
When \[{N_2}\] goes to \[{N_2}^ + \] , the \[N-N\] bond distance increases, and when \[{O_2}\] goes to \[{O_2}^ + \] , the \[O-O\]bond distance decreases.
Write whether the above statement is true or false.
Answer
589.2k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we must first understand the electronic configurations of the elements in the compounds. On the basis of the bonding between these atoms, we must find the bond order and then describe the relevant relation between the bond order and bond length.
Complete step by step answer:
Before we move forward with the solution of the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts.
-The atomic number of any element represents the number of protons or electrons present in the given atom. This number is unique to every element. On the basis of the atomic number and Aufbau’s principle, we can determine the electronic configuration of the given element. Ions of elements are formed when we either add or remove electrons from the valence shell of the given atom. Positive ions are formed when we remove electrons form the valence shell, while negative ions are formed when we add electrons to the valence shell.
-The atomic number of nitrogen is 7. Hence, the electronic configuration of nitrogen can be given as: \[1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^3}\] . Hence, when we form \[{N_2}\] molecule, the Lewis structure can be given as:
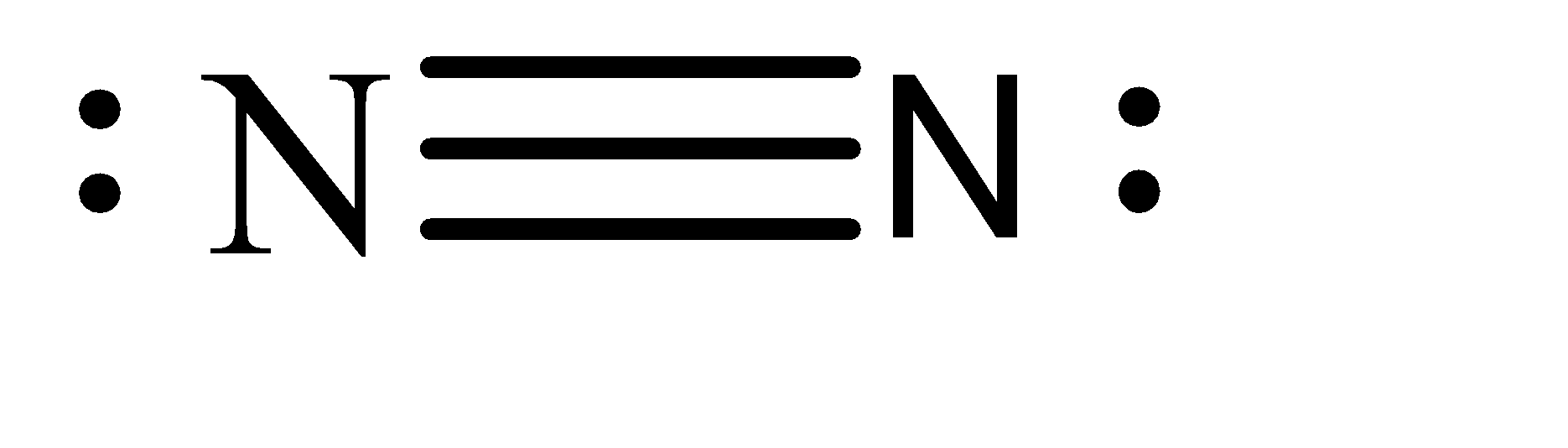
-Hence, there are 2 lone pairs, 2 pi bonds and 1 sigma bond present in the given molecule. Hence, when the \[{N_2}^ + \] ion is formed, one of the electrons is removed from the lone pair.
-On the other hand, the atomic number of oxygen is 8. Hence, the electronic configuration of oxygen can be given as: \[1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^4}\] . Hence, when we form \[{O_2}\] molecule, the Lewis structure can be given as:
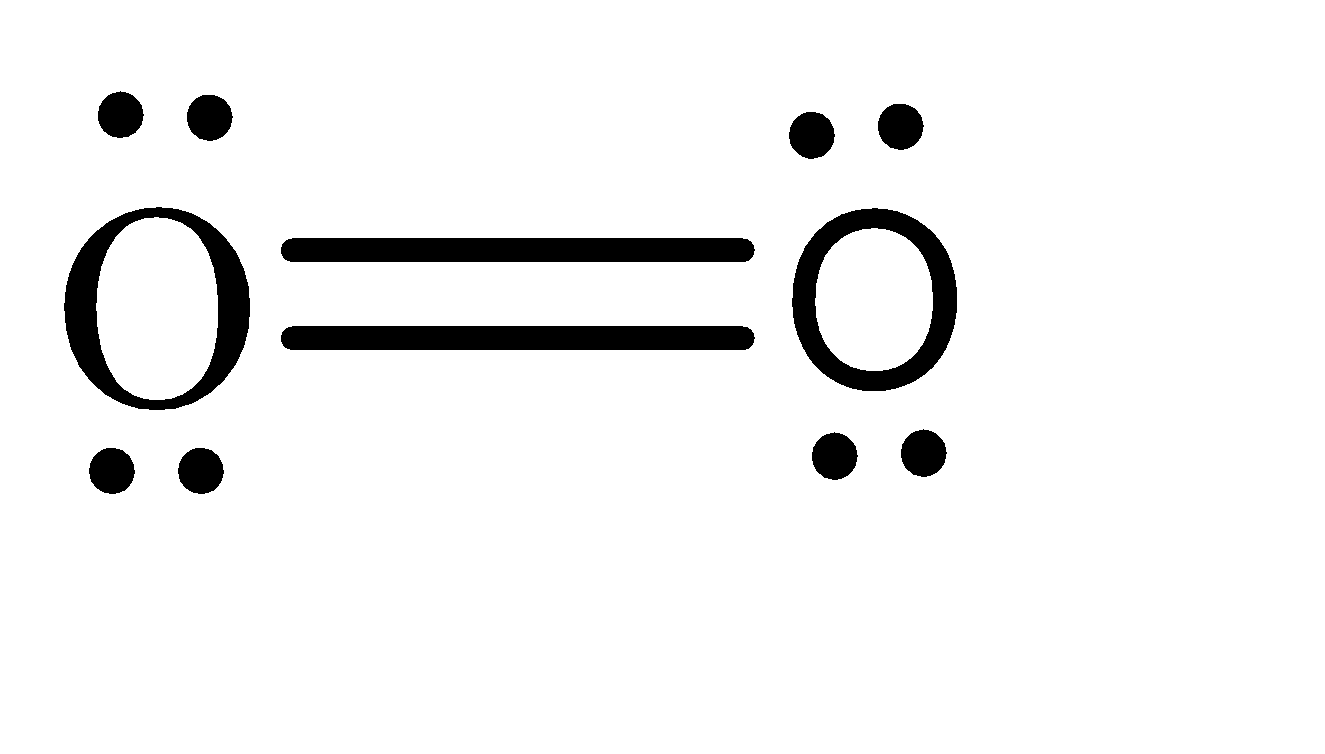
-Hence, there are 4 lone pairs, 1 pi bond and 1 sigma bond present in the given molecule. Hence, when the \[{O_2}^ + \] ion is formed, one of the electrons is removed from the lone pair.
-One trend in bond length we know is that the bond length decreases with the decrease in the bond order. The bond orders of the given species can be calculated as:
\[{N_2}\] - 3
\[{N_2}^ + \] - 2.5
\[{O_2}\] - 2
\[{O_2}^ + \] - 2.5
Hence, the bond order decreases from \[{N_2}\] to \[{N_2}^ + \] and increases from \[{O_2}\] to \[{O_2}^ + \] .
Hence, when \[{N_2}\] goes to \[{N_2}^ + \] , the N – N bond distance increases, and when \[{O_2}\] goes to \[{O_2}^ + \] , the \[O-O\] bond distance decreases.
This statement is true.
Note:
