
Name three classes of levers and distinguish between them. Give examples of each class of lever.
Answer
591k+ views
Hint: A rigid section resting on a pivot, which is used to lift a heavy firmly fixed body with one end when pressure is applied to another end of the pivot is known as a lever. By lifting the body the potential energy is also increased. Potential energy is amplified as it is dependent on the height at which the object is placed from the reference line.
Complete answer:
There are three types of lever. The difference between these classes depends on where the force is applied and where the fulcrum is and the position of the applied load. There are three classes of levers which are termed as
Class I levers
Class II levers
Class III levers
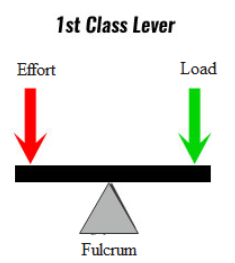
A. Class I levers: In these types of levers, the fulcrum F is in between the input force (effort) and the output force (load).
Example: A Seesaw, a pair of scissors, crowbar.
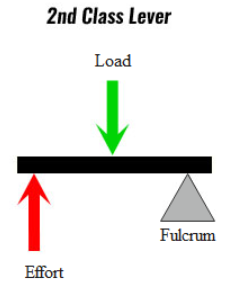
B. Class II levers: In these types of levers, the load L is in between the input and the fulcrum F. The input (effort) arm is thus always longer than the load arm.
Example: a nutcracker, a bottle opener.
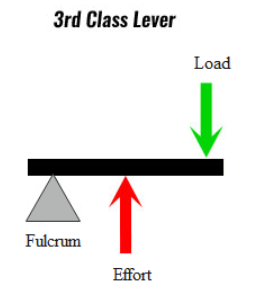
C. Class III levers: In these types of levers, the input (effort) is in between the fulcrum F and the load L and the effort arm is always smaller than the load arm.
Example: Sugar tongs, Forearm that is used for lifting a load.
Note:
The lever works on the principle according to which equilibrium can be established when the sum of the moments of the forces acting in a clockwise direction is made the same as the sum of the moments of the forces acting in a counterclockwise direction. This can be easily done, to overcome a large force at a short distance from the fulcrum by applying a small force at a great distance from the fulcrum.
Complete answer:
There are three types of lever. The difference between these classes depends on where the force is applied and where the fulcrum is and the position of the applied load. There are three classes of levers which are termed as
Class I levers
Class II levers
Class III levers
A. Class I levers: In these types of levers, the fulcrum F is in between the input force (effort) and the output force (load).
Example: A Seesaw, a pair of scissors, crowbar.

B. Class II levers: In these types of levers, the load L is in between the input and the fulcrum F. The input (effort) arm is thus always longer than the load arm.
Example: a nutcracker, a bottle opener.

C. Class III levers: In these types of levers, the input (effort) is in between the fulcrum F and the load L and the effort arm is always smaller than the load arm.
Example: Sugar tongs, Forearm that is used for lifting a load.

Note:
The lever works on the principle according to which equilibrium can be established when the sum of the moments of the forces acting in a clockwise direction is made the same as the sum of the moments of the forces acting in a counterclockwise direction. This can be easily done, to overcome a large force at a short distance from the fulcrum by applying a small force at a great distance from the fulcrum.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




