloropropane}}$.
Metamerism – Metamers are isomers which differ from each other due to the difference in nature of the alkyl group attached to the polyvalent atoms or functional group. They belong to the same homologous series. Some compounds which exhibit metamerism are ethers, ketones, thio-ethers, secondary amines etc.
Examples: ${\text{pentan - 2 - one, pentan - 3 - one}}$.
Functional isomerism – This type of isomerism occurs due to the difference in nature of functional groups present in the isomers. Some compounds which exhibit functional isomerism are alcohols and ethers, aldehydes and ketones etc.
Examples: Ethyl alcohol, dimethyl ether.
The structures of n-butane and isobutane are:
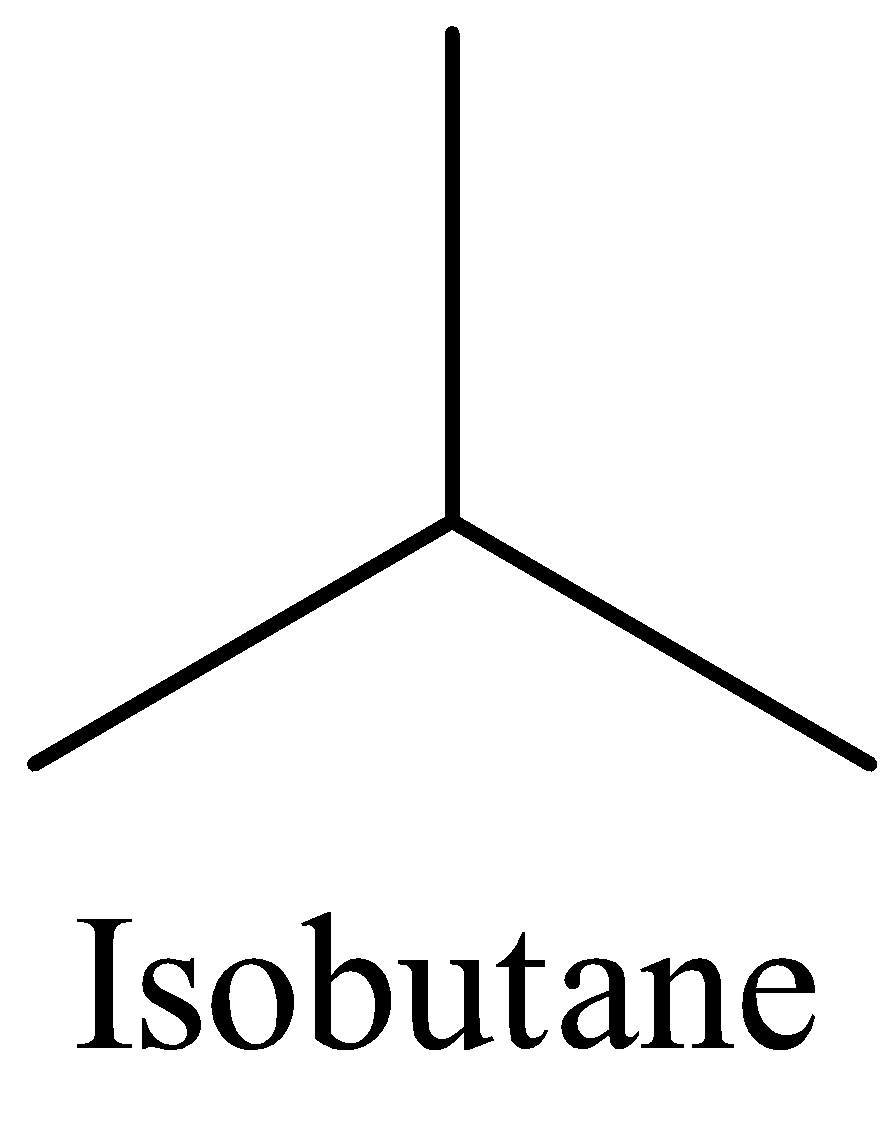
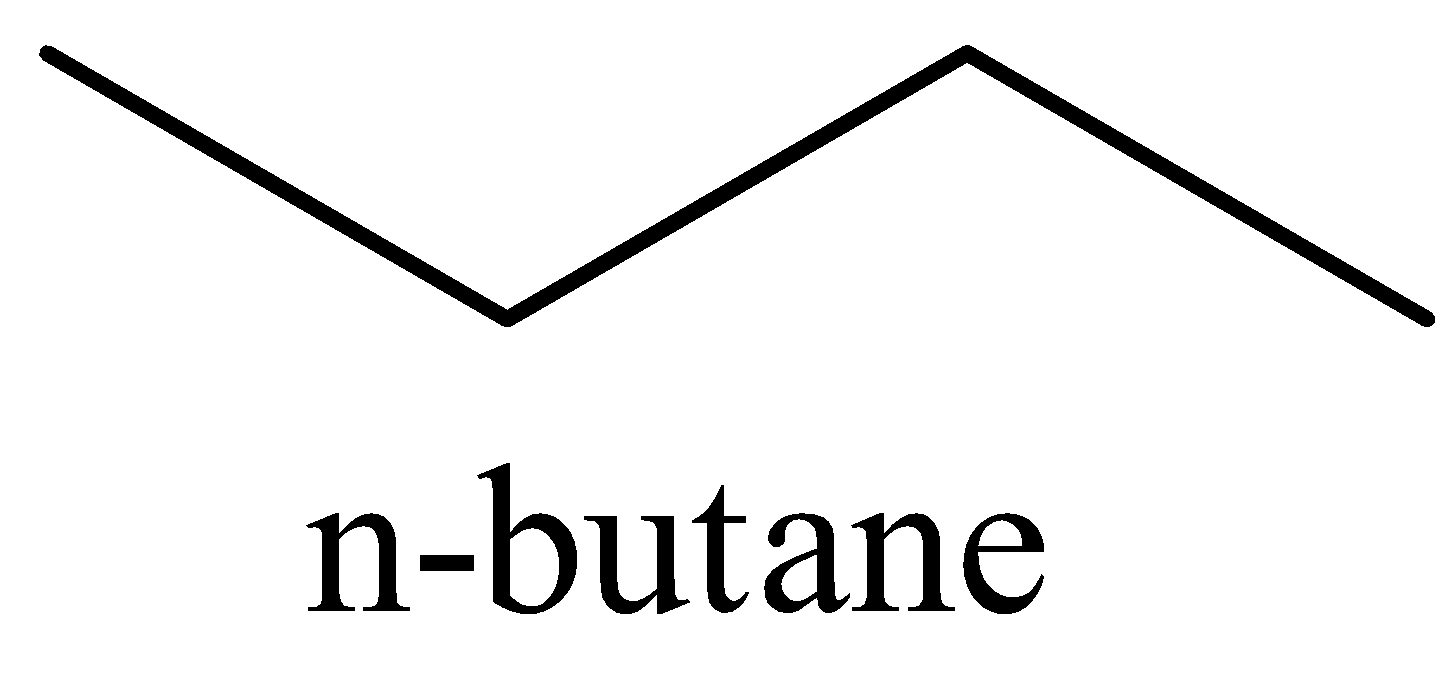
From the structures, it is clear that n-butane and isobutane differ in the skeletal carbon chain. So, they are chain isomers.
Hence, option (A) is the correct answer.
Note:
Isomers are organic compounds having the same molecular formula but different structures or at least some different physical or chemical properties. The difference in properties is mainly due to the difference in relative arrangements of various atoms or groups present in the molecules.
Complete step by step solution:
Chain isomerism – This type of isomerism occurs due to the difference in nature of the carbon chain (based on whether it is straight or branched) which gives a basic structure to the compound.
Examples: n-pentane, isopentane, neopentane.
Position isomerism – This type of isomerism is exhibited by compounds in which there is a difference in the position of the substituted group or an unsaturated linkage in the same carbon chain.
Examples: $2,2 - {\text{dichloropropane, 1,1 - dichloropropane}}$.
Metamerism – Metamers are isomers which differ from each other due to the difference in nature of the alkyl group attached to the polyvalent atoms or functional group. They belong to the same homologous series. Some compounds which exhibit metamerism are ethers, ketones, thio-ethers, secondary amines etc.
Examples: ${\text{pentan - 2 - one, pentan - 3 - one}}$.
Functional isomerism – This type of isomerism occurs due to the difference in nature of functional groups present in the isomers. Some compounds which exhibit functional isomerism are alcohols and ethers, aldehydes and ketones etc.
Examples: Ethyl alcohol, dimethyl ether.
The structures of n-butane and isobutane are:


From the structures, it is clear that n-butane and isobutane differ in the skeletal carbon chain. So, they are chain isomers.
Hence, option (A) is the correct answer.
Note:
Isomers are organic compounds having the same molecular formula but different structures or at least some different physical or chemical properties. The difference in properties is mainly due to the difference in relative arrangements of various atoms or groups present in the molecules.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