In molecules which have resonance or nonclassical bonding, bond number may not be an integer. In benzene, the delocalized molecular orbitals contain 6 pi electrons over six carbons essentially yielding half a pi bond together with the sigma bond for each pair of carbon atoms, giving a calculated bond number of 1.5.
Complete step by step answer:
Before we move forward with the solution of the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts.
-The atomic number of any element represents the number of protons or electrons present in the given atom. This number is unique to every element. On the basis of the atomic number and Aufbau’s principle, we can determine the electronic configuration of the given element. Ions of elements are formed when we either add or remove electrons from the valence shell of the given atom. Positive ions are formed when we remove electrons form the valence shell, while negative ions are formed when we add electrons to the valence shell.
-The atomic number of nitrogen is 7. Hence, the electronic configuration of nitrogen can be given as: \[1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^3}\] . Hence, when we form \[{N_2}\] molecule, the Lewis structure can be given as:

-Hence, there are 2 lone pairs, 2 pi bonds and 1 sigma bond present in the given molecule. Hence, when the \[{N_2}^ + \] ion is formed, one of the electrons is removed from the lone pair.
-On the other hand, the atomic number of oxygen is 8. Hence, the electronic configuration of oxygen can be given as: \[1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^4}\] . Hence, when we form \[{O_2}\] molecule, the Lewis structure can be given as:

-Hence, there are 4 lone pairs, 1 pi bond and 1 sigma bond present in the given molecule. Hence, when the \[{O_2}^ + \] ion is formed, one of the electrons is removed from the lone pair.
-One trend in bond length we know is that the bond length decreases with the decrease in the bond order. The bond orders of the given species can be calculated as:
\[{N_2}\] - 3
\[{N_2}^ + \] - 2.5
\[{O_2}\] - 2
\[{O_2}^ + \] - 2.5
Hence, the bond order decreases from \[{N_2}\] to \[{N_2}^ + \] and increases from \[{O_2}\] to \[{O_2}^ + \] .
Hence, when \[{N_2}\] goes to \[{N_2}^ + \] , the N – N bond distance increases, and when \[{O_2}\] goes to \[{O_2}^ + \] , the \[O-O\] bond distance decreases.
This statement is true.
Note:
In molecules which have resonance or nonclassical bonding, bond number may not be an integer. In benzene, the delocalized molecular orbitals contain 6 pi electrons over six carbons essentially yielding half a pi bond together with the sigma bond for each pair of carbon atoms, giving a calculated bond number of 1.5.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




