
How do you name and draw stereoisomers for \[2 - pentene\]?
Answer
552.3k+ views
Hint: Stereoisomers have a similar primary equation yet the direction of the segment particles varies from one stereoisomer to the next. Two kinds of stereoisomers will be concentrated in this unit, mathematical isomers and optical isomers.
With regards to naming the stereoisomers the prefix cis or trans is embedded toward the beginning of the IUPAC name.
For instance \[2 - pentene\] can have two stereoisomers relying upon the direction of the alkyl group around the double bond.
\[cis - 2 - pentene{\text{ }}and{\text{ }}trans - 2 - pentene\]
Complete step by step answer:
The equation for finding the most extreme number of stereoisomers X will be \[X{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}{2^n}\] , where n is the quantity of stereogenic atoms in the particle. The formula \[X{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}{2^n}\] dependably gives the most extreme number of stereoisomers, however in circumstances of high symmetry it fails to give the real number.
\[cis - pent - 2 - ene\] has the H - particles on a similar side of the double bond. \[trans - Pent - 2 - ene\] has the H - molecules on inverse sides of the twofold bond. You can likewise utilize the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog framework to name the isomers. On each finish of the double bond, the alkyl gatherings (ethyl and methyl) have upper need than the H particles.
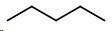
Pentane
Draw a double bond between carbons \[2\] and \[3\] .
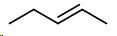
Pentene
You can also use the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog method to name the isomers.
On each end of the double bond, the alkyl groups (ethyl and methyl) have upper priority than the H atoms.
The first isomer has the higher-priority groups on reverse sides. This is \[\left( E \right) - pent - 2 - ene.\]
The second isomer has the higher-priority groups on the similar side. This is \[\left( Z \right) - pent - 2 - ene\]
Note: There are two ways to insert the double bond.
One has the H atoms on reverse sides of the double bond; the other has the H atoms on the similar side of the double bond.
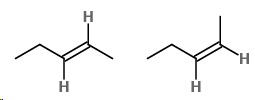
Cis/trans
\[cis - Pent - 2 - ene\] has the H-atoms on the similar side of the double bond.
\[Trans - Pent - 2 - ene\] has the H-atoms on reverse sides of the double bond.
The basic requirement for this stereoisomerism is that every carbon of the double bond should have two diverse substituent groups
With regards to naming the stereoisomers the prefix cis or trans is embedded toward the beginning of the IUPAC name.
For instance \[2 - pentene\] can have two stereoisomers relying upon the direction of the alkyl group around the double bond.
\[cis - 2 - pentene{\text{ }}and{\text{ }}trans - 2 - pentene\]
Complete step by step answer:
The equation for finding the most extreme number of stereoisomers X will be \[X{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}{2^n}\] , where n is the quantity of stereogenic atoms in the particle. The formula \[X{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}{2^n}\] dependably gives the most extreme number of stereoisomers, however in circumstances of high symmetry it fails to give the real number.
\[cis - pent - 2 - ene\] has the H - particles on a similar side of the double bond. \[trans - Pent - 2 - ene\] has the H - molecules on inverse sides of the twofold bond. You can likewise utilize the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog framework to name the isomers. On each finish of the double bond, the alkyl gatherings (ethyl and methyl) have upper need than the H particles.

Pentane
Draw a double bond between carbons \[2\] and \[3\] .

Pentene
You can also use the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog method to name the isomers.
On each end of the double bond, the alkyl groups (ethyl and methyl) have upper priority than the H atoms.
The first isomer has the higher-priority groups on reverse sides. This is \[\left( E \right) - pent - 2 - ene.\]
The second isomer has the higher-priority groups on the similar side. This is \[\left( Z \right) - pent - 2 - ene\]
Note: There are two ways to insert the double bond.
One has the H atoms on reverse sides of the double bond; the other has the H atoms on the similar side of the double bond.

Cis/trans
\[cis - Pent - 2 - ene\] has the H-atoms on the similar side of the double bond.
\[Trans - Pent - 2 - ene\] has the H-atoms on reverse sides of the double bond.
The basic requirement for this stereoisomerism is that every carbon of the double bond should have two diverse substituent groups
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




