
What is the \[n - factor\] of \[{H_3}P{O_2}\] in its disproportionation reaction.
\[3{H_3}P{O_2} \to P{H_3} + 2{H_3}P{O_3}\]
A.\[1\]
B.\[2\]
C.\[\dfrac{4}{3}\]
D.\[ - 4\]
Answer
518.1k+ views
Hint: A disproportionation reaction is a special type of redox reaction in which a single chemical species is being oxidized as well as reduced. The phosphorus atom is the important part of the reaction as its oxidation number changes on going from reactant side to product side.
Complete answer:
The \[n - factor\] is a number that measures the change in electrons taking place per molecule. The electrons in the process can be gained (reduction) as well as lost (oxidation). But in a balanced disproportionation reaction we observe that the number of electrons being gained or lost as a result of oxidation or reduction are the same.
Assign the oxidation numbers to phosphorus atoms in each reactant and product.
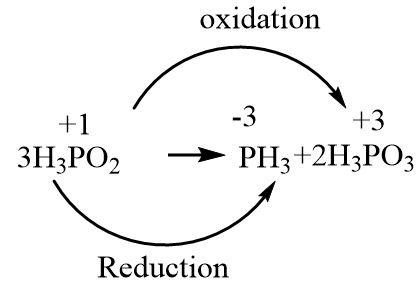
In order to find out the \[n - factor\] of \[{H_3}P{O_2}\], we need to break its disproportionation reaction into two halves where one represents the oxidation half and the other represents the reduction half. Each half must be written with the number of electrons involved in the process in such a way that the oxidation numbers on phosphorus atoms get balanced.
a.Reduction half
\[{H_3}P{O_2} + 4{e^ - } \to P{H_3}\]
b.Oxidation half
\[{H_3}P{O_2} \to {H_3}P{O_3} + 2{e^ - }\]
Since the electrons in both the half-reactions are not the same, the oxidation half needs to be multiplied by two to get the same number of electrons as the reduction half-reaction.
\[2{H_3}P{O_2} \to 2{H_3}P{O_3} + 4{e^ - }\]
Now that the number of electrons are balanced, the two half-reactions can be added to verify that we get the same net balanced equation as before.
\[3{H_3}P{O_2} + 4{e^ - } \to P{H_3} + 2{H_3}P{O_3} + 4{e^ - }\]
The net equation comes out to be the same, with the involvement of four electrons.
There are three molecules \[{H_3}P{O_2},{H_3}P{O_3}{\text{ and }}P{H_3}\] that are involved in the disproportionation process.
The formula of \[n - factor\] calculation is given as follows:
\[n - factor = \dfrac{{{\text{number of electrons involved}}}}{{{\text{number of molecules involved}}}}\]
Putting the number of involved electrons as four and number of involved molecules as three in the above formula we get
\[n - factor = \dfrac{4}{3}\]
Therefore, the correct option is option (C) with \[n - factor = \dfrac{4}{3}\].
Note:
All the reactants as well as products are neutral compounds, therefore the oxidation number of phosphorus atoms in each case can be determined by assuming it to be a variable and putting in the oxidation numbers of other atoms like oxygen and hydrogen. Simplifying the linear equation in one variable would give the oxidation states.
Complete answer:
The \[n - factor\] is a number that measures the change in electrons taking place per molecule. The electrons in the process can be gained (reduction) as well as lost (oxidation). But in a balanced disproportionation reaction we observe that the number of electrons being gained or lost as a result of oxidation or reduction are the same.
Assign the oxidation numbers to phosphorus atoms in each reactant and product.

In order to find out the \[n - factor\] of \[{H_3}P{O_2}\], we need to break its disproportionation reaction into two halves where one represents the oxidation half and the other represents the reduction half. Each half must be written with the number of electrons involved in the process in such a way that the oxidation numbers on phosphorus atoms get balanced.
a.Reduction half
\[{H_3}P{O_2} + 4{e^ - } \to P{H_3}\]
b.Oxidation half
\[{H_3}P{O_2} \to {H_3}P{O_3} + 2{e^ - }\]
Since the electrons in both the half-reactions are not the same, the oxidation half needs to be multiplied by two to get the same number of electrons as the reduction half-reaction.
\[2{H_3}P{O_2} \to 2{H_3}P{O_3} + 4{e^ - }\]
Now that the number of electrons are balanced, the two half-reactions can be added to verify that we get the same net balanced equation as before.
\[3{H_3}P{O_2} + 4{e^ - } \to P{H_3} + 2{H_3}P{O_3} + 4{e^ - }\]
The net equation comes out to be the same, with the involvement of four electrons.
There are three molecules \[{H_3}P{O_2},{H_3}P{O_3}{\text{ and }}P{H_3}\] that are involved in the disproportionation process.
The formula of \[n - factor\] calculation is given as follows:
\[n - factor = \dfrac{{{\text{number of electrons involved}}}}{{{\text{number of molecules involved}}}}\]
Putting the number of involved electrons as four and number of involved molecules as three in the above formula we get
\[n - factor = \dfrac{4}{3}\]
Therefore, the correct option is option (C) with \[n - factor = \dfrac{4}{3}\].
Note:
All the reactants as well as products are neutral compounds, therefore the oxidation number of phosphorus atoms in each case can be determined by assuming it to be a variable and putting in the oxidation numbers of other atoms like oxygen and hydrogen. Simplifying the linear equation in one variable would give the oxidation states.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




