
Name the stage of the cell cycle at which one of the following events occurs.
(i) Chromosomes are moved to the spindle equator
(ii) Centromere splits and chromatids separate
(iii) Pairing between homologous chromosomes takes place
(iv) Crossing over between homologous chromosomes takes place
Answer
594.3k+ views
Hint: The cell cycle is divided into two parts - interphase and the mitotic phase. The mitotic phase is the event of the nuclear division and is represented by mitosis and meiosis. The daughter cells have the same chromosome number as the parent cell in mitosis and half the chromosome number in meiosis.
Complete step by step answer:
M-phase in the cell cycle represents the phase of nuclear division in the cell. The nucleus may divide by mitosis or meiosis. Mitosis is divided into 4 phases namely Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Among them, metaphase is the stage where chromosomes move to the spindle equator. While in anaphase, the daughter chromosome separates into individual chromatids along with the splitting of the centromere.
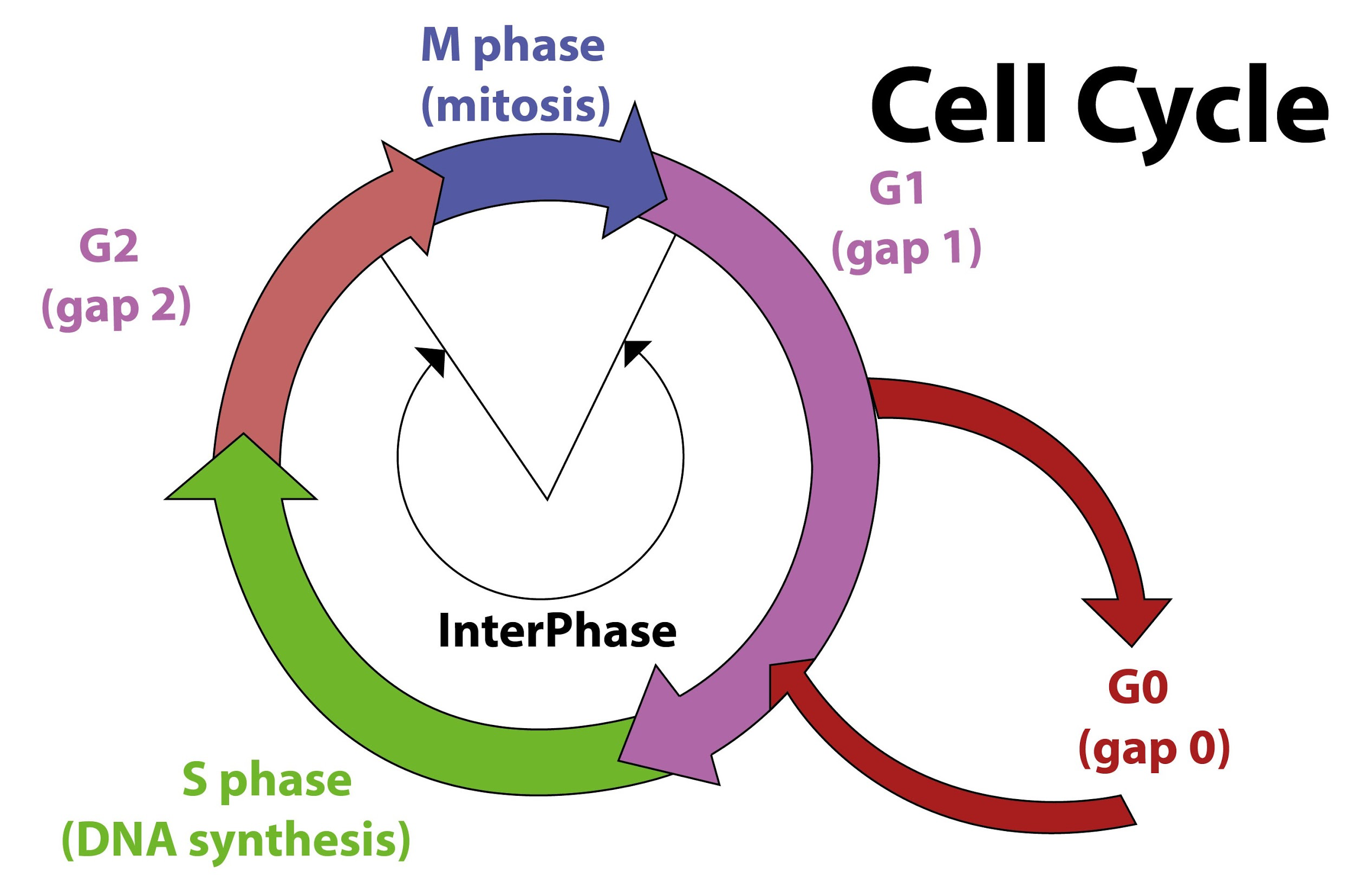
Meiosis is a two-stage process with meiosis-i and meiosis-iI. In meiosis-i, the pairing between homologous chromosomes occurs in the zygotene stage of prophase-i. The zygotene is followed by the pachytene stage, where crossing over between homologous chromosomes takes place.
- All three phases ${ G }_{ 1 }$, S phase, and ${ G }_{ 2 }$ together constitute interphase.
- ${ G }_{ 1 }$ phase: In this phase, the cell mainly grows in size and synthesizes protein. This growth is an increase in the number of cell organelles and an increase in the volume of the cytoplasm.
- S Phase: In the synthesis phase, the cell spends all its energy on doubling the DNA. Though the DNA is doubled, the number of chromosomes remains the same.
- ${ G }_{ 2 }$Phase: This is also called the gap phase. Here the cell resumes its growth and prepares for cell division. Mitochondria and chloroplast divide during this phase.
Note::
- A cell may temporarily or permanently exit the cell cycle and enters a stage designated as ${ G }_{ 0 }$. It is also known as the quiescent stage.
- They are not dormant as they are busy carrying out their functions like excretion, secretion, synthesis, etc in the organisms.
Complete step by step answer:
M-phase in the cell cycle represents the phase of nuclear division in the cell. The nucleus may divide by mitosis or meiosis. Mitosis is divided into 4 phases namely Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Among them, metaphase is the stage where chromosomes move to the spindle equator. While in anaphase, the daughter chromosome separates into individual chromatids along with the splitting of the centromere.

Meiosis is a two-stage process with meiosis-i and meiosis-iI. In meiosis-i, the pairing between homologous chromosomes occurs in the zygotene stage of prophase-i. The zygotene is followed by the pachytene stage, where crossing over between homologous chromosomes takes place.
- All three phases ${ G }_{ 1 }$, S phase, and ${ G }_{ 2 }$ together constitute interphase.
- ${ G }_{ 1 }$ phase: In this phase, the cell mainly grows in size and synthesizes protein. This growth is an increase in the number of cell organelles and an increase in the volume of the cytoplasm.
- S Phase: In the synthesis phase, the cell spends all its energy on doubling the DNA. Though the DNA is doubled, the number of chromosomes remains the same.
- ${ G }_{ 2 }$Phase: This is also called the gap phase. Here the cell resumes its growth and prepares for cell division. Mitochondria and chloroplast divide during this phase.
Note::
- A cell may temporarily or permanently exit the cell cycle and enters a stage designated as ${ G }_{ 0 }$. It is also known as the quiescent stage.
- They are not dormant as they are busy carrying out their functions like excretion, secretion, synthesis, etc in the organisms.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




