
Name the type of triangle PQR formed by the points \[P(-\sqrt{2},\sqrt{2})\], \[Q(-\sqrt{2},-\sqrt{2})\] and \[R(-\sqrt{6},\sqrt{6})\].
Answer
609.3k+ views
Hint: Find the distance between the PQ, QR and RP using the distance formula. Then check, if all the distances are same then it is equilateral triangle, or if two distances are same then it is isosceles triangle else scalene triangle. The distance formula, \[d=\sqrt{{{({{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}})}^{2}}+{{({{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}})}^{2}}}\]. Here \[({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})\]and \[({{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}})\] are two points between which the distance (d) is to be found.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the question, we have to find the type of triangle PQR formed by the points \[P(-\sqrt{2},\sqrt{2})\], \[Q(-\sqrt{2},-\sqrt{2})\] and \[R(-\sqrt{6},\sqrt{6})\].
So, we will use the distance formula here and will find the length of each line that joins points PQ, QR and PR.
Now, the distance formula between the two points is given as follows.
Now, distance (d) between points \[({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})\] and \[({{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}})\]
is found using the formula: \[d=\sqrt{{{({{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}})}^{2}}+{{({{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}})}^{2}}}\]
So now, the distance between \[P(-\sqrt{2},\sqrt{2})\] and \[Q(-\sqrt{2},-\sqrt{2})\] is given by:
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow PQ=\sqrt{{{\left( -\sqrt{2}-(-\sqrt{2}) \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -\sqrt{2}-(\sqrt{2}) \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \because {{x}_{2}}=-\sqrt{2}\,,\,\,{{x}_{1}}=-\sqrt{2},\,\,{{y}_{2}}=-\sqrt{2}\,,\,\,{{y}_{1}}=\sqrt{2} \\
& \Rightarrow PQ=\sqrt{{{0}^{2}}+{{\left( -2\sqrt{2} \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow PQ=2\sqrt{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Next, the distance between \[Q(-\sqrt{2},-\sqrt{2})\] and \[R(-\sqrt{6},\sqrt{6})\], is given by:
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow QR=\sqrt{{{\left( -\sqrt{6}-(-\sqrt{2}) \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \sqrt{6}-(-\sqrt{2}) \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \because {{x}_{2}}=-\sqrt{6}\,,\,\,{{x}_{1}}=-\sqrt{2},\,\,{{y}_{2}}=\sqrt{6}\,,\,\,{{y}_{1}}=-\sqrt{2} \\
& \Rightarrow QR=\sqrt{{{\left( -\sqrt{6}+\sqrt{2} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \sqrt{6}+\sqrt{2}) \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow QR=\sqrt{\left( 6+2-2\sqrt{12} \right)+\left( 6+2+2\sqrt{12} \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow QR=4 \\
\end{align}\]
Next, we will find the distance between \[R(-\sqrt{6},\sqrt{6})\] and \[P(-\sqrt{2},\sqrt{2})\], which is given by:
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow RP=\sqrt{{{\left( -\sqrt{2}-(-\sqrt{6}) \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \sqrt{2}-(\sqrt{6}) \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \because {{x}_{2}}=-\sqrt{2}\,,\,\,{{x}_{1}}=-\sqrt{6},\,\,{{y}_{2}}=\sqrt{2}\,,\,\,{{y}_{1}}=\sqrt{6} \\
& \Rightarrow RP=\sqrt{{{\left( -\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{6} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \sqrt{2}-\sqrt{6} \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow QR=\sqrt{\left( 2+6-2\sqrt{12} \right)+\left( 2+6-2\sqrt{12} \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow QR=\left( 8-2\sqrt{12} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
So, here we can see that all three distances points PQ, QR and PR are unequal. Hence, this is a scalene triangle with no two sides lengths equal.
Note: The alternative method to solve this problem is graphically. We will first plot all the points and then draw the line joining them to form a triangle. So, the diagram will look as follows:
