
NADP reduces to $NADP{ H }_{ 2 }$ in
A. PS- I
B. PS- II
C. Calvin cycle
D. Non-cyclic photophosphorylation
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: Reduction of NADP to $NADP{ H }_{ 2 }$ occurs in a type of phosphorylation that is absent in autotrophic bacteria as only one photosystem is present in them. Both ATP and $NADP{ H }_{ 2 }$ are formed in this type of photophosphorylation.
Complete answer:
The non-cyclic photophosphorylation is known as Z-scheme and it involves both PS-I and PS-II photosystems.
The reduction of NADP to $NADP{ H }_{ 2 }$ takes place in PS-I in non-cyclic photophosphorylation. This NADP reductase reacts with NADP and reduces it to $NADP{ H }+{ H }^{ + }$. This ${ H }^{ + }$ is obtained from the stroma.
Additional Information:
The steps involved in non-cyclic photophosphorylation are as follows:
-Absorption of light energy of specific wavelength by the chlorophyll and accessory pigments. These pigments absorb energy and transfer it to the reaction center of PS- II P680. This results in photoexcitation of the P680 reaction center and it discharges one electron which is passed to a pigment named pheophytin.
-This loss of electron is compensated by absorbing electrons released during the photolysis of water.
-After passing through a series of carriers plastoquinone, cytochromes, ${ b }_{ 6 }-f$ complex, and plastocyanin the electron is passed to photo center P700 of PS-1 by plastocyanin.
-P700 releases this electron on absorbing light energy of a suitable wavelength.
-This electron is transferred through several quinones, FeS complexes, Ferredoxin, and NADP reductase.
So, the correct answer is, ” NADP reduces to $NADP{ H }_{ 2 }$ in Non-cyclic photophosphorylation. ”
Note: It should be noted that the PS- I and PS- II photosystems are named just in the order in which they were discovered. In cyclic photophosphorylation of PS-I is involved but both photosystems are involved in the non-cyclic type of photophosphorylation. In the non-cyclic type of photophosphorylation both ATP and NADPH are formed, which are considered as assimilatory power, but in the cyclic type of photophosphorylation only ATP formation takes place.
