
What is multiple fission? How does it occur in an organism? Explain briefly. Name one organism which exhibits this type of reproduction.
Answer
599.1k+ views
Hint: Fission, in biology, is the division of a single cell into two or more cells and the regeneration of those parts to separate entities resembling the original organism. Some groups of organisms in which multiple fission occurs are protists, algae, etc.
Complete answer:
In the multiple fission, the nucleus of the parent cell divides multiple times by amitosis (direct cell division), producing several nuclei. The cytoplasm, later on, separates, creating multiple daughter cells. Multiple fission occurs during unfavorable conditions.
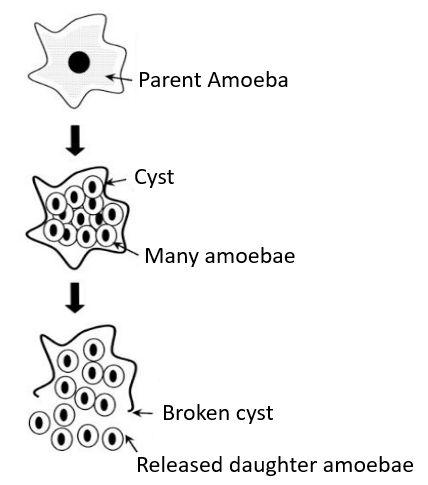
Multiple fission in Amoeba: It is a unicellular organism. To survive and reproduce under the unfavorable conditions, Amoeba withdraws its pseudopodia and becomes almost round in shape. It secretes a hard covering around its cell called a cyst. The cyst forms a thick protective coating around the cell. Inside the cyst, the nucleus of the Amoeba undergoes repeated divisions to form many nuclei. After nuclear division, cytoplasmic division occurs. Hence, eventually, many new daughter cells are formed from the parent cell. On the return of favorable conditions, the cyst bursts open to release these daughter cells in the environment.
Amoeba reproduces by multiple fissions.
Additional Information:
- In multiple fissions occurs rapidly in organisms.
- There is no definite pattern of cell division in multiple fissions.
- Multiple fission is asexual reproduction and occurs with the presence of only one parent.
- All the daughter cells in multiple fission are equal-sized and are similar.
Note: In asexual reproduction, the daughter cells are identical to each other, both physically as well as genetically. So, they are called ‘clones.’ Asexual reproduction occurs in both unicellular and multicellular organisms.
Complete answer:
In the multiple fission, the nucleus of the parent cell divides multiple times by amitosis (direct cell division), producing several nuclei. The cytoplasm, later on, separates, creating multiple daughter cells. Multiple fission occurs during unfavorable conditions.
Multiple fission in Amoeba: It is a unicellular organism. To survive and reproduce under the unfavorable conditions, Amoeba withdraws its pseudopodia and becomes almost round in shape. It secretes a hard covering around its cell called a cyst. The cyst forms a thick protective coating around the cell. Inside the cyst, the nucleus of the Amoeba undergoes repeated divisions to form many nuclei. After nuclear division, cytoplasmic division occurs. Hence, eventually, many new daughter cells are formed from the parent cell. On the return of favorable conditions, the cyst bursts open to release these daughter cells in the environment.
Amoeba reproduces by multiple fissions.

Additional Information:
- In multiple fissions occurs rapidly in organisms.
- There is no definite pattern of cell division in multiple fissions.
- Multiple fission is asexual reproduction and occurs with the presence of only one parent.
- All the daughter cells in multiple fission are equal-sized and are similar.
Note: In asexual reproduction, the daughter cells are identical to each other, both physically as well as genetically. So, they are called ‘clones.’ Asexual reproduction occurs in both unicellular and multicellular organisms.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE




