
Name the different elements of xylem. Collect information about the uses of the elements of xylem.
Answer
517.5k+ views
Hint: Xylem is a complex tissue that helps in the conduction of water and minerals to the plant body.
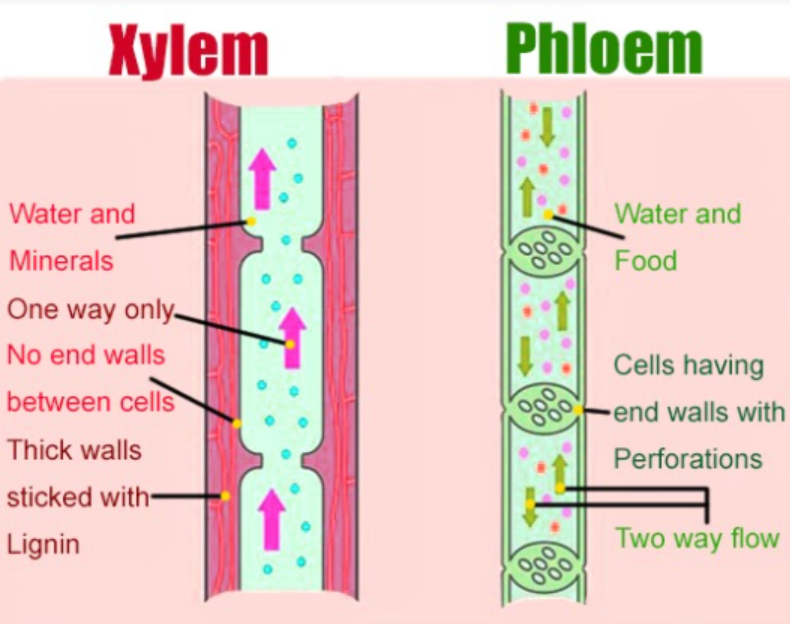
Xylem is a conducting tissue and is composed of elements of different kinds namely tracheids, vessels, xylem fibres and xylem parenchyma.
Complete answer:
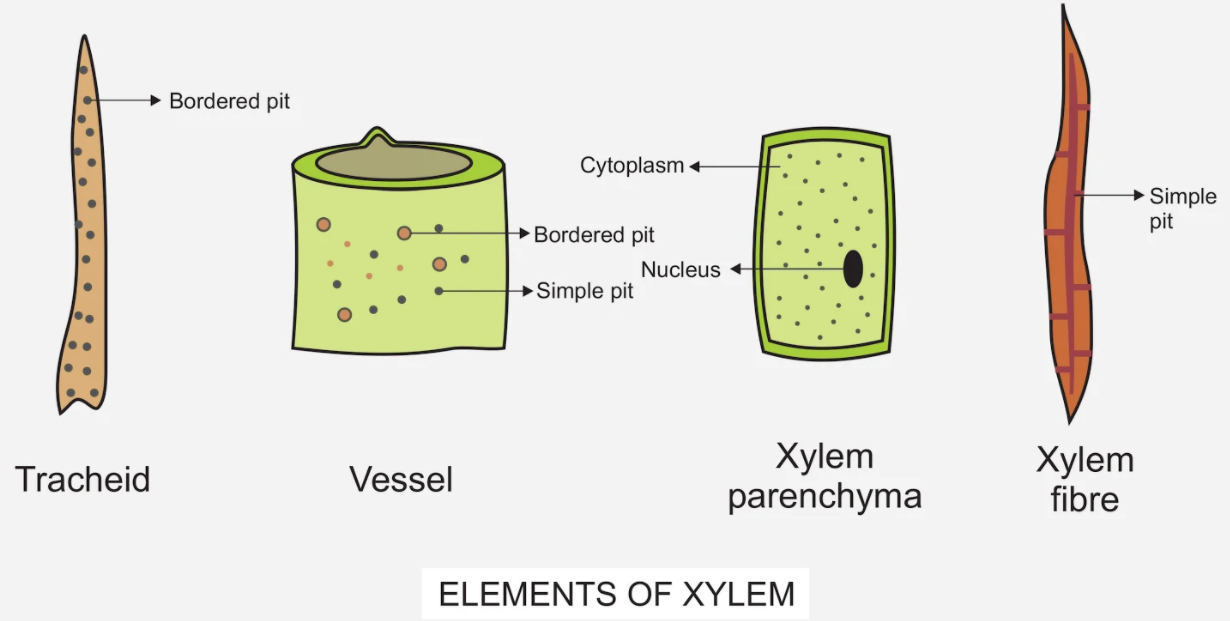
Xylem tracheids
Xylem tracheids are elongated narrow tube-like cells with hard thick and lignified walls with large cell cavities. They are dead empty cells with their walls having bordered pits. Tracheids occur alone in the wood of ferns and gymnosperms but in angiosperm, they occur with vessels.
Function - Tracheids help in conduction of water and minerals. They also provide mechanical strength to the plant body.
Vessels
Vessels are cylindrical tubular structures. The vessel members are connected by means of plates with pores and are known as perforation plates through which water moves upward. So, the whole structure resembles a series of water pipes forming a pipeline.
Function - The conduction of water and minerals from the root to the leaves and giving mechanical support to the plant body.
Xylem fibres
Sclerenchyma fibres seen associated with xylem are xylem fibres. Their walls are highly lignified and have no protoplast. Their walls are thicker than tracheids. The pits are usually simple and rarely bordered.
Function – Provide mechanical support to plants.
Xylem parenchyma
Parenchyma cells associated with xylem are xylem parenchyma. They are the only living and thin tissues in the xylem.
Function – It serves for the storage of food.
Note:
Bordered pits are cavities seen in the lignified cell walls of xylem.
In cold or temperate climates, the annual xylem rings formed at the base of the trunk determine the age of trees.
Xylem is a conducting tissue and is composed of elements of different kinds namely tracheids, vessels, xylem fibres and xylem parenchyma.
Complete answer:

Xylem tracheids
Xylem tracheids are elongated narrow tube-like cells with hard thick and lignified walls with large cell cavities. They are dead empty cells with their walls having bordered pits. Tracheids occur alone in the wood of ferns and gymnosperms but in angiosperm, they occur with vessels.
Function - Tracheids help in conduction of water and minerals. They also provide mechanical strength to the plant body.
Vessels
Vessels are cylindrical tubular structures. The vessel members are connected by means of plates with pores and are known as perforation plates through which water moves upward. So, the whole structure resembles a series of water pipes forming a pipeline.
Function - The conduction of water and minerals from the root to the leaves and giving mechanical support to the plant body.
Xylem fibres
Sclerenchyma fibres seen associated with xylem are xylem fibres. Their walls are highly lignified and have no protoplast. Their walls are thicker than tracheids. The pits are usually simple and rarely bordered.
Function – Provide mechanical support to plants.
Xylem parenchyma
Parenchyma cells associated with xylem are xylem parenchyma. They are the only living and thin tissues in the xylem.
Function – It serves for the storage of food.
Note:
Bordered pits are cavities seen in the lignified cell walls of xylem.
In cold or temperate climates, the annual xylem rings formed at the base of the trunk determine the age of trees.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