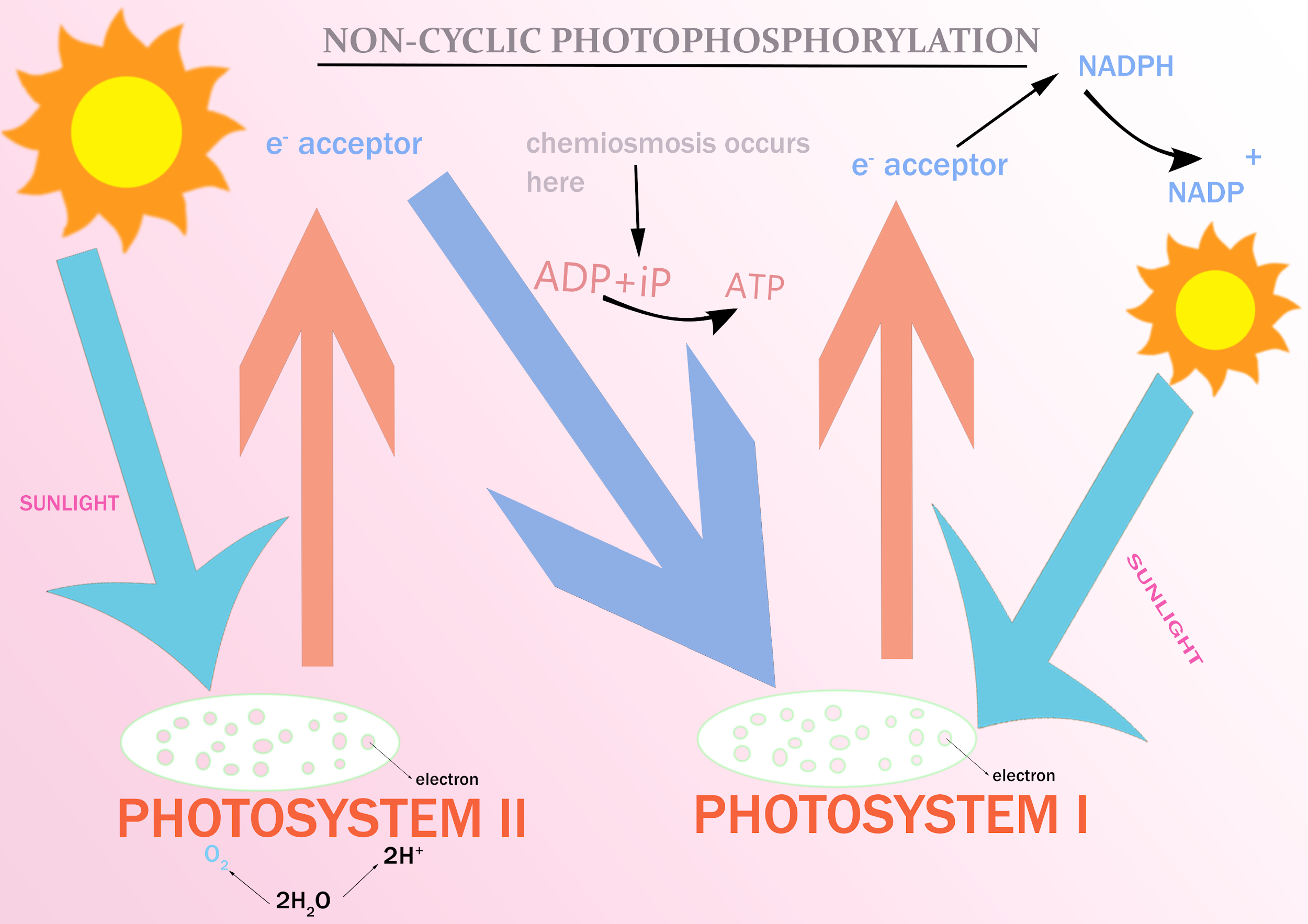
Complete answer:
The non-cyclic photophosphorylation is known as Z-scheme and it involves both PS-I and PS-II photosystems.
The reduction of NADP to $NADP{ H }_{ 2 }$ takes place in PS-I in non-cyclic photophosphorylation. This NADP reductase reacts with NADP and reduces it to $NADP{ H }+{ H }^{ + }$. This ${ H }^{ + }$ is obtained from the stroma.
Additional Information:
The steps involved in non-cyclic photophosphorylation are as follows:
-Absorption of light energy of specific wavelength by the chlorophyll and accessory pigments. These pigments absorb energy and transfer it to the reaction center of PS- II P680. This results in photoexcitation of the P680 reaction center and it discharges one electron which is passed to a pigment named pheophytin.
-This loss of electron is compensated by absorbing electrons released during the photolysis of water.
-After passing through a series of carriers plastoquinone, cytochromes, ${ b }_{ 6 }-f$ complex, and plastocyanin the electron is passed to photo center P700 of PS-1 by plastocyanin.
-P700 releases this electron on absorbing light energy of a suitable wavelength.
-This electron is transferred through several quinones, FeS complexes, Ferredoxin, and NADP reductase.
So, the correct answer is, ” NADP reduces to $NADP{ H }_{ 2 }$ in Non-cyclic photophosphorylation. ”
Note: It should be noted that the PS- I and PS- II photosystems are named just in the order in which they were discovered. In cyclic photophosphorylation of PS-I is involved but both photosystems are involved in the non-cyclic type of photophosphorylation. In the non-cyclic type of photophosphorylation both ATP and NADPH are formed, which are considered as assimilatory power, but in the cyclic type of photophosphorylation only ATP formation takes place.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