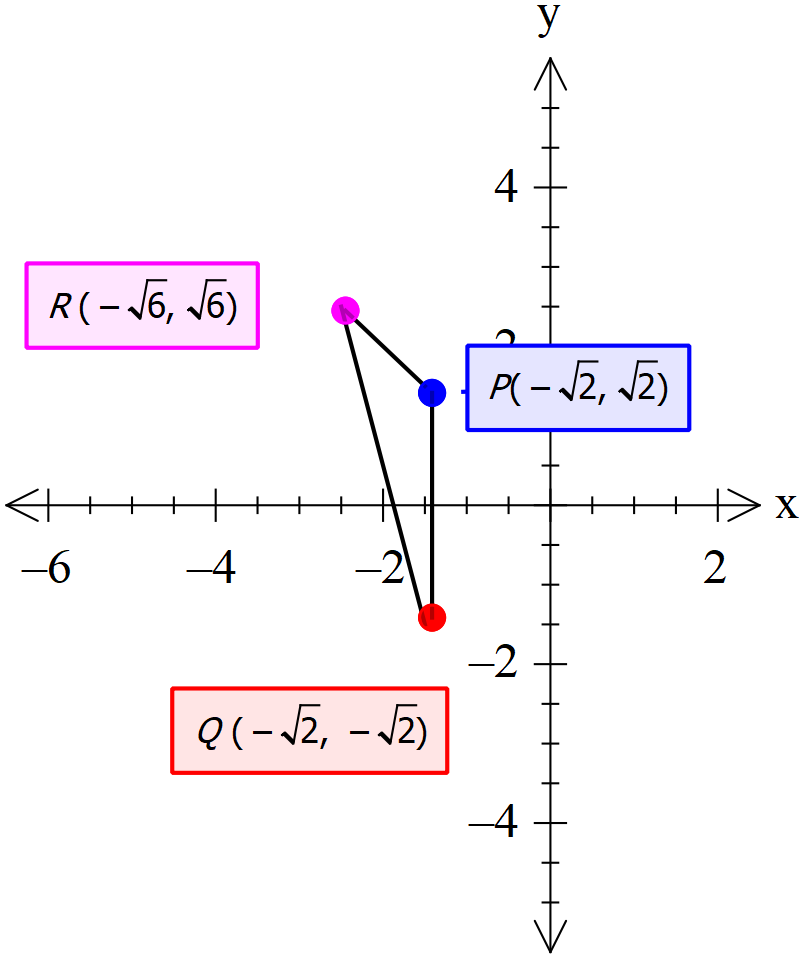
Now, here all the three sides are unequal as can be seen graphically. So, it is a scalene triangle with all three sides of unequal lengths.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the question, we have to find the type of triangle PQR formed by the points \[P(-\sqrt{2},\sqrt{2})\], \[Q(-\sqrt{2},-\sqrt{2})\] and \[R(-\sqrt{6},\sqrt{6})\].
So, we will use the distance formula here and will find the length of each line that joins points PQ, QR and PR.
Now, the distance formula between the two points is given as follows.
Now, distance (d) between points \[({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})\] and \[({{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}})\]
is found using the formula: \[d=\sqrt{{{({{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}})}^{2}}+{{({{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}})}^{2}}}\]
So now, the distance between \[P(-\sqrt{2},\sqrt{2})\] and \[Q(-\sqrt{2},-\sqrt{2})\] is given by:
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow PQ=\sqrt{{{\left( -\sqrt{2}-(-\sqrt{2}) \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -\sqrt{2}-(\sqrt{2}) \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \because {{x}_{2}}=-\sqrt{2}\,,\,\,{{x}_{1}}=-\sqrt{2},\,\,{{y}_{2}}=-\sqrt{2}\,,\,\,{{y}_{1}}=\sqrt{2} \\
& \Rightarrow PQ=\sqrt{{{0}^{2}}+{{\left( -2\sqrt{2} \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow PQ=2\sqrt{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Next, the distance between \[Q(-\sqrt{2},-\sqrt{2})\] and \[R(-\sqrt{6},\sqrt{6})\], is given by:
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow QR=\sqrt{{{\left( -\sqrt{6}-(-\sqrt{2}) \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \sqrt{6}-(-\sqrt{2}) \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \because {{x}_{2}}=-\sqrt{6}\,,\,\,{{x}_{1}}=-\sqrt{2},\,\,{{y}_{2}}=\sqrt{6}\,,\,\,{{y}_{1}}=-\sqrt{2} \\
& \Rightarrow QR=\sqrt{{{\left( -\sqrt{6}+\sqrt{2} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \sqrt{6}+\sqrt{2}) \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow QR=\sqrt{\left( 6+2-2\sqrt{12} \right)+\left( 6+2+2\sqrt{12} \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow QR=4 \\
\end{align}\]
Next, we will find the distance between \[R(-\sqrt{6},\sqrt{6})\] and \[P(-\sqrt{2},\sqrt{2})\], which is given by:
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow RP=\sqrt{{{\left( -\sqrt{2}-(-\sqrt{6}) \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \sqrt{2}-(\sqrt{6}) \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \because {{x}_{2}}=-\sqrt{2}\,,\,\,{{x}_{1}}=-\sqrt{6},\,\,{{y}_{2}}=\sqrt{2}\,,\,\,{{y}_{1}}=\sqrt{6} \\
& \Rightarrow RP=\sqrt{{{\left( -\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{6} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \sqrt{2}-\sqrt{6} \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow QR=\sqrt{\left( 2+6-2\sqrt{12} \right)+\left( 2+6-2\sqrt{12} \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow QR=\left( 8-2\sqrt{12} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
So, here we can see that all three distances points PQ, QR and PR are unequal. Hence, this is a scalene triangle with no two sides lengths equal.
Note: The alternative method to solve this problem is graphically. We will first plot all the points and then draw the line joining them to form a triangle. So, the diagram will look as follows:

Now, here all the three sides are unequal as can be seen graphically. So, it is a scalene triangle with all three sides of unequal lengths.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Who is known as the "Little Master" in Indian cricket history?

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

State and explain Ohms law class 10 physics CBSE

Distinguish between soap and detergent class 10 chemistry CBSE

a Why did Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments class 10 biology CBSE

Draw the diagram of the sectional view of the human class 10 biology CBSE




