
$ NaHS{{O}_{3}} $ is an ambident nucleophile but how?
Answer
529.2k+ views
Hint :We know that the sodium bisulphite (sodium hydrogen sulphite) is a chemical mixture with the approximate chemical formula $ NaHS{{O}_{3}} $ . Sodium bisulphite is a mixture of salts that dissolve in water to give solutions composed of sodium and bisulfite ions. It is a white solid with an odour of sulphur dioxide.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The ligand is an ion or a molecule that donates a pair of electrons to the central metal atom or to ion to form a coordination complex compound. Generally, the bonding with the metal involves formal donation of one or more ligand electron pairs. The nature of metal and ligand bonding can range from covalent to ionic. Ambidentate ligand is a type of ligand that has the ability to bind to the central atom through two ways that the atoms of two different elements.
Examples: thiocyanate ion $ (NC{{S}^{}}) $ which can bind to the central metal atom or ion with either nitrogen or sulphur atoms. The ambient ligands have two or more donor atoms, but only one donor participates to attach the metal during the formation of complex.
Example; The structure of $ NaHS{{O}_{3}} $ ;
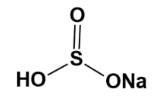
If we observe the hybrid structure, we are able to see the partial negative charge $ (\delta -) $ .
Hence, due to its $ \pi $ system about the sulphur atom, its charge is delocalized.
Due to this reason, it is an ambident molecule.
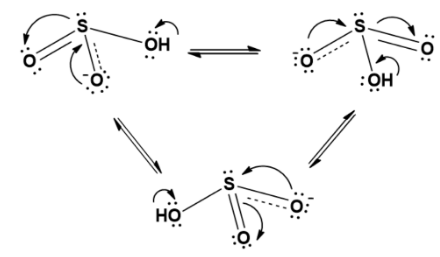
The resonating structure can be rewritten as;
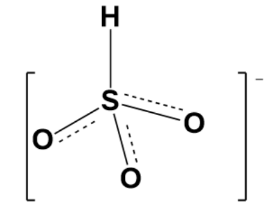
Therefore, Lewis structure is given bellows as follow as for above structure;
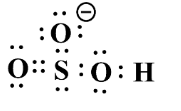
Note :
Note that an ambident nucleophile is an anionic nucleophile whose negative charge is delocalized by resonance over two unlike atoms or over two like but non-equivalent atoms. The most common ambient nucleophiles are enolate ions. For example, the resonance forms of acetone enolate are shown below.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The ligand is an ion or a molecule that donates a pair of electrons to the central metal atom or to ion to form a coordination complex compound. Generally, the bonding with the metal involves formal donation of one or more ligand electron pairs. The nature of metal and ligand bonding can range from covalent to ionic. Ambidentate ligand is a type of ligand that has the ability to bind to the central atom through two ways that the atoms of two different elements.
Examples: thiocyanate ion $ (NC{{S}^{}}) $ which can bind to the central metal atom or ion with either nitrogen or sulphur atoms. The ambient ligands have two or more donor atoms, but only one donor participates to attach the metal during the formation of complex.
Example; The structure of $ NaHS{{O}_{3}} $ ;

If we observe the hybrid structure, we are able to see the partial negative charge $ (\delta -) $ .
Hence, due to its $ \pi $ system about the sulphur atom, its charge is delocalized.
Due to this reason, it is an ambident molecule.

The resonating structure can be rewritten as;

Therefore, Lewis structure is given bellows as follow as for above structure;
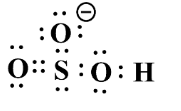
Note :
Note that an ambident nucleophile is an anionic nucleophile whose negative charge is delocalized by resonance over two unlike atoms or over two like but non-equivalent atoms. The most common ambient nucleophiles are enolate ions. For example, the resonance forms of acetone enolate are shown below.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




